New Simplified Chemistry Class 9 ICSE Solutions The Language Of Chemistry
ICSE SolutionsSelina ICSE SolutionsML Aggarwal Solutions
Viraf J Dalal Chemistry Class 9 Solutions and Answers
Simplified ChemistryPhysicsChemistryBiologyMathsGeographyHistoryCivics
Exercise
Question.1 (1985)
XCl2 is the chloride of a metal X. State the formula of the sulphate and the hydroxide of the metal X.
Answer:
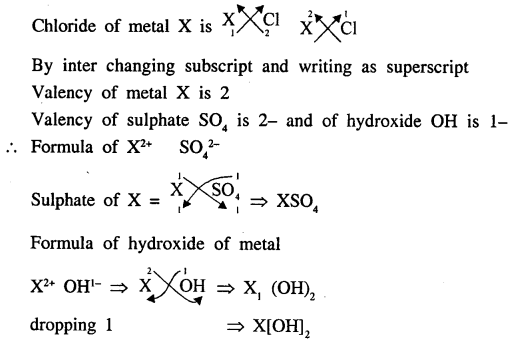
Question.1 (1987)
An element X is trivalent. Write the balanced equation for the combustion of X in oxygen.
Answer:
Combustion of X3+ in oxygen means oxide of X
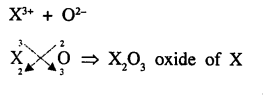
Question.1 (1991)
The formula of the nitride of a metal X is XN, state the formula of :
- its sulphate
- its hydroxide.
Answer:
Formula of nitride of metal X is XN
Since valency of nitrogen is 3-
∴ Valency of X is 3+
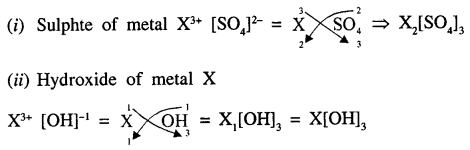
Question.1 (1992)
What is the valency of nitrogen in :
- NO
- N2O
- NO2
Answer:

Additional Questions
Question 1.
What is meant by the term ‘symbol’. Give the qualitative and quantitative meaning of the term ‘symbol’.
Answer:
Symbol : “Is the short form that stands for the atom of a specific element.”
Qualitative meaning : C is the symbol of atom of element carbon
S is the symbol of atom of element sulphur.
This means symbol stand for a specific element.
No two elements can have the same symbol.
Quantitative meaning : A symbol also represents quantity of the element i.e. atomic mass of element. Symbol C represents 12 g of carbon. In other words how many times that element is heavier than 1/12 th C12
Question 2.
Name three metals whose symbols are derived from :
(a) the first letter of the name of the element
(b) from their Latin names.
Answer:

Question 3.
Explain the meaning of the term ‘valency’.
State why the valency of the metal potassium is +1 and of the non-metal chlorine is -1.
Answer:
Valency : “Is the combining capacity of atom or of a radical.” OR
“Valency is the number of electrons, which an atom can lose/gain/share during a chemical reaction.”
Metal potassium (K) has 1 electron in outer most shell which it loses and becomes K+ has valency [+1] whereas
Non-metal chlorine [Cl] has 7 electrons in valence shell and gains 1 electron and becomes [Cl–] has valency [-1]
Question 4.
What is meant by the term ‘variable valency’. Give a reason why silver exhibits a valency of +1 and +2.
Answer:
Variable valency : “Certain elements exhibit more than one valency and show variable valency.”
Reason : Why silver exhibits valency +1 and +2 Ag 47 [2, 8, 18, 18, 1] has 1 electron in the outermost shell when loses this electron shows [+1] valency but when penultimate shell has not attained stability and one more electron jumps to the outermost shell there by increasing valency electron and new configuration [2, 8, 18, 17, 2] loses two electrons and has valency [+2]
∴ Silver exhibits Ag1+ [ous] and Ag2+ [ic]
Question 5.
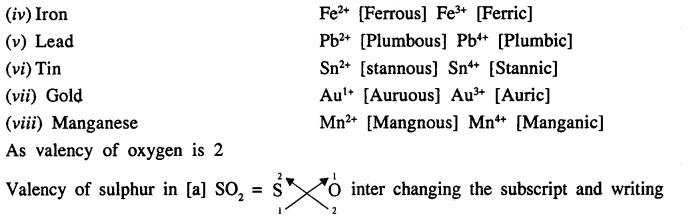
Give examples of eight metals which shows variable valency. State the valency of sulphur in :
(a) SO2
(b) SO3
Answer:
Eight metals which show variable valency are
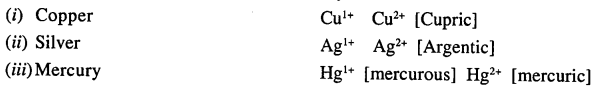
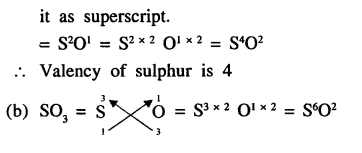
Question 6.
State the valency in each case and name the following elements or radicals given below
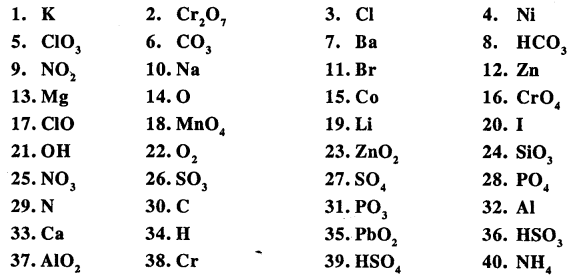
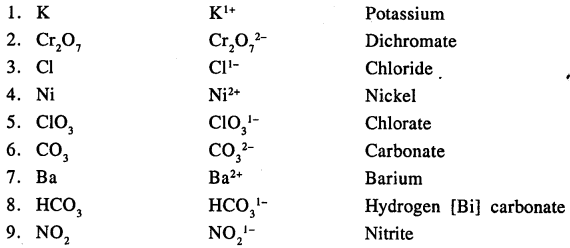
Answer:


Question 7.
State the variable valencies of the following elements and give their names.
(a) Cu, (b) Ag, (c) Hg, (d) Fe, (e) Pb, (f) Sn, (g) Mn, (h) Pt, (i) Au
Answer:


Question 8.
State which of the following elements or radicals are divalent –
(a) Lithium, (b) Nickel, (c) Ammonium, (d) Bromide, (e) Sulphite, (f) Nitride, (g) Carbide, (h) Chromium, (i) Bisulphite, (j) Dichromate, (k) Permanganate.
Answer:
(b) Nickel
(e) Sulphite
(j) Dichromate are divalent
Question 9.
Explain the meaning of the term ‘compound’ with a suitable example. State the main characteristics of a compound with special reference to the compound iron [II] sulphide.
Answer:
Compound : “Is a pure substance made up of two or more elements combined chemically by in a fixed proportion.”
Example : CO2 carbon dioxide is made up of two elements carbon and oxygen C,
12 parts by weight and oxygen
2 × 16 = 32 parts by weight
i.e. in ratio C : O = 12 : 16 = 3 : 4
CHARACTERISTICS OF COMPOUND :
- Components in definite proportion e.g. compound iron [II] sulphide FeS element Iron and sulphur are in definite ratio.
- Compound is Homogeneous.
- Particles in a compound are of J kind composition of iron (II) sulphide is uniform and components cannot be seen separately.
- Compound has definite set of properties.
- Component in FeS do not retain their original properties, i.e. iron cannot be attracted by a magnet, sulphur is insoluble in CS2 and Fe does not giyes H2 with dil. acid. This means compound formed has new properties.
Question 10.
Name the elements in the compound and give the formula – of the following compounds :
(a) Nitric acid, (b) Carbonic acid, (c) Phosphoric acid, (d) Acetic acid, (e) Blue vitriol, (f) Green vitriol, (g) Glauber’s salt, (h) Ethane, (i) Ethanol
Answer:

Question 11.
Explain the term ‘chemical formula’. State why the molecular formula of zinc carbonate is ZnCO3
Answer:
Chemical Formula : “A molecule of a substance element or compound could be represented by symbols. Representation known as chemical formula i.e. molecular formula of oxygen gas is O2 water H2O, hydrochloric acid HCl etc.
Molecular formula of zinc carbonate : Zinc and carbonate both have valency
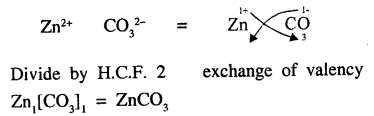
Question 12.
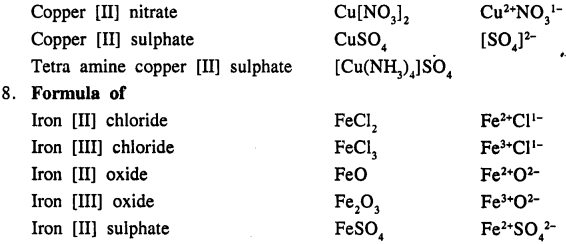
Write the formula of the following compounds :



Answer:





Question 13.
Write the names of the following compounds :
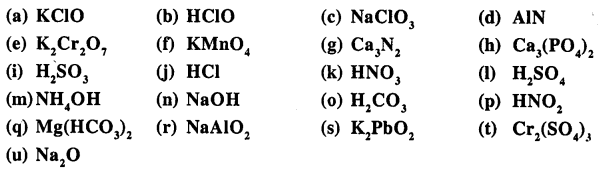
Answer:


Question 14.
Explain the term ‘chemical equation’. What is meant by ‘reactants’ and ‘products’ in a chemical equation.
Answer:
Chemical equation : “Is the symbolic representation of a chemical reaction using symbols and the formulae of the substances involved in the reaction.”
Sulphur bums in oxygen is a chemical reaction and sulphur dioxide is formed. This can be represented as sulphur + oxygen \(\underrightarrow { heating } \) sulphur dioxide is word equation.
![]()
Reactants : Substances taking part in a reaction separated by (+) sign on the left hand side of arrow are called reactants.
Products : Substances formed in the reaction are called products.
Question 15.
Give an example of a chemical equation in which two reactants form –
(a) one product
(b) two products
(c) three products
(d) four products
Answer:
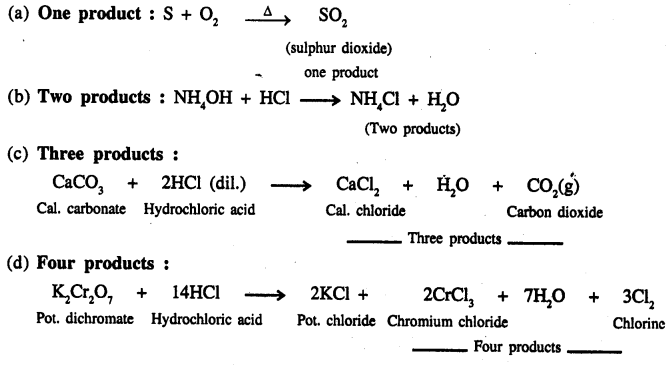
Question 16.
![]()
(a) State what is a ‘balanced equation’.
(b) Give a reason why the above equation is balanced.
(c) State why the compound MnO2 is written above the arrow.
Answer:
(a) Balanced equation : “Equation in which the total number of atoms of each element in the reactants, on the left side of the equation is equal to the number of atoms of each element in the products formed, on the right side of the equation.”
(b) As the total number of [K, Cl, 0] atoms on the L.H.S. is equal to the number of the given atoms on the R.H.S., the given equation is balanced.
(c) MnO2 is a catalyst in the reaction which does not under go any change and simply increases the rate of reaction is written above the arrow.
Question 17.
What do the symbols —
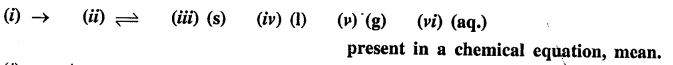
Answer:

Question 18.
![]()
(a) State the information provided by the above chemical equation.
(b) State the information not conveyed by the above chemical equation.
Answer:
(a) Information provided by equation
![]()
- Calcium carbonate reacts with [dil.] hydrochloric acid to produce calcium chloride, water and Carbondioxide.
- One molecule of calcium carbonate reacts with two molecules of acid to produce one molecule of calcium chloride, one molecule of water and one molecule of carbondioxide.
- About the chemical composition of respective, molecules like one molecule of calcium chloride contains one atom of calcium, one atom of carbon and three atoms of oxygen.
- Molecular masses
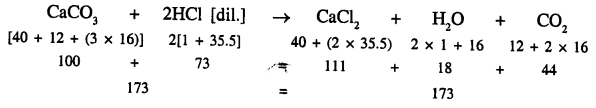
that 100 parts by weight of calcium carbonate reacts with 73 parts by weight of hydrochloric acid to produce 111 parts by weight of calcium chloride 18 parts by weight of water and 44 parts by weight of carbon dioxide. - That reaction is irreversible.
- That about the state of substances present i.e. solid, liquid or gas.
(b) Information not conveyed are :
- Time, reaction takes to complete.
- About the concentrations of reactants and products.
- Speed of reaction.
- Changes in colour occuring – during the reaction.
- Whether heat is given out or absorbed during the reaction.
- The physical state of reactants and products.
Question 19.
Balance the following simple equation :
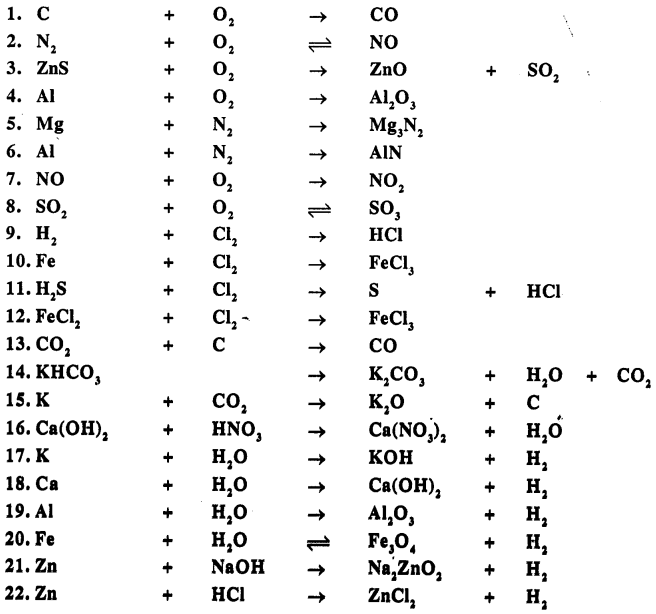
Answer:
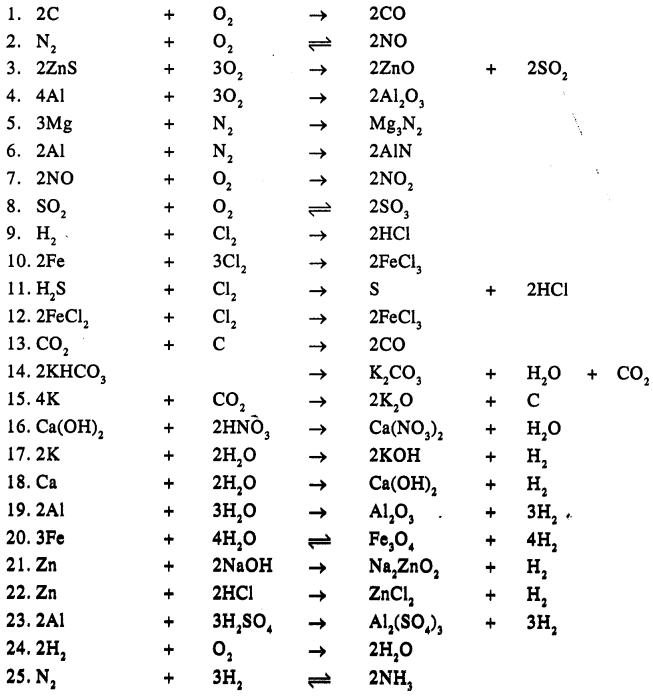
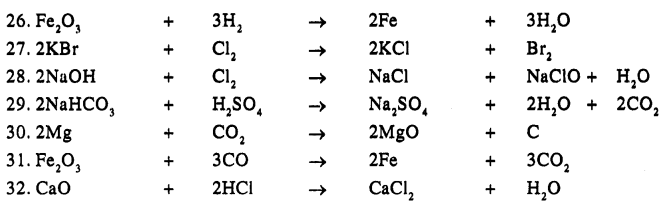
Question 20.
Write balanced equations for the following word equations :
- Potassium nitrate → Potassium nitrite + Oxygen
- Calcium + Water → Calcium hydroxide + Hydrogen
- Iron + Hydrochloric acid → Iron [II] chloride + Hydrogen
- Nitrogen dioxide + Water + Oxygen → Nitric acid
- Lead dioxide [lead (IV) oxide] → Lead monoxide + Oxygen
- Aluminium + Oxygen → Aluminium oxide
- Iron + Chlorine → Iron [III] chloride
- Potassium bromide + Chlorine → Potassium chloride + Bromine
- Potassium bicarbonate → Potassium carbonate + Water + Carbon dioxide
- Calcium hydroxide + Ammonium chloride → Calcium chloride + Water + Ammonia
Answer:
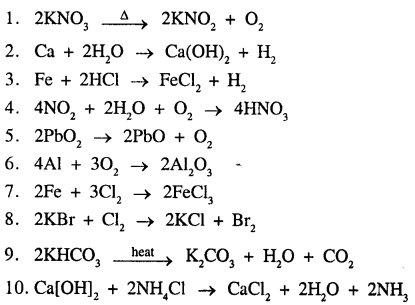
Question 21.
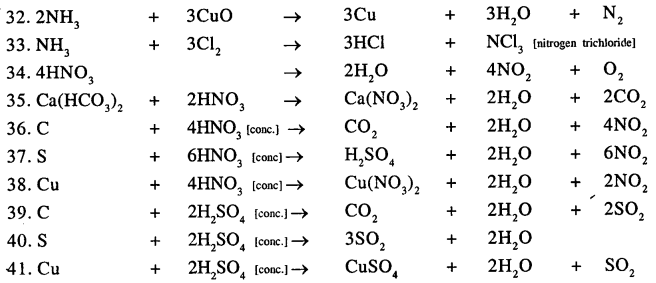
Balance the following important equations :
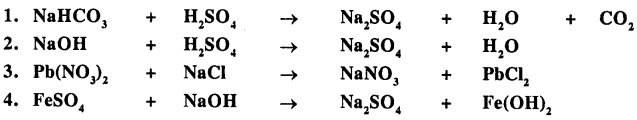
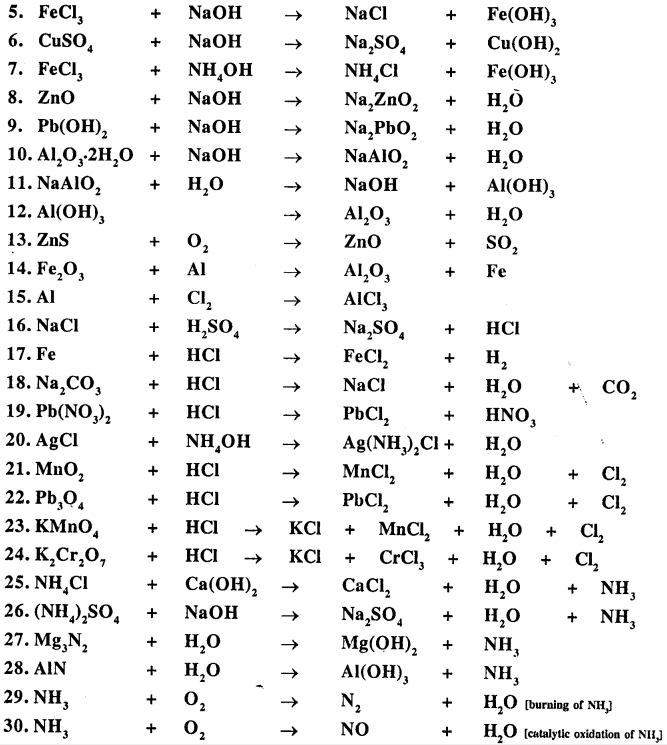
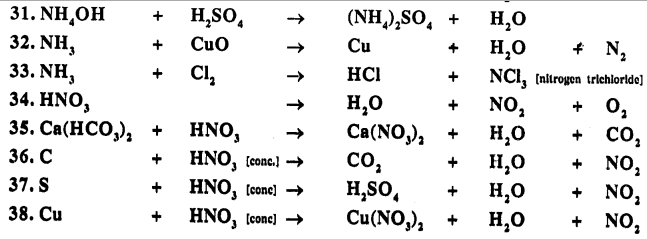
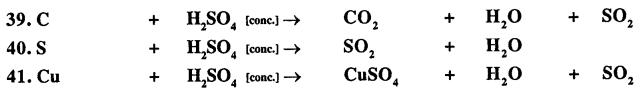
Answer:

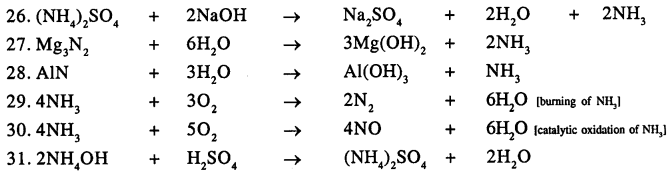
Question 22.
Give balanced equations for (1) & (2) by partial equation method, [steps are given below]
(1) Reaction of excess ammonia with chlorine – Ammonia as a reducing agent
(a) Ammonia first reacts with chlorine to give hydrogen chloride and nitrogen.
(b) Hydrogen chloride then further reacts with excess ammonia to give ammonium chloride.
(2) Oxidation of Lead [II] Sulphide by Ozone
(a) Ozone first decomposes to give molecular oxygen & nascent oxygen.
(b) Nascent oxygen then oxidises lead [II] sulphide to lead [II] sulphate.
Answer:
(1)
(a) Ammonia reacts with chlorine to give hydrogen chloride and nitrogen.
(b) Hydrogen chloride reacts with excess ammonia to give ammonium chloride.
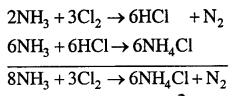
(2)
(a) ozone decomposes to O2 (molecular) and nascent oxygen.
(b) Nascent oxygen oxidises Pb [II] sulphide to Lead [II] sulphate and needs 4 atoms of oxygen to form sulphate. Hence 1st equation must be multiplied by 4. Cancelling 4 atom of oxygen from both sides and adding.
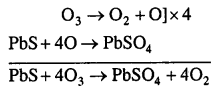
Question 23.
Define the terms – (a) Relative atomic mass (b) Relative molecular mass. State why indirect methods are utilised to determine the absolute mass of an atom. Explain in brief the indirect method used.
Answer:
(a) Relative atomic mass [RAM] of an element :
“is the number of times one atom of an element is heavier than 1/12 the mass of an atom of carbon [C12]”
or
“Mass of an atom of an element as compared with 1/12 mass of an atom of carbon [C12]”
(b) Relative molecular mass [RMM] of an element/compound : “Is the number of times one molecule of the substance is heavier than 1/12 the mass of an atom of carbon [C12].
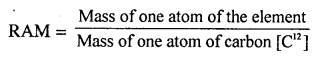
or
“Mass of one molecule as compared with the 1/12 mass of an atom of carbon[C12]”

To determine the absolute mass of an atom indirect methods are utilised as Atom are extremely small and very light.
An isotope of carbon C12 [carbon -12 atom] has been assigned atomic mass of exactly 12 atomic mass unit] is used.
Question 24.
1. Calculate relative molecular mass of
(a) ZnCO3
(b) CaSO4 [Zn = 65, S=32, O = 16, Ca = 40, C = 12]
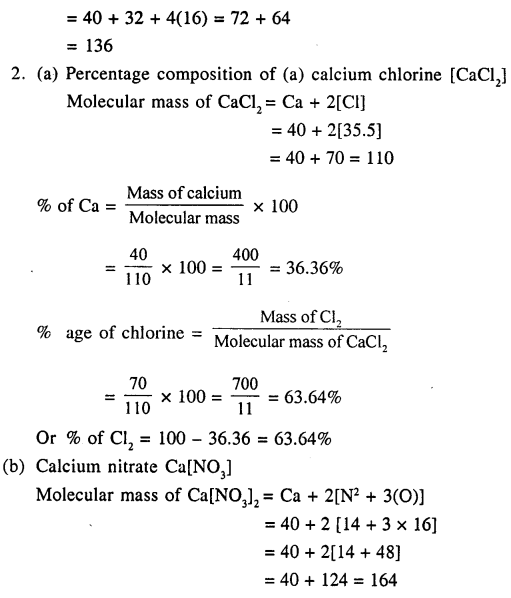
2. Calculate the percentage composition of
(a) calcium chloride
(b) calcium nitrate [Ca = 40 , Cl = 35.5 , N = 14 , O = 16]
Answer:
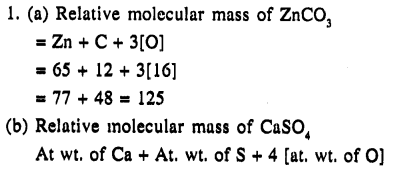
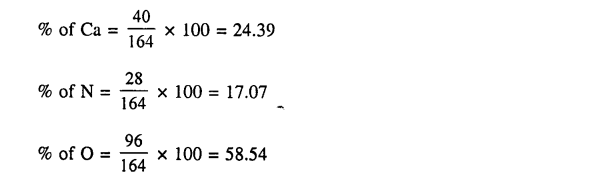
The Language Of Chemistry Unit Test Paper 1
Q.1. Match the names of ions and radicals from 1 to 10 with their correct answer from A to Q.

Answer:

Q.2. State which of the following formulas of compounds A to J are incorrect. incorrect write the correct formula.
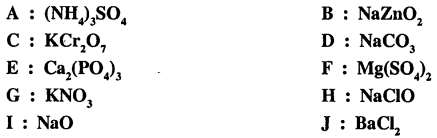
Answer:

Q.3. Fill in the blanks with the correct word from the words in brackets :
Question 1.
A symbol represents a short form of a / an ____ [atom / element / molecule]
Answer:
A symbol represents a short form of a / an element.
Question 2.
Compounds are always ____ (heterogeneous/homogeneous) in nature.
Answer:
Compounds are always homogeneous in nature.
Question 3.
Variable valency is exhibited, since electrons are lost from an element from the ____ [valence / penultimate] shell.
Answer:
Variable valency is exhibited, since electrons are lost from an element from the penultimate shell.
Question 4.
A chemical equation is a shorthand form for a ____ [physical / chemical] change.
Answer:
A chemical equation is a shorthand form for a chemical change.
Question 5.
Relative molecular mass of an element/compound is the number of times one ____ of the substance is heavier than -1/12th the mass of an atom of carbon [C12]. (atom/ion/molecule)
Answer:
Relative molecular mass of an element/compound is the number of times one molecule of the substance is heavier than -1/12 th the mass of an atom of carbon
[C12].
Q.4. Underline the compound in each equation given below, which is incorrectly balanced and write the correct balancing for the same.
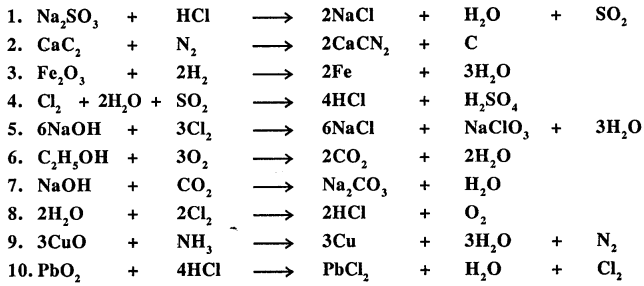
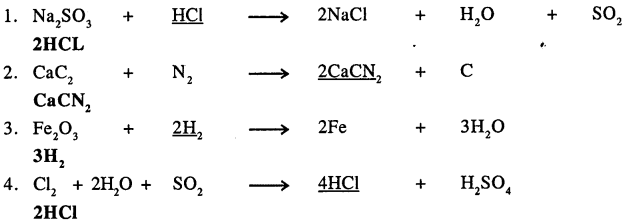
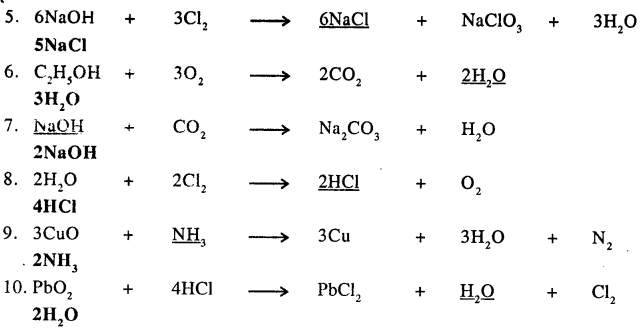
Answer:
Q.5. With reference to a chemical equation state which of the statements 1 to 5 pertain to A or B.
A : Information provided by a chemical equation. .
B : Limitations of a chemical equation
- The nature of the individual elements.
- The speed of the reaction.
- The state of matter in which the substance is present.
- The completion of the reaction.
- The direction of the reaction.
Answer:
A : Information provided by a chemical equation.
1. The nature of the individual elements.
3. The state of matter in which the substance is present.
5. The direction of the reaction.
B : Limitations of a chemical equation
2. The speed of the reaction.
4. The completion of the reaction.