What is the Radioactive Isotope?
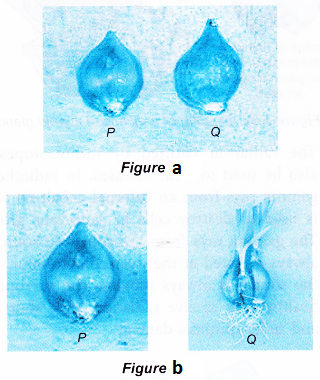
- Figure (a) shows two fresh onions. After being left aside for 2 weeks, P remains the same but Q has sprouted, as shown in Figure (b).
- Onion P had been irradiated with gamma radiation. The gamma rays passing through the onion had caused some changes in the onion that delayed the sprouting process. This useful procedure delays sprouting when food items such as onions, potatoes and ginger are exported from one country to another.
- The gamma rays used to irradiate the onion is emitted by the radioisotope cobalt-60.
- Radioisotopes are unstable isotopes which decay and give out radioactive emissions.
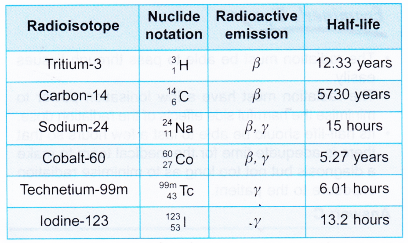
- Table gives a list of some radioisotopes.

People also ask
- Radioactivity: Types of Radioactive Emissions
- How do you detect radioactivity?
- What are the different types of radioactive decay?
- What are the Isotopes, Isobars and Isotones of an Element
- Importance of Proper Management of Radioactive Substances
- What is nucleus of an atom?
- What is the half life of a radioactive element?
- What is Nuclear Energy?
- What is nuclear fission and how does it occur?
- How is energy released in a nuclear fusion reaction?
- What happens in a nuclear chain reaction?
How are radioactive isotopes produced?
- Some radioisotopes exist naturally. Uranium-235 and uranium-238 are two naturally occurring radioisotopes of uranium.
- Radioisotopes can also be produced artificially when certain nuclides are bombarded by high energy particles or gamma rays.
(a) One of the earliest radioisotopes to be produced artificially was phosphorus-32. It is produced when sulphur-32 is bombarded by neutrons.

What is the use of radioactive isotopes?
Applications of Radioisotopes:
- There is a wide range of uses for the radiation emitted by radioisotopes.
- A radioisotope will spontaneously emit radiation even after it has entered a living organism. It will also remain radioactive even though it has been mixed with another substance to form a compound.
- Radioisotopes are used as tracers where the radiation emitted is detected continuously to monitor the movement of the radioisotope in a system.
- The radiation emitted by radioisotopes can also be used for specific purposes.
- Isotopes are used in almost all the fields such as medicines, agriculture, biology, chemistry, engineering and industry.
- Radioactive isotopes are used as a fuel in nuclear reactors of nuclear power plants for generating electricity.
Example: Uranium-235 isotope is used as a fuel in the reactors of nuclear power plants for generating electricity. - Radioactive isotopes are used as ‘tracers’ in medicine to detect the presence of tumors and blood clots, etc., in the human body.
Example: Arsenic-74 tracer is used to detect the presence of tumors and sodium-24 tracer is used to detect the presence of blood clots. - Radioactive isotopes are used to determine the activity of thyroid gland which helps in the treatment of diseases like goitre.
Example: Iodine-131 - Radioactive isotopes are used in the treatment of cancer.
Example:Cobalt-60 radioisotope is used to cure cancer. - Radioactive isotopes are used in industry to detect the leakage in underground oil pipelines, gas pipelines and water pipes.
How are radioactive isotopes used in medicine?
Nuclear Medicine:
- Nuclear medicine is a branch of medicine and medical imaging that uses radioisotopes in its diagnosis and treatment of diseases.
- In diagnosis, radioactive substances ar.e administered to patients and the radiation emitted is detected.
The radioisotope, known as the radioactive tracer, is given to the patient by injection, inhalation or orally (through the mouth). - Radioactive tracers usually emit gamma rays which can easily pass through the tissues in the patient’s body to detectors outside the body.
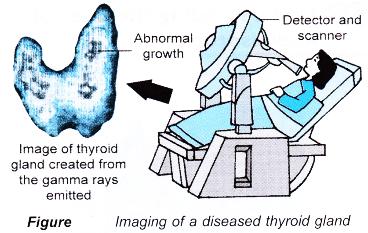
- The detection of the gamma rays enable organs such as the thyroid gland, bones, heart, liver and kidney to be imaged to reveal disorders in their functions.
- One radioisotope that is widely used is the artificially produced technetium-99m. The following characteristics make it almost ideal for nuclear medicine.
- It has a half-life of six hours. This is long enough for the medical team to examine metabolic processes in the body. At the same time, it is short enough to minimise the radiation dose to the patient. After 24 hours, that is 4 half-lives, the radiation would have dropped to 1/16 or 6.25% of its initial value.
- Technetium-99m decays by emitting gamma rays and low energy electrons. Since there is no high energy beta emission, the harmful radiation dose to the patient is low.
- The low energy gamma rays pass through the body without much ionisation of molecules. Therefore, the harmful side- effects of a radiation dose to the patient is minimised.
- Technetium can be readily incorporated into a wide range of biologically-active substances that can be concentrated in the tissue or organ to be examined.
- Figure shows the imaging of a diseased thyroid gland.
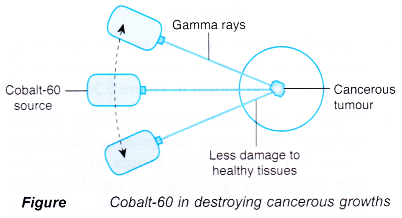
- The radiation emitted by radioisotopes can also be used to treat diseases. In radiotherapy, gamma rays from an external cobalt-60 source is used to destroy cells in cancerous growths. The gamma rays from the cobalt-60 source are always directed at the cancerous tumour. Since the source is always moving, the surrounding healthy cells receive radiation for a short time and suffer minimal damage.
- A new field of radiotherapy is the Targeted Alpha Therapy (TAT) which uses alpha particles for the control of dispersed cancers. The short range of very energetic alpha particles means that a large fraction of that radiation goes into the targeted cancer cells once a carrier has taken the alpha-emitting radionuclide to the location of the cancer cells. An experimental development of this is the Boron Neutron Capture Therapy (BNCT) which uses boron-10 and concentrates on malignant brain tumours.
- Radioisotopes are also used in the sterilisation of medical instruments. The plastic syringe and needle used for giving injections are irradiated by gamma rays after they have been packed and sealed. The strong gamma rays kill any bacteria or microbes that may still be found in the package.
Agriculture
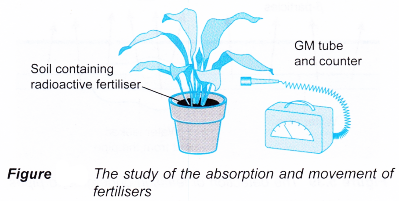
- Phosphorus-32 is used as a tracer to study the absorption and movement of fertilisers in plants. It behaves identically to the non-radioactive isotope phosphorus-31 found in common fertilisers. It has a half-life of 14 days and emits β-particles.
A Geiger-Muller counter is used to detect the β-particles emitted by the radioactive fertiliser absorbed by the plant, as shown in Figure.
- Seeds of plants exposed to radiation can develop changes to produce new strains of plants with certain good characteristics. For example, the exposure of wheat to radiation has produced new strains which are more disease-resistant and have a higher yield.
- Radioisotopes are used in the eradication of insect pests. For example, male screw-worm flies are bred and sterilised by radiation before releasing them to the environment. These sterilised male insects are unable to reproduce. Over a period of time, the population of the screw-worm flies can be reduced.
- Radioisotopes are also used to kill bacteria to control the ripening of fruits.
Industry
- There is a wide range of uses for radioisotopes in the industry.
- The research and development of lubricating oil uses specially prepared radioactive lubricating oil to determine how efficiently the oil gets to work after the start-up of the engine. It can also be used to measure engine wear.
- Gamma γ-rays are used to penetrate deep into welding joints to detect faults.
- In gamma radiography, powerful y-rays are used to photograph the inside of steel plates as to reveal internal cracks. Iridium-192 emits y-rays that can penetrate steel sheets that are 12 to 60 mm thick and light alloys up to 190 mm thick.
- The movement of liquids in complicated factory systems can be monitored by dissolving radioactive salts which contain sodium-24. The β-particles emitted is then detected by a Geiger- Muller counter.
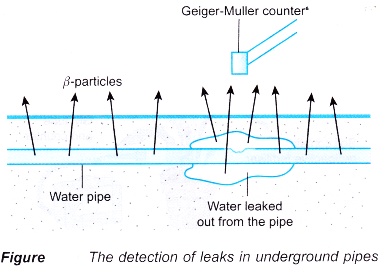
- Leaks in underground water pipes can be detected using radioisotopes. A radioactive salt is dissolved into the water at treatment plants. The β-particles are detected above the ground. A larger increase in the count rate will indicate that there is leak in that area.
- The α-particles from polonium-210 are used to neutralise static charges in photographic plates and other materials.
Carbon Dating
- Living plants continuously absorb carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. This carbon dioxide contains carbon-12 and carbon-14.
Carbon-12 is stable but carbon-14 is radioactive. The radioisotope carbon-14 is continuously being formed by radiation from the outer atmosphere of the Earth. In living plants, the proportion of carbon-12 and carbon-14 remain the same. - When a plant dies or is eaten by an animal, it no longer takes in carbon-14. The carbon-14 already present in the plant decays slowly with a half-life of 5730 years while the carbon-12 does not change. The proportion of the remaining carbon-14 can be determined by measuring the carbon-14 activity. The age of the plant can then be calculated.