Nuclear Energy Advantages and Disadvantages: Nuclear energy is generated by fusion or fission. It is a cost-effective means to generate power. Atoms unite to generate a bigger atom in nuclear fusion. Atoms are divided to produce smaller atoms in nuclear fission, which generates energy. Nuclear power facilities use nuclear fission to make electricity. Nuclear fusion is the means through which the sun generates electricity.
The accompanying is some of the most significant advantages of nuclear energy and some of the current disadvantages that the sector is experiencing.
Students can also find more Advantages and Disadvantages articles on events, persons, sports, technology, and many more.
What is Nuclear Energy? Advantages and Disadvantages of Nuclear Energy 2022
Electricity may be manufactured in a range of ways. It may be generated, for instance, with solar panels, coal, or the heat captured by atoms splitting apart. Nuclear electricity is generated when atoms break apart to produce power.
Steam is used in all power plants to transform heat into energy. At nuclear power plants, heat is released by atoms splitting apart, a phenomenon known as fission. Heat is released when atoms divide apart. A chain reaction happens when a process is performed over and over again. The element implemented in the fission process in a nuclear power plant is uranium.
The heat from fission boils water and drives a turbine via steam. The generator runs while the turbine rotates, and its magnetic field provides electricity. The energy may then be forwarded to your house.
Benefits and Limitations of Nuclear Energy
- Advantages of Nuclear Energy
- Disadvantages of Nuclear Energy
- Comparison Table for Advantages & Disadvantages of Nuclear Energy
- FAQs on Pros & Cons of Nuclear Energy

Advantages of Nuclear Energy
Mentioned below are a few of the main advantages of nuclear energy.
- Clean source of energy: Nuclear power facilities generate power without releasing greenhouse gases into the atmosphere. This technology eliminates the utilization of typical thermal power stations. They consume as little fossil fuel as practicable. As a consequence, nuclear power plants end up producing minimal toxins (CO2 and others).
- With a modest amount of nuclear fuel, you can output a huge amount of energy: Nuclear Power Plant can yield massive amounts of energy with a significant supply of uranium. It entails cost reductions in terms of raw materials, transportation, extraction, and uranium management. The cost of uranium is comparable to 20% of the value of the power generated.
- It is self-sufficient: Nuclear energy, unlike solar and wind energy, is not completely reliant on external factors. Solar energy is proportional to the number of hours the sun is shining. The strength of the wind determines eolic power. As a consequence, peak energy demand hours do not automatically equate with peak energy demand hours. Electrical planning is supported by atomic energy. It is also plannable in terms of expense. Uranium does not fluctuate in prices like other resources like oil and natural gas.
- Nuclear energy is one of the strongest concentrated forms of energy that we are acquainted with: When contrasted to other sources of energy production, the percentage of fuel required for nuclear energy production is relatively minimal. When weighed pound for pound, uranium generates 16,000 times more power than coal. When analyzing new nuclear fission or fusion processes, the comparability ratio may be as high as 2 million to 1. Nuclear reactions beat chemical reactions by a factor of ten million to one.
- It produces its own fuel to suit future manufacturing requirements: Many nuclear power reactors may utilize their expended fuel to produce more power. Thorium recycling promotes fission in a comparable pattern as uranium.
Although nuclear energy is relatively distant from now being an authentic “renewable” power source, we have made significant strides in significantly reducing the environmental hazards that have traditionally been associated with it.
Disadvantages of Nuclear Energy
Following the advantages, below are a few disadvantages:
Nuclear Accidents Have Serious Repercussions: Nuclear power facilities have incredibly high safety mechanisms. The human aspect, on the other side, has a distinct influence. Choices made in the midst of an unexpected catastrophe may be incorrect. Chernobyl and Fukushima are crucial points.
Chernobyl is the world’s scariest nuclear disaster. The atomic reactor exploded due to a series of poor judgments made by the crew.
The situation at Fukushima was distinctive. External factors influenced the accident. Following the tragedy, however, several nuclear officials questioned the verdict. It was the second-worst disaster in living memory.
It has the potential to be converted into a lethal weapon: Nuclear energy may also be employed to deliver explosive devices that release massive amounts of energy. According to Popular Mechanics, the nuclear bombs unleashed on Japan were 3,000 times weaker than contemporary nuclear weapons attainable today.
Little Boy, as one of the bombs launched on Japan, was nicknamed, emitted around 15 kilotons of energy.
As a result of the bombing, Hiroshima and Nagasaki were obliterated in a matter of minutes. It was the first and only occasion a country deployed nuclear weapons in a retaliatory operation.
Several countries later signed accords to prevent them from spreading. Despite this, nuclear weapons have been constructed and are still in existence. As a result, the serious possibility of a future atomic strike looms.
Nuclear power yields toxic waste: It produces radioactive waste that is highly hazardous to individuals and the environment. If this waste is not taken care of, the consequences might outlast hundreds, albeit not thousands, of years.
There are confinement options available, but radioactive waste does not cease to exist.
Facilities with a Deadline: Nuclear reactors have an expiration date. Owners of Nuclear power plants must demolish them after this deadline.
Analysts claim that about 80 new nuclear reactors will be expected every ten years.
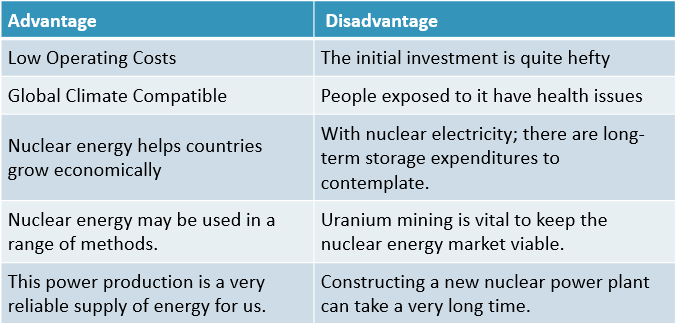
Comparison Table for Advantages & Disadvantages of Nuclear Energy
| Advantage | Disadvantage |
| Low Operating Costs | The initial investment is quite hefty |
| Global Climate Compatible | People exposed to it have health issues |
| Nuclear energy helps countries grow economically | With nuclear electricity; there are long-term storage expenditures to contemplate. |
| Nuclear energy may be used in a range of methods. | Uranium mining is vital to keep the nuclear energy market viable. |
| This power production is a very reliable supply of energy for us. | Constructing a new nuclear power plant can take a very long time. |
FAQ’s on Pros & Cons of Nuclear Energy
Question 1.
When it pertains to a nuclear power plant, what are the potential risks of energy loss?
Answer:
When transmission deficiencies are coupled with theft, India might lose up to 30% of the energy provided through the customary distribution infrastructure. Because the necessary infrastructure is not in play in the United States, electricity losses from nuclear power can be as significant as 13%.
To facilitate the nuclear energy industry, high-voltage, low-loss transmission lines must be provided to help minimize power dissipation. When particularly in comparison to standard low-voltage transmission lines, which encounter higher levels of loss, this extension to a network or grid comes at an increased price.
Question 2.
What are the foreign dependency considerations that governments must consider when adopting nuclear power?
Answer:
Adopting nuclear energy places a country in a position of reliance on other countries. Uranium mines are accessible in just a few nations. Additionally, nuclear technology is not viable in all countries. As a result, they’ll have to outsource each of these services.
Question 3.
What are the typical operating expenses of nuclear power plants?
Answer:
Nuclear power facilities are less expensive to operate than coal or natural gas plants. The running costs are between 20% and 50% of what a fossil fuel plant would require. In particular, the amount of power generated is vastly greater than in most other modes.
