New Simplified Chemistry Class 9 ICSE Solutions Chemical Changes and Reactions
ICSE SolutionsSelina ICSE SolutionsML Aggarwal Solutions
Viraf J Dalal Chemistry Class 9 Solutions and Answers
Simplified ChemistryPhysicsChemistryBiologyMathsGeographyHistoryCivics
Exercise
Question 1.(1986)
Explain : Silver nitrate solution is kept in coloured reagent bottles in the laboratory.
Answer:
![]()
Silver nitrate gets decomposed by sunlight. Hence silver nitrate is stored in coloured reagent bottles.
Question 1.(1987)
Give an example of an endothermic reaction.
Answer:
![]()
Question 1.(1988)
State in each case if the reaction represents oxidation or reduction
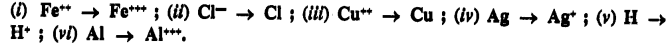
Answer:

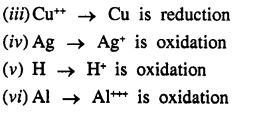
Question 1.(1989)
Reactions can be classified as : Direct combination, decomposition, simple displacement, double decomposition, Redox reactions. State which of the following types, takes place in the reactions given below
- Cl2 + 2KI → 2KCl + l2
- 2Mg + O2 → 2MgO
- SO2 + 2H2O + Cl2 → 2HCl + H2SO4
- AgNO3 + HCl → AgCl + HNO3
- 4HNO3 → 4NO2 + 2H2O + O2
Answer:
- Cl2 + 2KI → 2KCl + I2 — Simple displacement
- 2Mg + O2 → 2MgO — Direct combination
- SO2 + 2H2O + Cl2 → 2HCl + H2SO4 — Redox reaction
- AgNO3 + HCl → AgCl + HNO3 — Double decomposition
- 4HNO3 → 4NO2 + 2H2O + O2 — Decomposition reaction
Question 1.(1990)
Give one reason why magnetizing a piece of steel is a physical change.
Answer:
There is no change in composition.
Question 1.(1993)
State whether the following are oxidation or reduction
![]()
Answer:
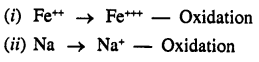
Additional Questions
Question 1.
Explain the term chemical reaction with special reference to reactants and products.
Answer:
Chemical change : “Is reprsentation of a chemical change in substances taking part and are called reactants written on left side of →
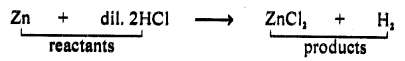
When Zn react with dil HCl, new substance ZnCl and H2 are produced as a result of chemical change reactants are seperated by + sign and products formed are also separated by + sign.
Question 2.
Give a suitable example with equation to show the representation of a chemical reaction.
Answer:
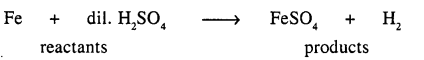
Iron and sulphuric acid dilute which react to produce ferrous sulphate and hydrogen gas can be represented by a chemical equation.
Iron + dil. sulphuric acid → ferruous sulphate and hydrogen
Question 3.
A chemical reaction is often accompanied by external indications or characteristics.
Give two examples where a chemical reaction is accompanied by a change in colour of the reactants & products on completion of the reaction.
Answer:
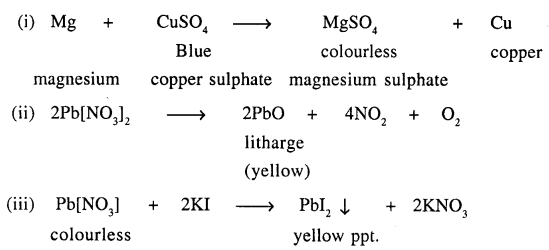
A chemical reaction is accompanied by change in colour of reactants and products
Question 4.
Give balanced equations for reactions involving evolution of a gas on addition of dilute acid to
(a) sodium sulphite
(b) calcium carbonate.
Answer:
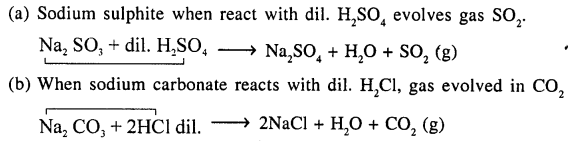
Question 5.
Give a balanced equation for conversion of
(a) an ammonium salt to a basic gas
(b) a soluble lead salt to an insoluble lead salt – formed as a white precipitate.
Answer:
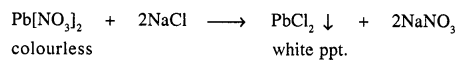
(a) Ammonium salt [NH4Cl] on heating produces NH3(g) which is a basic gas
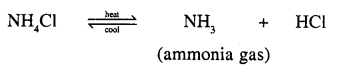
(b) Lead nitrate when reacts with sodium chloride insoluble white ppt. of lead chloride is formed
Question 6.
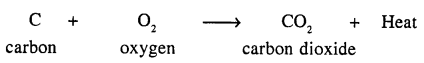
Chemical reactions may proceed with evolution or absorption of heat. Give an example of each.
Answer:
Chemical reaction is characterised by evolution of heat :
Chemical reaction is characterised by absorption of heat :
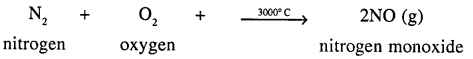
Question 7.
Define the following types of chemical changes or reactions with a suitable example each.
(a) Direct combination reaction or synthesis
(b) Decomposition reaction
(c) Displacement reaction or substitution reaction
(d) Double decomposition reaction
Answer:
(a) Direct Combination Reaction Of Synthesis :
“Those reactions in which two or more substances [element or elements and compound or compounds] combine and form a new substance”
H2 + O2 → H2O Hydrogen combines with oxygen to produce a new substance water.
(b) Decomposition Reaction :
“Those reactions in which a compound splits up into two or more simpler substances”

(c) Displacement Reaction Or Substitution Reaction :
“Those reactions in which one element takes place of another element in a compound, are known as substitution reactions.”
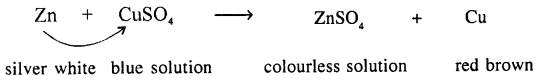
(d) Double-De-Composition Reaction :
“Those reactions in which two compounds react by an exchange of ions to form two new compounds are called double displacement reactions.”
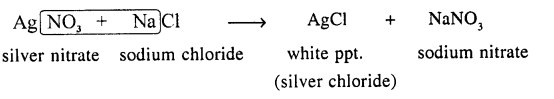
Question 8.
Give a balanced equation for a direct combination reaction involving :
(a) Two elements — one of which is a neutral gas and the other a yellow non¬metal
(b) Two elements – one of which is a neutral gas and the other a monovalent metal
(c) Two compounds – resulting in formation of a weak acid
Answer:
(a) Direct Combination of two elements one of which is a neutral gas and the other a yellow non-metal
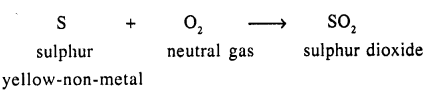
(b) Direct Combination of two elements one of which is a neutral and the other a monovalent metal
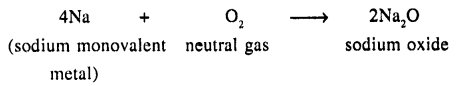
(c) Direct Combination of two compounds to form weak acid.
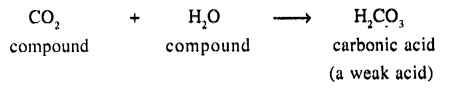
Question 9.
Give balanced equations for the following reactions of synthesis involving formation of :
(a) An acid – from sulphur dioxide gas
(b) An alkali – from a basic oxide – sodium oxide
(c) A salt – from a trivalent metal and a coloured gas.
Answer:
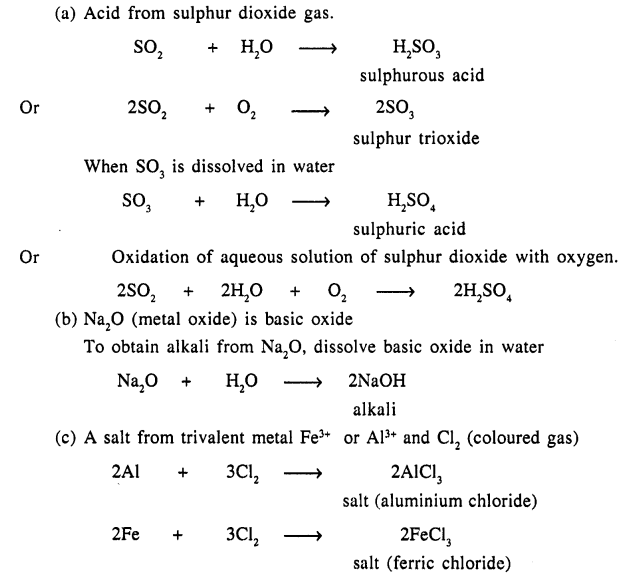
Question 10.
Convert — (a) nitrogen to ammonia (b) hydrogen to hydrogen chloride – by a direct combination reaction.
Answer:
By direct combination reaction :
(a) Nitrogen to ammonia
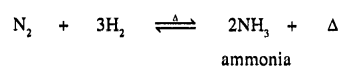
(b) Hydrogen to hydrogen chloride
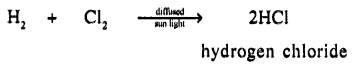
Question 11.
Give balanced equations for thermal decomposition of :
(a) lead carbonate
(b) lead nitrate
(c) ammonium dichromate
(d) mercury [II] oxide
(e) calcium hydroxide
Answer:
Decomposition of :
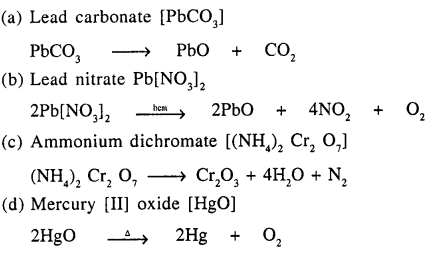
Question 12.
Define – a thermal dissociation reaction with a suitable example. Give an example of a photochemical decomposition reaction. Name a metallic oxide which on thermal decomposition is reduced to a metal.
Answer:
Thermal Dissociation :
“A decomposition reaction — in which a substance dissociates — into two or more simpler substances on application of heat.”
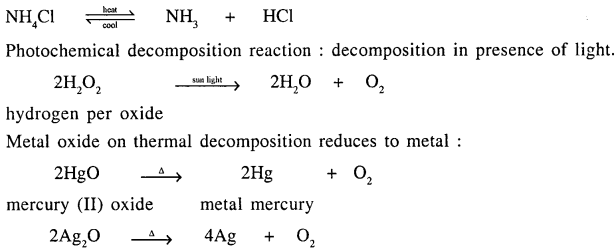
Question 13.
Define a displacement reaction with a suitable example. State how it is represented. Give a reason why zinc displaces hydrogen from dilute sulphuric acid but copper docs not.
Answer:
Displacement reaction : “Is a chemical reaction in which an element [or radical] replaces another element in a compound.”
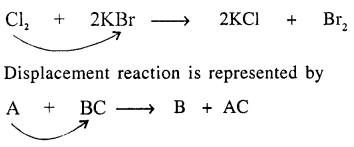
Zinc (more electropositive) and being above [H] in activity series displaces hydrogen from dilute sulphuric acid but copper is below [H] in electrochemical series cannot displace hydrogen from sulphuric acid.
Question 14.
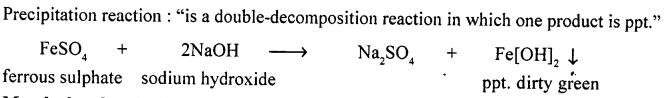
Explain the term double decomposition — precipitation reaction. Give a balanced equation for the preparation of two different insoluble lead salts from their salt solutions by — double decomposition — precipitation.
Answer:
Double decomposition reaction is precipitation reaction.
i. e. in which ppt. is formed
“Reaction between two compounds in aqueous state, to give two new compounds one of which is precipitate (or insoluble).”
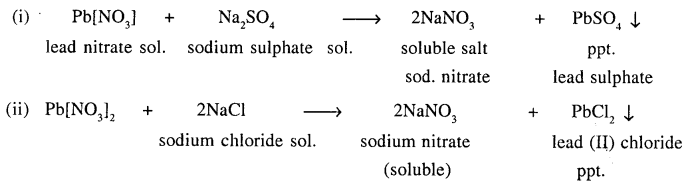
Question 15.
Explain with the help of balanced equations, how precipitation reactions are used for identifying the positive radicals in three different salts, each having a different cation [positive ion].
Answer:
Precipitation reactions are used to identify the positive ions from their colours.
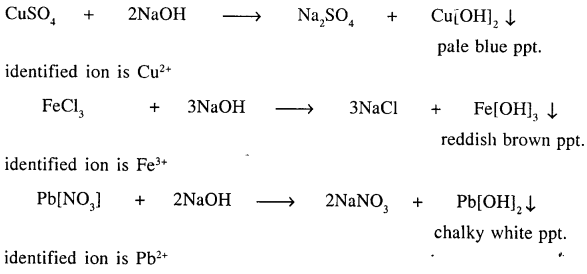
Question 16.
Define the term – double decomposition – neutralization reaction with a suitable representation.
Convert :
(a) an insoluble base
(b) a soluble base to their respective soluble salts by neutralization reaction.
Answer:
When acid reacts with a base salt and water are formed and this is called Neutralisation.
Double-decomposition — Neutralisation reaction :
“Is the chemical reaction between two compounds (acid and base) to interchange radicals and produce salt and water.”
This is represented as :
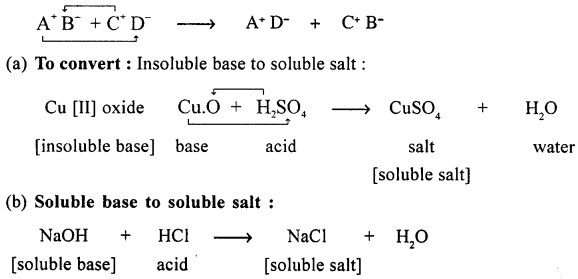
Question 17.
Explain the term energy changes in a chemical change or reaction. Give an example with a balanced equation, for each of the following reactions:
(a) exothermic reaction
(b) endothermic reaction
(c) photochemical reaction
(d) electrochemical reaction.
Answer:
Energy Changes In A Chemical Reaction :
“Is the difference between the chemical energy of the REACTANTS and the PRODUCTS”.
Example of :
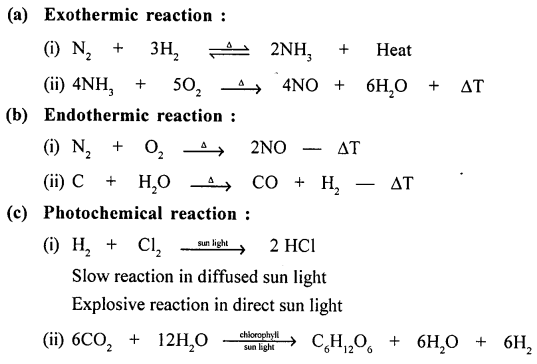
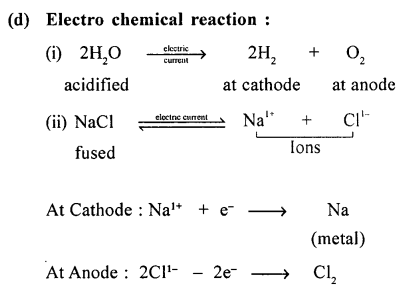
Question 18.
Supply of energy maybe required to initiate a reaction. State the different forms with a suitable example of reactions initiated by supply of energy.
Answer:
To Start A Reaction Energy Needed In The Form :
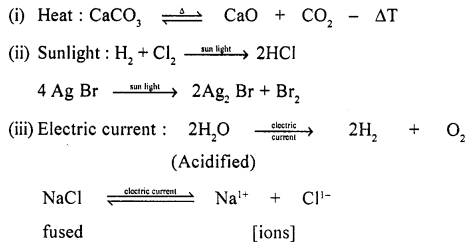
Chemical Changes & Reactions – Unit Test Paper 2
Q.1. Complete the statements by filling in the blank with the correct word/s :
Question 1.
Direct combination reaction of sulphur dioxide with water gives [H2SO4/H2SO3/H2S2O7].
Answer:
Direct combination reaction of sulphur dioxide with water gives H2SO3.
Question 2.
Formation of hydrogen chloride from hydrogen and chlorine is an example of [photochemical reaction/electrochemical reaction].
Answer:
Formation of hydrogen chloride from hydrogen and chlorine is an example of photochemical reaction.
Question 3.
The reaction of hydrogen burning in oxygen to give a neutral liquid is an example of [exothermic/ endothermic] reaction.
Answer:
The reaction of hydrogen burning in oxygen to give a neutral liquid is an example of exothermic reaction.
Question 4.
The neutral gas evolved when lead nitrate undergoes thermal decomposition is [nitrogen dioxide/oxygen/nitrogen].
Answer:
The neutral gas evolved when lead nitrate undergoes thermal decomposition is nitrogen dioxide.
Question 5.
The reddish brown precipitate obtained during a double decomposition precipitation reaction between an iron salt and an alkali is [iron [III] hydroxide/iron [III] hydroxide]
Answer:
The reddish brown precipitate obtained during a double decomposition – precipitation reaction between an iron salt and an alkali is iron [III] hydroxide.
Q.2. Select the correct answer from A, B, C, D and E for each statement given below :
A : Ammonia
B : Hydrogen chloride
C : Hydrogen
D : Nitrogen dioxide
E : Nitric oxide
State the gaseous product formed, when
Question 1.
An active metal reacts with dilute sulphuric acid.
Answer:
C : Hydrogen
Question 2.
A metallic nitrate undergoes thermal decomposition giving a coloured gas.
Answer:
D : Nitrogen dioxide
Question 3.
Two gases one of them neutral, combines by absorption of light energy.
Answer:
B : Hydrogen chloride
Question 4.
An ammonium salt reacts with an alkali.
Answer:
A: Ammonia
Question 5.
An exothermic reaction takes place between ammonia and a neutral gas.
Answer:
E : Nitric oxide
Q.3. Give a balanced equation for each of the following types of reactions :
Question 1.
A direct combination reaction between phosphorus and a neutral gas.
Answer:
Phosphorus with neutral gas (O2)
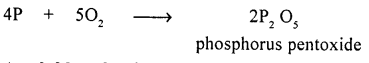
Question 2.
A soluble salt of lead formed from an insoluble base by double decomposition – neutralisation.
Answer:
Soluble salt of lead formed from insoluble base by double-decomposition by neutralization.
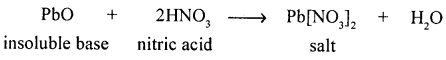
Question 3.
A thermal decomposition reaction of a salt – which results in the formation of nitrogen gas.
Answer:
Thermal decomposition of a salt with the formation of nitrogen gas.
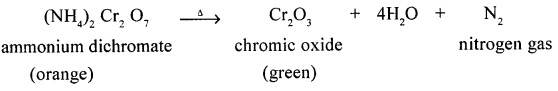
Question 4.
A synthesis reaction between a metal & a non-metal resulting in formation of an insoluble salt of iron.
Answer:
Synthesis reaction between a metal and non-metal to form insoluble salt of iron [FeS]
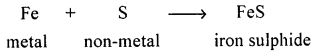
Question 5.
A decomposition reaction of a salt which leaves behind a silvery metal.
Answer:
Decomposition reaction of a salt leaving behind a silvery metal.
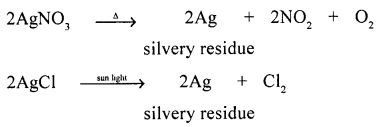
Q.4. Differentiate between the following :
Question 1.
Synthesis reaction & a substitution reaction.
Answer:
Synthesis and substitution reaction :
- Synthesis reaction : “Is a chemical reaction in which two or more elements or an element and a compound or two compound combine to form a new compound.”
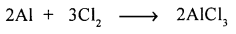
- Substitution reaction : “Is a chemical reaction takes place when an element or radical (more reactive) replaces another element in a compound.”
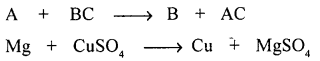
Question 2.
Electrolytic decomposition & photochemical decomposition.
Answer:
Electrolytic decomposition and photochemical decomposition :
- Electrolytic decomposition : “A chemical reaction which takes place with absorption of — electrical energy”
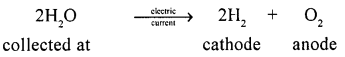
- Photochemical decomposition : “A chemical reaction which takes place with absorption of light energy :

Question 3.
Thermal decomposition & thermal dissociation.
Answer:
Thermal decomposition and thermal dissociation.
- Thermal decomposition : “A chemical reaction in which a compound decomposes into two new substance by heat.” It is not reversible reaction.
CaCO3Cao + CO2
- Thermal dissociation : “Is decomposition of a compound into two or more new substances by heat energy.” It is reversible reaction.
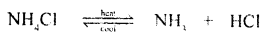
Question 4.
Decomposition reaction & a double decomposition reaction
Answer:
Decomposition reaction and double decomposition reaction :
- Decomposition reaction : A compound decomposes into two or more new substances.
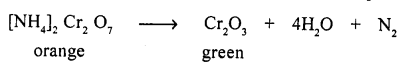
- Double-decomposition : “Two substances exchange their ions and two new substances are produced one of which is insoluble i.e. ppt.”
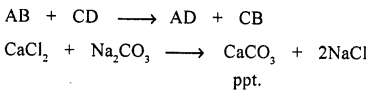
Question 5.
Neutralization reaction & a precipitation reaction.
Answer:
Neutralization reaction and a precipitation reaction :
Neutralization reaction “is a double — decomposition reaction in which acid neutralizes a base and salt and water is formed.”
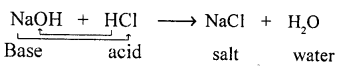
Q.5. Match the chemical reactions in List I with the appropriate answer in List II. List I
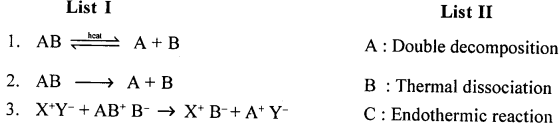

Answer:
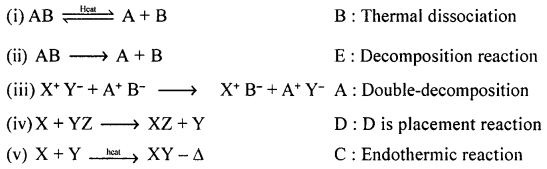
Q.6. Name the solid residual product formed in each reaction and state its colour during – thermal decomposition of the following substances.
- Copper nitrate.
- Ammonium dichromate.
- Zinc carbonate.
- Lead nitrate.
- Calcium hydroxide.
Answer:
Solid residual product of thermal decomposition of :
