New Simplified Chemistry Class 6 ICSE Solutions – Elements, Compounds & Mixtures
ICSE SolutionsSelina ICSE SolutionsML Aggarwal Solutions
Simplified ChemistryChemistryPhysicsBiologyMathsGeographyHistory & Civics
Exercise
Elements and Compounds
Question 1.
Classify substances into pure and impure substances in the form of a chart or tabulation.
Answer:
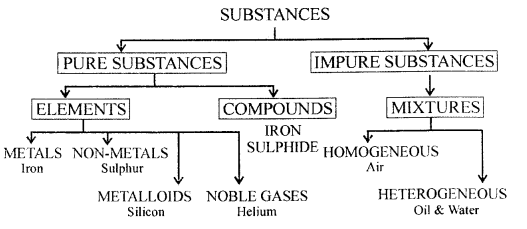
Question 2.
Differentiate between the terms – elements, compounds & mixtures.
Answer:
Element is a pure substance.
- It is the basic unit of matter and cannot be broken down into two or more simpler substances by any means.
- It is mainly classified into metals, non-metals, metalloids and noble gases.
Compound is a pure substance.
- It is formed by combination of two or more elements.
- The elements are combined together in a fixed ratio.
- It can be broken down into its elements by chemical means.
Mixture is an impure substance.
- It is formed by combination of two or more elements, compounds or both.
- The substances are mechanically mixed together in any ratio.
Question 3.
The important physical properties of substances are colour, odour, nature, density & solubility in water. Name –
(a) two coloured gases (with their colours)
(b) a gas with a pungent, choking odour which is lighter than air
(c) a poisonous gas almost as heavy as air.
Answer:
(a)
- Chlorine – greenish yellow
- Nitrogen dioxide – reddish brown.
(b) Ammonia.
(c) Carbon monoxide
Question 4.
Complete the statement – an element is a pure substance made up of (identical/different) atoms.
Answer:
An element is a pure substance made up of identical atoms.
Question 5.
Draw a labelled diagram of an atom including its nucleus, orbits & their contents.
Answer:
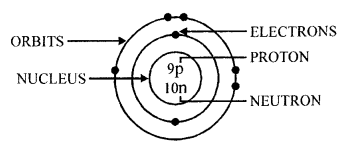
Question 6.
Elements are classified into – Metals – Non-metals – Metalloids – Noble gases. State which of A, B, C, D is a –
- Metallic element
- Non-metallic element
- Metalloid
- Noble gas.
A : Is non-malleable, non-ductile & a poor conductor of electricity____
B : Has lustre, is malleable and ductile & a good conductor of heat ____
C : Is unreactive and inert and present in traces in air____
D : Shows properties of both metals and non-metals____
Answer:
A : Is non-malleable, non-ductile & a poor conductor of electricity Non-metallic element
B : Has lustre, is malleable and ductile & a good conductor of heat Metallic element
C : Is unreactive and inert and present in traces in air Noble gas.
D : Shows properties of both metals and non-metals Metalloid
Question 7.
An atom of an element is denoted by a ‘symbol’. Explain the meaning of the term “symbol” State a reason for representing the following elements by their symbols.
(a) Hydrogen by ‘H’
(b) Helium by ‘He’
(c) Copper by ‘Cu’
Answer:
Symbols : The short form or abbreviated name of the element (or radicals)
The reason for representing the following elements by their symbols are as follow :
(a) Hydrogen by ‘H’ – First letter of the name of element
(b) Helium by He – First two letters of the name of Noble gases.
(c) Copper by ‘Cu’ – Deriving symbols from their Latin names
Question 8.
Match the metallic elements – with their correct symbols Metallic elements (a) Potassium (b) Sodium (c) Calcium (d) Magnesium (e) Zinc
(f) Aluminium (g) Iron (h) Lead (i) Copper (j) Mercury (k) Silver (l) Platinum (m) Gold
Symbols : (1) Ca ; (2) Zn ; (3) Pb ; (4) Hg ; (5) Cu ; (6) Au ; (7) K ; (8) Fe ; (9) Al ; (10) Na ; (11) Mg ; (12) Pt ; (13) Ag
Answer:
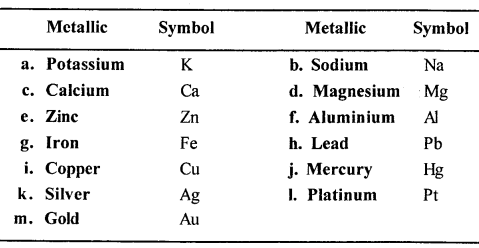
Question 9.
Match the non-metallic elements – with their correct symbols
Non-metallic elements :
(a) Carbon (b) Chlorine (c) Oxygen (d) Phosphorus (e) Hydrogen (f) Nitrogen (g) Iodine (h) Bromine (i) Fluorine (j) Silicon (k) Sulphur
Symbols : (1) O (2) 1 (3) Si (4) C (5) Cl (6) P (7) F (8) H (9) S (10) Br (11) N
Answer:
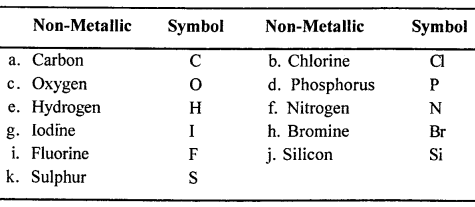
Question 10.
Match the noble gases – with their correct symbols Noble gases : (a) Helium (b) Neon (c) Argon (d) Krypton (e) Xenon (f) Radon
Symbols : (1) Ar (2) Xe (3) Rn (4) He (5) Kr (6) Ne
Answer:
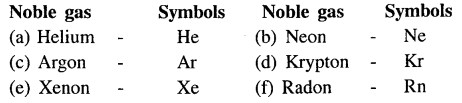
Question 11.
Give a reason why elements are tabulated in a table called the ‘Periodic table’.
Answer:
For arranging all the elements in a systematic and simple manner. The arrangement of elements was done in the form of a table called Periodic Table in which elements are arranged in increasing order of their atomic numbers. Elements in the Periodic Table are arranged in Horizontal rows called Periods and vertical columns called Groups. Metallic elements are placed on the left non-metallic on the right and noble gases on the extreme right of the Periodic table.
Question 12.
Give the names and symbols of the first twenty elements of the periodic table. Differentiate them into metals, non-metals, metalloids and noble gases.
Answer:
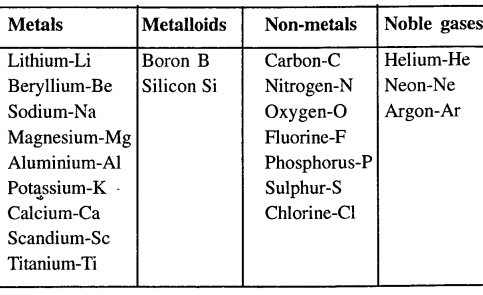
Question 13.
Explain the term – molecules. Give three examples of atoms of the same element forming a molecule. State the atomicity of the same.
Answer:
Atoms of the same element or different elements combine to form a molecule.
Atoms of the same element forming a molecule
- Oxygen
- Nitrogen
- Hydrogen

Atomicity is the number of atoms present in one molecule of the element.
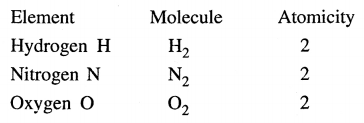
Question 14.
Give one example of
(a) a triatomic molecule
(b) a polyatomic molecule.
Answer:
(a) a triatomic molecule
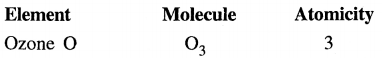
(b) a polyatomic molecule.
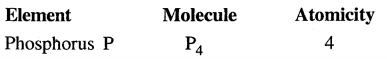
Question 15.
Explain the term compounds. Give the example of a compound containing
(a) hydrogen and oxygen
(b)carbon and oxygen
(c) nitrogen and oxygen
(d) calcium and oxygen.
Answer:
A compound is a pure substance made up of two or more different elements combined chemically in a fixed proportion.
Example of Atoms of different elements forming a compound
(a) 2 Atom of H and 1 atom of O = H2O
(b) Carbon dioxide, 1 atom of carbon and 2 atom of O = CO2
(c) Nitrogen dioxide, 1 atom of nitrogen 2 atom of O = NO2
(d) Calcium oxide, 1 atom of calcium 1 atom of O = CaO
Question 16.
State two characteristics of water which prove that it is a – compound.
Answer:
Characteristics of compounds
- Elements in a compound are present in a definite proportion.
Example 2 atoms of hydrogen combine with 1 atom of oxygen to give 1 molecule of water (compound)
H2 + O = H2O (water) - Compounds have a definite set of properties example :
The properties of the compound water are different from the properties of the elements hydrogen and oxygen in water.
Question 17.
Explain the terms ‘chemical formula\ State what a chemical formula denotes.
Answer:
- Chemical formula is a representation of a substance either element or compound by means of symbols.
- Chemical formula denotes the number of atoms of each element present in a compound.
Question 18.
Give the symbols and the number of atoms of each element present in
(a) sodium chloride
(b) water
(c) carbon dioxide
(d) zinc chloride.
Answer:

Question 19.
For writing a chemical formula – ‘symbols’ and combining capacity of an element with hydrogen i.e. ‘valency’ should be known. Explain the term – combining capacity of an element i.e. valency.
Answer:
The combining power of an element especially as measured by the number of hydrogen atoms can combine or displace with the element.
Question 20.
State what are radicals. Give the names of the radicals –
(a) NO3
(b) OH
(c) SO4
(d) CO3
Answer:
A radical is an atom or group of atom of same or different elements that behaves in the manner of positive or negative ions.
(a) NO3 – nitrate
(b) OH – hydroxide
(c) SO4 – sulphate
(d) CO3 – carbonate
Question 21.
Match the symbols of metallic elements – with their correct combining power or capacity.
(a) K
(b) Zn
(c) Al
(d) Na
(e) Ca
Combining power or capacity – A : 3 ; B : 2 ; C : 1. (positive valencies)
Answer:
(a) K — Valency-1 (C)
(b) Zn — Valency-2 (B)
(c) Al — Valency-3 (A)
(d) Na— Valency-1 (C)
(e) Ca — Valency-2 (B)
Question 22.
Match the symbols of non-metallic elements with their correct combining power or capacity.
(a) O
(b) S
(c) Cl
Combining power or capacity A : 3; B : 2; C : 1. (negative valencies)
Answer:
(a) O — Valency-2 (B)
(b) S — Valency-2 (B)
(c) Cl — Valency-1 (C)
Question 23.
Match the symbols of – radicals – with their correct combining power or capacity, (valency).
(a) OH
(b) SO4
(c) NO3
(d) CO3
Combining power or capacity – A : 3; B : 2; C : 1. (negative valencies)
Answer:
(a) OH— Valency- 1 (C)
(b) SO4 — Valency- 2 (B)
(c) NO3— Valency- 1 (C)
(d) CO3 — Valency- 2 (B)
Question 24.
Write the formula of the compound formed – given “symbols and combining power or capacity (valency) of each element in the compound.
(a) K1+ Cl1-
(b) Na1+ Cl1-
(c) Ca2+ NO31-
Answer:
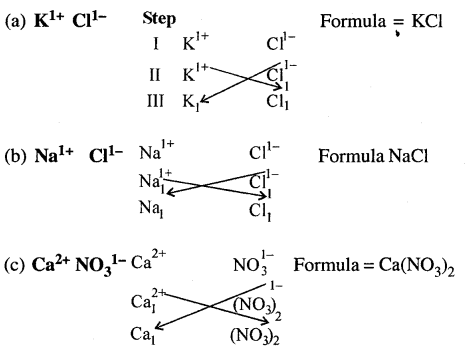
Question 25.
Match the formulas of the following – gases – with their correct names :
Gases : (a) H2, (b) N2, (c) O2, (d) Cl2, (e) HCl, (f) NH3, (g) CO, (h) CO2, (i) SO2, (j) NO, (k) NO2
Names :
(1) Ammonia, (2) Nitrogen dioxide, (3) Oxygen, (4) Hydrogen, (5) Nitrogen, (6) Chlorine, (7) Carbon monoxide, (8) Sulphur dioxide, (9) Nitrogen monoxide, (10) Carbon dioxide, (11) Hydrogen chloride
Answer:


Question 26.
Match the formulas of the following – acids – with their correct names
Acids : (a) HCl, (b) HNO3, (c) H2SO4, (d) H2CO3
Names : (1) Carbonic acid, (2) Sulphuric acid, (3) Hydrochloric acid, (4) Nitric acid
Answer:

Question 27.
Match the formulas of the following – bases – with their correct names.
Bases : (a) NaOH, (b) KOH, (c) Ca(OH)2, (d) Zn(OH)2
Names : (1) Potassium hydroxide, (2) Zinc hydroxide, (3) Aluminium hydroxide, (4) Calcium hydroxide, (5) Sodium hydroxide
Answer:

Question 28.
Complete the statements with the correct words.
(a) Acid’s – are chemicals which are ____ in taste and derived from plants and ____
Answer:
Acids – are chemicals which are sour in taste and derived from plants and minerals.
(b) Bases – are chemicals which are hydroxide (or oxides) of ____ eg. sodium hydroxide.
Answer:
Bases – are chemicals which are hydroxide (or oxides) of metals eg. sodium hydroxide.
(c) Salts- are chemicals formed on reaction of a base with an ____ giving salt and water.
Answer:
Salts- are chemicals formed on reaction of a base with an acid giving salt and water.
Question 29.
In the chemical word equation – Zinc + Sulphuric acid → Zinc sulphate + Hydrogen
(a) State the reactants and products of the above reaction. What does the arrow indicate.
Answer:

(b) The molecular equation is :
Zn + H2SO4 → ZnSO4 + H2[g]. State what [g] represents.
Answer:
[g] represents gas.
Objective Type Questions
Q.1. Complete the statements given below by filling in the blank with the correct word/s.
- An element is a pure substance which cannot be broken down by physical or chemical methods.
- The basic unit of an element is an atom.
- Atom contains nucleus, with positively charged protons.
- Element silver has the symbol derived from its Latin name ‘argentum’.
- From the elements – He, Br, Pt and O ; the element which is metallic is Pt, an inert element is He, forms a triatomic molecule is O, is liquid at room temperature is Br.
- From the elements nitrogen, chlorine, bromine, the element present in the atmosphere is nitrogen.
Q.2. Match the statements in List I – 1 to 10 with their correct answers in List II – A to J.

Answer:
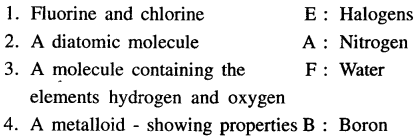

Q.3. Select the correct answer from the choice in brackets.
Question 1.
The symbol of – mercury [Mg / Hg / Ag]
Answer:
Hg
Question 2.
The type of element-phosphorus [metallic/non-metallic/noble gas]
Answer:
non-metallic
Question 3.
The type of molecule- bromine [monoatomic/diatomic/triatomic]
Answer:
diatomic
Question 4.
A compound [nitrogen/ozone/zinc chloride]
Answer:
zinc chloride
Question 5.
The unreactive non-metallic element [chlorine / argon / sulphur]
Answer:
argon
Question 6.
The negatively charged particles in an atom [protons/neutrons/electrons]
Answer:
electrons
Question 7.
The element which is malleable [sulphur / carbon / iron]
Answer:
iron
Question 8.
An impure substance [element / mixture / compound]
Answer:
mixture
Question 9.
An element which is a poor conductor of heat [copper / carbon / aluminium]
Answer:
carbon
Question 10.
A group of atoms of elements [ion / radical / combining power]
Answer:
radical
Q.4. Match the compounds in List I – 1 to 20 with their correct formulas from in List II – A to T.
1. Hydrochloric acid, 2. Potassium hydroxide, 3. Sulphuric acid, 4. Zinc hydroxide, 5. Sodium chloride, 6. Nitric acid, 7. Calcium hydroxide, 8. Carbonic acid, 9. Sodium hydroxide, 10. Copper sulphate, 11. Potassium chloride, 12. Calcium carbonate, 13. Magnesium suiphide, 14. Zinc sulphate, 15. Aluminium hydroxide, 16. Sodium carbonate, 17. Calcium sulphide, 18. Magncsium oxide, 19. Zinc oxide, 20. Ammonium chloride.
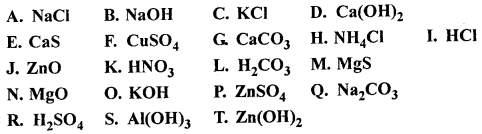
Answer:


Exercise
Mixtures
Question 1.
Explain the term mixtures. Give an example of mixtures of –
(a) two elements
(b) two compounds
(c) elements and compounds.
Answer:
Mixture : A mixture is an impure substance made up of two or more elements or compounds mechanically mixed together in any proportion.
Examples :
(a) Of two elements

(b) Of two compounds
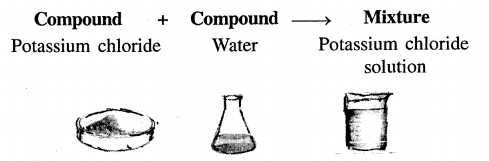
(c) Of elements and compounds

Question 2.
Differentiate between homogeneous and heterogeneous mixtures with suitable examples.
Answer:
The main characteristics of mixture (Iron + Sulphur) are :
Homogeneous mixtures :
- There constituents are uniformly mixed.
- The properties and composition are same throughout the mixture.
- Examples :
(a) alcohol and water
(b) salt and water
(c) sugar and water
Heterogeneous mixtures :
- There constituents are not uniformly mixed.
- The properties and composition vary throughout the mixture.
- Examples :
(a) oil and water
(b) sand and water
(c) chalk and water
Question 3.
With reference to the mixture of iron and sulphur, state the main characteristics of mixture.
Answer:
The main characteristics of mixture (Iron + Sulphur) are :
- The mixture of iron and sulphur may contain iron and sulphur in varying proportions.
- The original properties of each element are retained in the mixture of iron and sulphur.
- Mixture of the two elements iron and sulphur can be separated by i.e. a physical method, i.e. by using a magnet since iron is attracted to the magnet.
Question 4.
Tabulate a comparative chart – to differentiate between elements, compounds and mixtures. Differentiate them with reference to
(a) the term
(b) existence
(c) properties
(d) separation of components.
Answer:
(a) Term —
- Elements – Pure substance made up of one kind of atoms only. e.g. Iron [Fe], Sulphur [S]
- Compounds – Pure substance made up of two or more different elements, e.g. Iron sulphide [FeS]
- Mixtures – Impure substance made up of two or more elements or compounds, e.g. Iron and sulphur mixture.
(b) Existence—
- Elements – Elements i.e. atoms are present on their own. e.g. Iron and sulphur exist on their own as elements iron and sulphur.
- Compounds – Components in a compound present in a definite proportion.
e.g. Iron and sulphur are chemically combined in a fixed ratio in iron sulphide. - Mixtures – Components in a mixture present in any proportion.
e.g. Iron and sulphur are mixed in any ratio in the mixture of iron and sulphur.
(c) Properties —
- Elements – Elements have a definite set of properties.
Elements classified into metal and non-metals each with its own properties. - Compounds – Compounds have a definite set of properties. Elements of a compound do not retain their original properties.
- Mixtures – Mixture not have a definite set of properties.
Components of a mixture do retain their original properties.
(d) Separation of compound —
- Elements – Elements occur on their own or as compounds and can be separated by chemical and physical methods.
Example : Iron, copper. - Compounds – Elements in a compound are chemically combined and can be separated by chemical methods only.
Example : Iron Sulphide, copper oxide. - Mixtures – Components in a mixture can be separated by , physical methods only.
Example : Iron + sulphur
Question 5.
State the principle involved in separation of solid-solid mixtures by –
(a) sieving
(b) magnetic separation
(c) sublimation.
Answer:
(a) Sieving
- Principle — Based on the difference in size of the solid particles.
- Examples — Mixture of Rice powder and soil, mixture of different sized particles of diamond and of sand.
(b) Magnetic separation
- Principle — One component of the mixture is a magnetic substance.
- Example — Mixture of iron ore and sand, Mixture of cobalt and lead.
(c) Sublimation
- Principle — One of the components sublimes on heating.
- Example — Mixture of iodine and salt, Mixture of ammounium chloride and sand.
Question 6.
State the principle involved in separation of solid-liquid mixtures by –
(a) sedimentation and decantation
(b) filtration
(c) evaporation
Answer:
(a) Sedimentation and decantation —
- Principle — The solid component is insoluble and heavier than the liquid component.
- Example — Mixture of sand and water
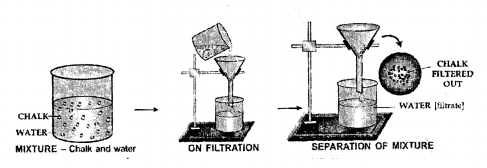
(b) Filtration —
- Principle — Seperation of insoluble solid component by “ passing through a porous material like filter paper.
- Example — Mixture of chalk and water, Mixture of Agcl and Water.
(c) Evaporation —
- Principle — Seperation of the mixture by evaporating the liquid component. The solid should be soluble in the liquid and should not sublime.
Question 7.
Explain the term ‘sieving’. State the structure of a sieve and explain the separation of different sized particles by sieving.
Answer:
Sieving is a method of separation, which is used for separating substances of different sizes that cannot be separated in hand picking.
Principle — Based on the difference in size of the solid particles.

- Technique of Separation — The large sized par icles are separated from the small or finer particles by passing the mixture through a sieve.
The sieve has a wooden frame, with a metal mesh at its base.
The mixture is added from the top of the sieve, when the larger particles stay above and the finer particles collect below it on shaking the sieve. - Examples — Separation of rice powder from soil, seperation of different sized particles of diamond and of sand.
Question 8.
State what is meant by ‘magnetic separation of two mixtures’. Explain how iron particles can be separated from sulphur particles.
Answer:
Magnetism is ideal for separating mixtures of two solids with one part having magnetic properties. Some metals like iron, nickel and cobalt have magnetic properties whiles gold, silver and aluminum do not. Magnetic elements are attracted to a magnet.
- Principle — Based on the difference in magnetic and non-magnetic nature of particles.

- Technique of Separation — The magnetic particles such as iron are separated from the non-magnetic particles such as sulphur – by utilizing the magnetic properties of iron. The iron gets attracted to the magnet and seperates from the non-magnetic substance.
Question 9.
Give a reason why sublimable and non-sublimable substances can be separated easily, but two sublimable substance cannot.
Answer:
While seperating the mixture sublimable and non- sublimable substances, sublimable substance turns directly into vapour on heating whereas non-sublimable solid remains behind. Since, if we try to seperate the mixture of two sublimable substances, then both the sublimable substances turns into vapour on heating and vapour on cooling give back the pure same solid.
Question 10.
Explain the technique for separating – insoluble solid particles in a solid-liquid mixture.
Answer:
The insoluble solid particles in a solid-liquid mixture can be seperated by filtration.
Technique of Seperation — A filter paper is made into a cone & placed in a funnel. The solid particles remain behind on the filter paper while the liquid collects below.
Question 11.
Differentiate between the terms sedimentation and decantation with a suitable experimental technique.
Answer:
Sedimentation and decantation are two very different terms. Sedimentation is defined as the process of settling down of the heavier components present in a mixture.
For example : When the mixture of sand in water is allowed to stand undisturbed for some time, it is observed that sand settles at the bottom.
Decantation is defined as the process of separating the Liquid portion of a mixture when the heavier component settles at the bottom as sediments.
In other words, it is the process of transferring a liquid from one container to another without disturbing the sediments that are present at its bottom.
For example : When a mixture of sand and water is allowed to stand, sand settles at the bottom of a container since it is heavier. Water is present in the upper portion of the container. This can be separated from sand settled at the bottom simply by pouring in a different container without using any other separating device. This is known as decantation.
Question 12.
Explain how a solid component is separated in a soluble solid-liquid mixture.
Answer:
A Solid component is separated in a soluble solid-liquid mixture by evaporation.
Principle — Seperation of the mixture by evaporating the liquid component. The solid should be soluble in the liquid and should not sublime.
Technique of Separation : The soluble solid can be seperated from its liquid component by allowing the liquid component to evaporate either on its own or by heating. During evaporation, the liquid component is lost to the atmosphere & the solid remains behind.
Example : Evaporation of a common salt solution or sea water leaves behind common salt.
Common salt remains behind whereas water lost to the atmoshphere.

Question 13.
Draw a neat labelled diagram for separation of the following mixtures.
(a) Coarse sand from fine sand
(b) A magnetic particle from a non-magnetic particle
(c) Naphthalene from sodium chloride
(d) Chalk and water using a filter paper
(e) Sand and water without using a filter paper
(f) Common salt from a solution of common salt and water
Answer:
(a) Coarse sand from fine sand
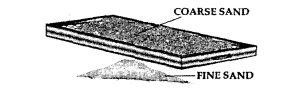
Separation of particles of sand, Coarse sand stays above and fine sand below.
(b) A magnetic particle from a non-magnetic particle

(c) Naphthalene from sodium chloride
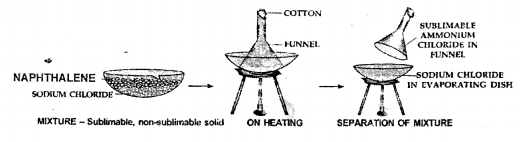
(d) Chalk and water using a filter paper
Filtration of chalk particles in water.
Filtered out solid chalk particles.
(e) Sand and water without using a filter paper
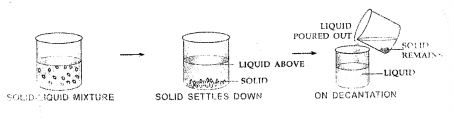
(f) Common salt from a solution of common salt and water
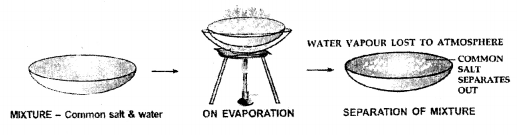
Common salt remains behind.
Question 14.
State the technique involved in separating the following:
(a) Iodine crystals and potassium chloride
(b) Iron and chalk powder
(c) Potassium chloride from an aqueous solution of potassium chloride.
(d) Rice powder from soil particles
(e) Iron filings from pieces of copper wire
(f) Large diamonds from very small diamonds
Answer:
(a) Sublimation
(b) Magnetic separation
(c) Evaporation
(d) Seiving
(e) Magnetic separation
(f) Seiving
Objective Type Questions
Q.1. Match the statements in List I with the correct answer in List II.

Answer:

Q.2. State whether the following statements are true or false. If false write – the correct statement.
1. Components in a mixture are present in a definite proportion.
Ans. False.
Correct — Components in a mixture are present in a varying proportion.
2. Mixture have no definite set of properties.
Ans. True.
3. Components in a mixture can be separated by physical and chemical methods.
Ans. False.
Correct — Components in a mixture can be separated by physical methods.
4. Sodium chloride and water is an example of a mixture of elements and compounds.
Ans. False.
Correct — Sodium chloride and water is an example of a mixture of compounds.
5. Heterogeneous mixtures have different composition and properties throughout the mixture.
Ans. True.
Q.3. Name the following :
Question 1.
A black non-metallic component of the mixture gunpowder.
Answer:
Carbon.
Question 2.
A physical method of separating iron from an iron- sulphur mixture.
Answer:
Magnetic separation.
Question 3.
The component of the soluble solid-liquid mixture, which is lost to the atmosphere on heating.
Answer:
Liquid component i.e. water.
Question 4.
The component of a naphthalene-sodium chloride mixture, which remains in the evaporating dish when heated together, covered with a funnel.
Answer:
Sodium chloride.
Question 5.
A mixture of two immiscible liquids.
Answer:
Kerosene oil and water.
Q.4. Give reasons for the following :
Question 1.
Naphthalene and camphor cannot be separated by sublimation.
Answer:
Because both of these are sublimable solids and they sublimes on heating.
Question 2.
Sodium chloride cannot be separated out from its aqueous solution by filtration.
Answer:
Filtration is a method that is used to separate insoluble solids from liquids, since both salt dissolve in water.
Question 3.
Two varieties of wheat flour cannot be separated by sieving.
Answer:
Since in sieving we can separate larger particle but in this case both particles are finer in nature.
Question 4.
Sulphur and charcoal powder cannot be separated by magnetic separation.
Answer:
Because both are non-magnetic particles.
Question 5.
Both components of a soluble solid-liquid mixture cannot be recovered by evaporation.
Answer:
Because liquid is lost/evaporated in atmosphere.