ML Aggarwal Class 9 Solutions for ICSE Maths Chapter 14 Theorems on Area
Question 1.
Prove that the line segment joining the mid-points of a pair of opposite sides of a parallelogram divides it into two equal parallelograms.
Solution:
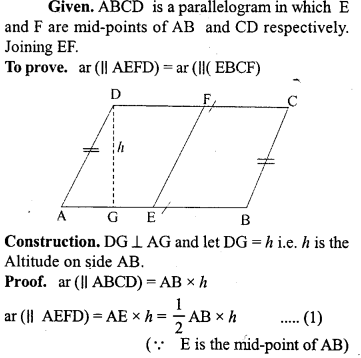

Question 2.
Prove that the diagonals of a parallelogram divide it into four triangles of equal area.
Solution:
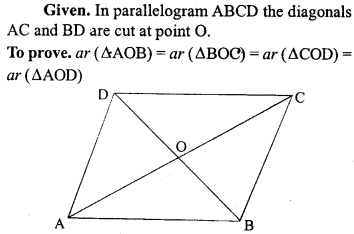

Question 3.
(a) In the figure (1) given below, AD is median of ∆ABC and P is any point on AD. Prove that
(i) area of ∆PBD = area of ∆PDC.
(ii) area of ∆ABP = area of ∆ACP.
(b) In the figure (2) given below, DE || BC. prove that (i) area of ∆ACD = area of ∆ ABE.
(ii) area of ∆OBD = area of ∆OCE.
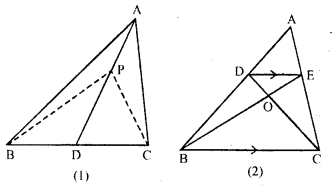
Solution:

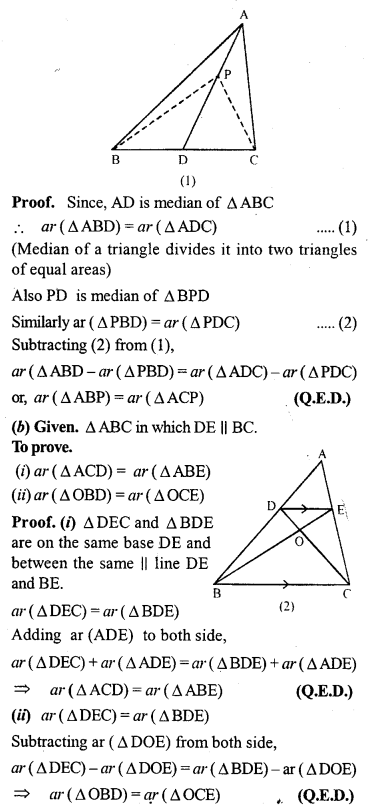
Question 4.
(a) In the figure (1) given below, ABCD is a parallelogram and P is any point in BC. Prove that: Area of ∆ABP + area of ∆DPC = Area of ∆APD.
(b) In the figure (2) given below, O is any point inside a parallelogram ABCD. Prove that:
(i) area of ∆OAB + area of ∆OCD = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) area of || gm ABCD.
(ii) area of ∆ OBC + area of ∆ OAD = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) area of ||gmABCD
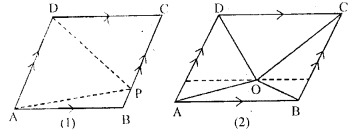
Solution:


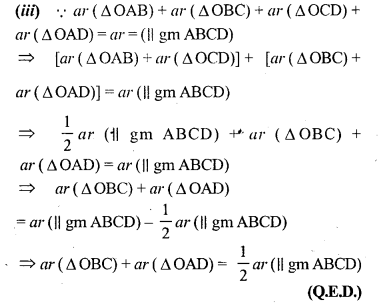
Question 5.
If E, F, G and H are mid-points of the sides AB, BC, CD and DA respectively of a parallelogram ABCD, prove that area of quad. EFGH = 1/2 area of || gm ABCD.
Solution:
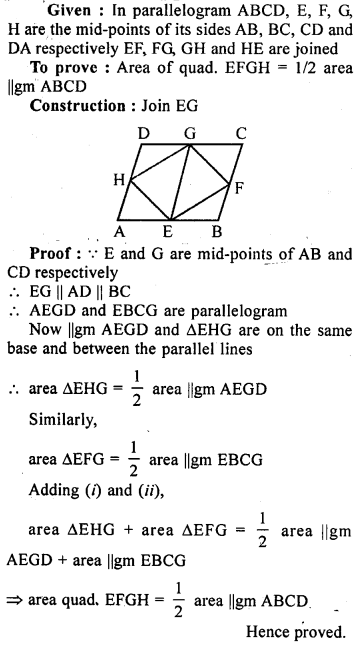
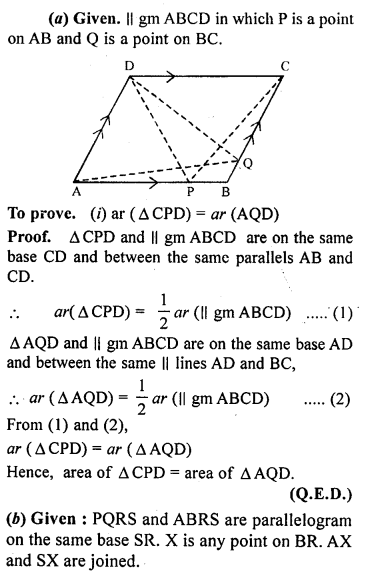
Question 6.
(a) In the figure (1) given below, ABCD is a parallelogram. P, Q are any two points on the sides AB and BC respectively. Prove that, area of ∆ CPD = area of ∆ AQD.
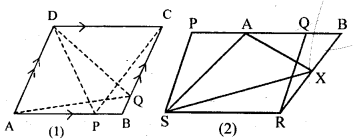
(b) In the figure (2) given below, PQRS and ABRS are parallelograms and X is any point on the side BR. Show that area of ∆ AXS = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) area of ||gm PQRS
Solution:

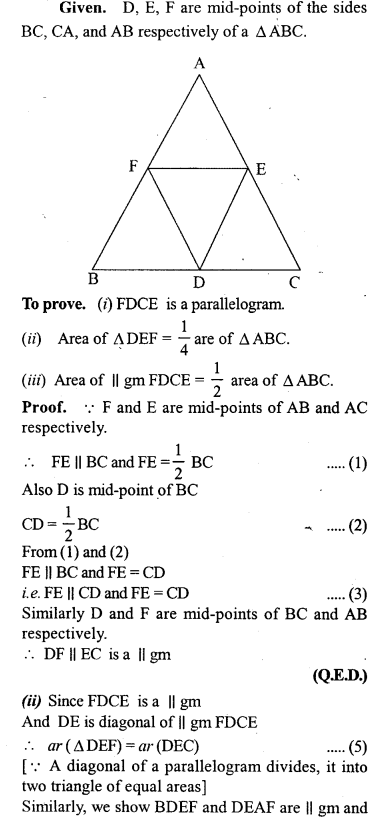
Question 7.
D,EandF are mid-point of the sides BC, CA and AB respectively of a ∆ ABC. Prove that
(i) FDCE is a parallelogram
(ii) area of ADEF = \(\frac { 1 }{ 4 }\) area of A ABC
(iii) area of || gm FDCE = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) area of ∆ ABC.
Solution:

Question 8.
In the given figure, D, E and F are mid points of the sides BC, CA and AB respectively of AABC. Prove that BCEF is a trapezium and area of trap. BCEF = \(\frac { 3 }{ 4 }\) area of ∆ ABC.
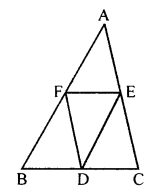
Solution:

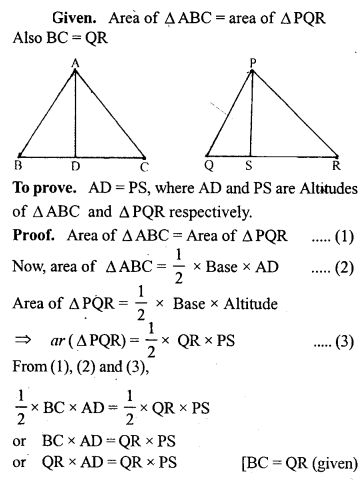
Question P.Q.
Prove that two triangles having equal areas and having one side of one of the triangles equal to one side of the other, have their corresponding altitudes equal.
Solution:
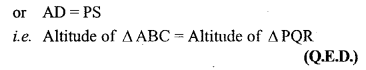
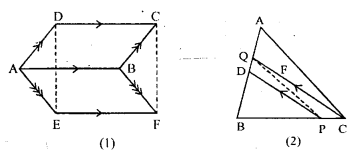
Question 9.
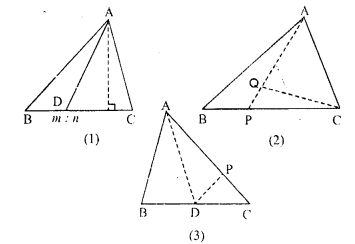
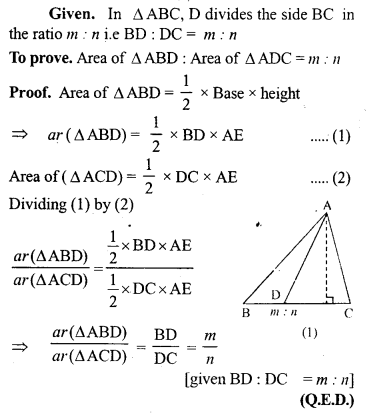
(a) In the figure (1) given below, the point D divides the side BC of ∆ABC in the ratio m : n. Prove that area of ∆ ABD: area of ∆ ADC = m : n.
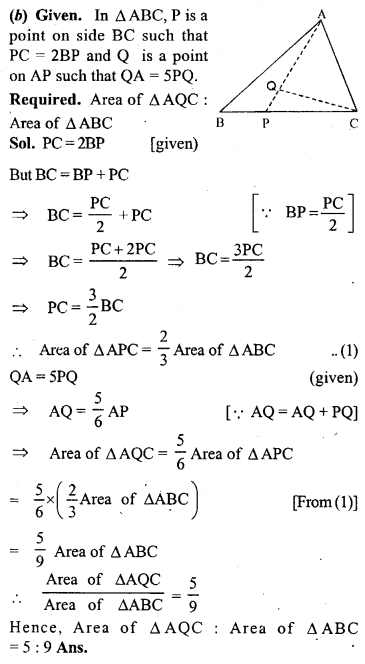
(b) In the figure (2) given below, P is a point on the sidoBC of ∆ABC such that PC = 2BP, and Q is a point on AP such that QA = 5 PQ, find area of ∆AQC : area of ∆ABC.
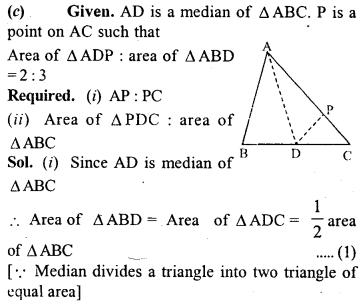
(c) In the figure (3) given below, AD is a median of ∆ABC and P is a point in AC such that area of ∆ADP : area of AABD = 2:3. Find
(i) AP : PC (ii) area of ∆PDC : area of ∆ABC.
Solution:

Question 10.
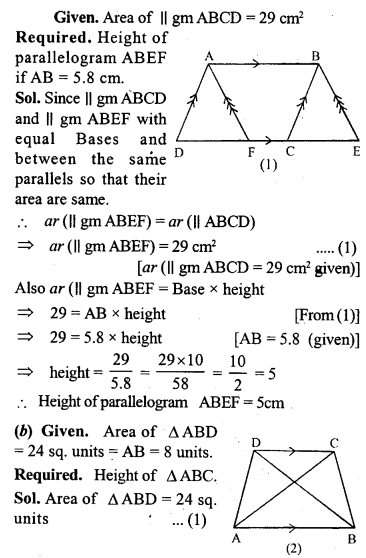
(a) In the figure (1) given below, area of parallelogram ABCD is 29 cm2. Calculate the height of parallelogram ABEF if AB = 5.8 cm
(b) In the figure (2) given below, area of ∆ABD is 24 sq. units. If AB = 8 units, find the height of ABC.
(c) In the figure (3) given below, E and F are mid points of sides AB and CD respectively of parallelogram ABCD. If the area of parallelogram ABCip is 36 cm2.
(i) State the area of ∆ APD.
(ii) Name the parallelogram whose area is equal to the area of ∆ APD.
Solution:
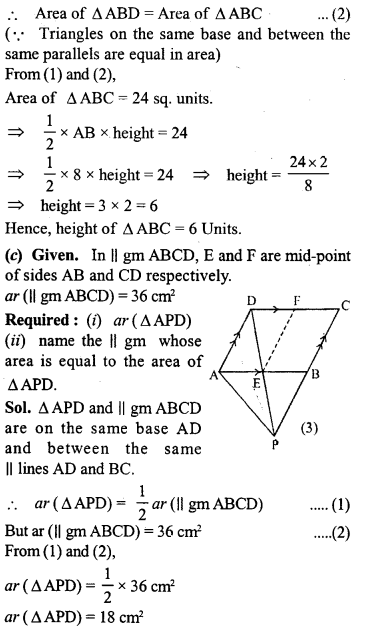

Question 11.
(a) In the figure (1) given below, ABCD is a parallelogram. Points P and Q on BC trisect BC into three equal parts. Prove that :
area of ∆APQ = area of ∆DPQ = \(\frac { 1 }{ 6 }\) (area of ||gm ABCD)
(b) In the figure (2) given below, DE is drawn parallel to the diagonal AC of the quadrilateral ABCD to meet BC produced at the point E. Prove that area of quad. ABCD = area of ∆ABE.
(c) In the figure (3) given below, ABCD is a parallelogram. O is any point on the diagonal AC of the parallelogram. Show that the area of ∆AOB is equal to the area of ∆AOD.
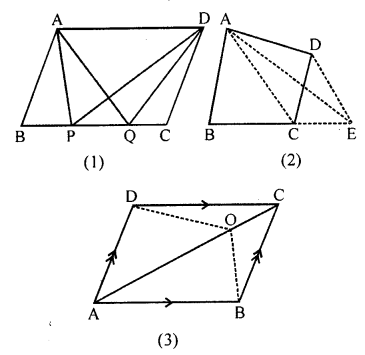
Solution:
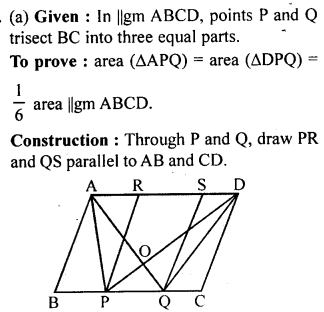


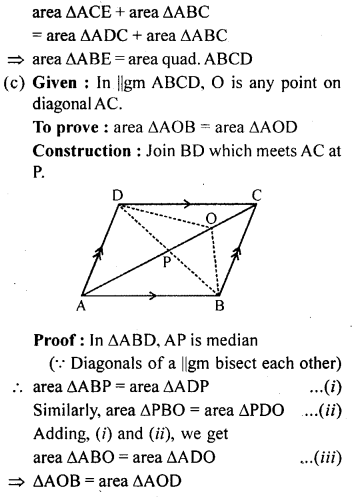
Question P.Q.
(a) In the figure (1) given below, two parallelograms ABCD and AEFB are drawn on opposite sides of AB, prove that: area of || gm ABCD + area of || gm AEFB = area of || gm EFCD.
(b) In the figure (2) given below, D is mid-point of the side AB of ∆ABC. P is any point on BC, CQ is drawn parallel to PD to meet AB in Q. Show that area of ∆BPQ = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) area of ∆ABC.
(c) In the figure (3) given below, DE is drawn parallel to the diagonal AC of the quadrilateral ABCD to meet BC produced at the point E. Prove that area of quad. ABCD = area of ∆ABE.
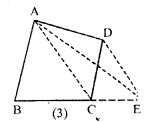
Solution:

Question 12.
(a) In the figure given, ABCD and AEFG are two parallelograms.
Prove that area of || gm ABCD = area of || gm AEFG.
(b) In the fig. (2) given below, the side AB of the parallelogram ABCD is produced to E. A st. line At through A is drawn parallel to CE to meet CB produced at F and parallelogram BFGE is Completed prove that area of || gm BFGE=Area of || gmABCD.
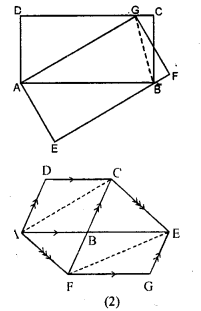
(c) In the figure (3) given below AB || DC || EF, AD || BEandDE || AF. Prove the area ofDEFH is equal to the area of ABCD.
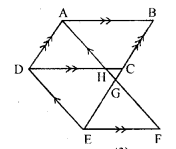
Solution:
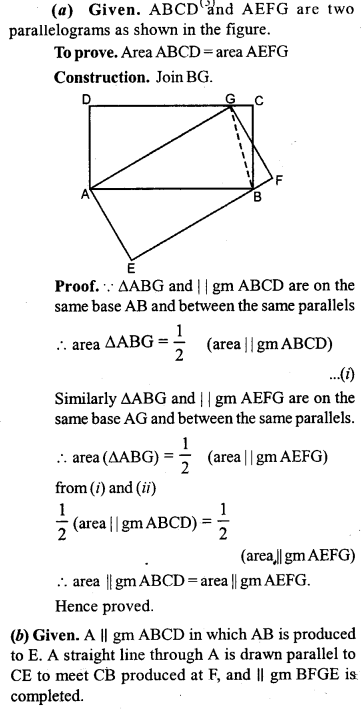
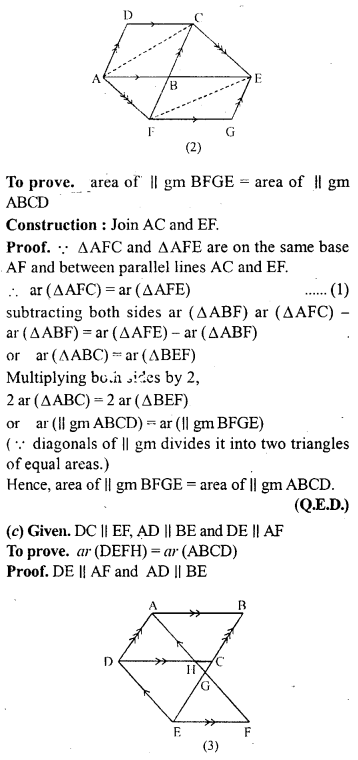


Question 13.
Any point D is taken on the side BC of, a ∆ ABC and AD is produced to E such that AD=DE, prove that area of ∆ BCE = area of ∆ ABC.
Solution:
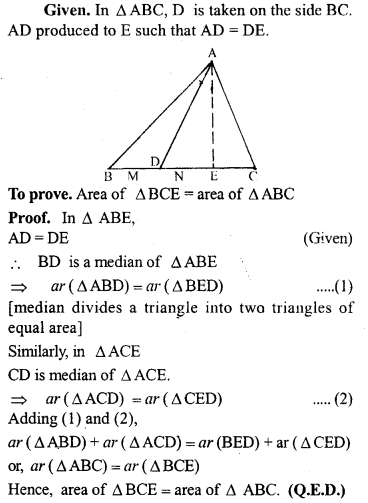
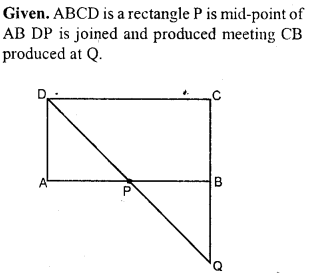
Question 14.
ABCD is a rectangle and P is mid-point of AB. DP is produced to meet CB at Q. Prove that area of rectangle ∆BCD = area of ∆ DQC.
Solution:

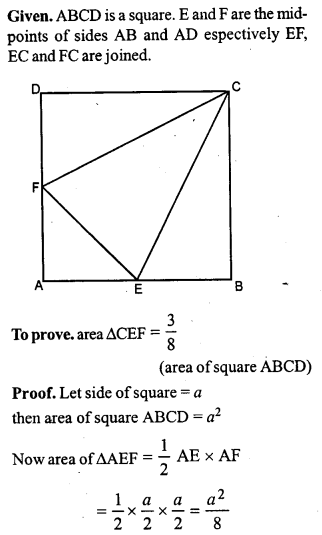
Question P.Q.
ABCD is a square, E and F are mid-points of the sides AB and AD respectively Prove that area of ∆CEF = \(\frac { 3 }{ 8 }\) (area of square ABCD).
Solution:

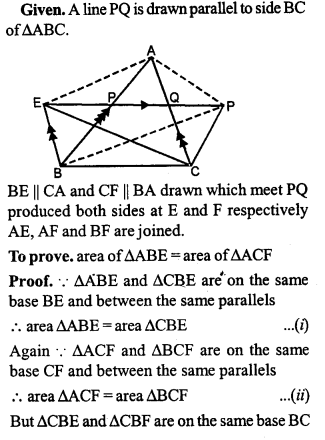
Question P.Q.
A line PQ is drawn parallel to the side BC of ∆ABC. BE is drawn parallel to CA to meet QP (produced) at E and CF is drawn parallel to BA to meet PQ (produced) at F. Prove that
area of ∆ABE=area of ∆ACF.
Solution:

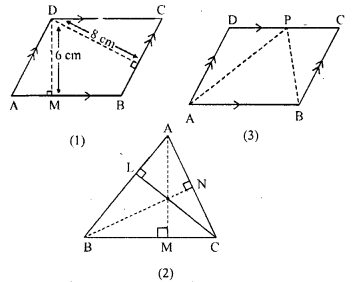
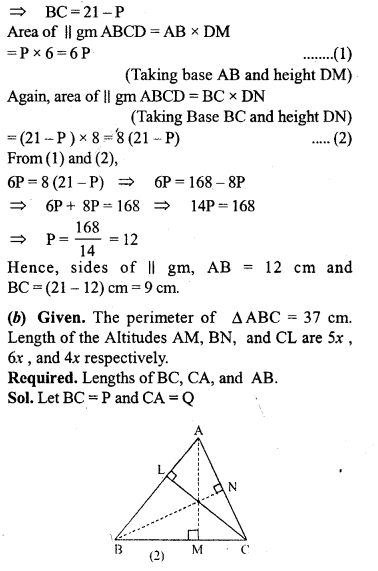
Question 15.
(a) In the figure (1) given below, the perimeter of parallelogram is 42 cm. Calculate the lengths of the sides of the parallelogram.
(b) In the figure (2) given below, the perimeter of ∆ ABC is 37 cm. If the lengths of the altitudes AM, BN and CL are 5x, 6x, and 4x respectively, Calculate the lengths of the sides of ∆ABC.
(c) In the fig. (3) given below, ABCD is a parallelogram. P is a point on DC such that area of ∆DAP = 25 cm² and area of ∆BCP = 15 cm². Find
(i) area of || gm ABCD
(ii) DP : PC.
Solution:



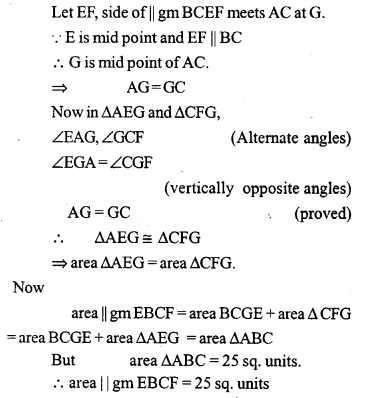
Question 16.
In the adjoining figure, E is mid-point of the side AB of a triangle ABC and EBCF is a parallelogram. If the area of ∆ ABC is 25 sq. units, find the area of || gm EBCF.
Solution:

Question 17.
(a) In the figure (1) given below, BC || AE and CD || BE. Prove that: area of ∆ABC= area of ∆EBD.
(b) In the llgure (2) given below, ABC is right angled triangle at A. AGFB is a square on the side AB and BCDE is a square on the hypotenuse BC. If AN ⊥ ED, prove that:
(i) ∆BCF ≅ ∆ ABE.
(ii)arca of square ABFG = area of rectangle BENM.
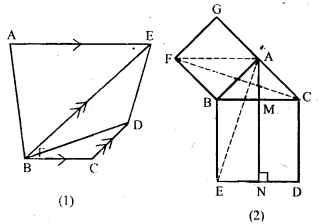

Solution:

Multiple Choice Questions
Choose the correct answer from the given four options (1 to 8):
Question 1.
In the given figure, if l || m, AF || BE, FC ⊥ m and ED ⊥ m , then the correct statement is
(a) area of ||ABEF = area of rect. CDEF
(b) area of ||ABEF = area of quad. CBEF
(c) area of ||ABEF = 2 area of ∆ACF
(d) area of ||ABEF = 2 area of ∆EBD
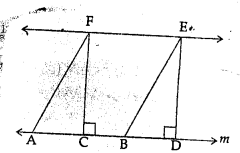
Solution:
In the given figure,
l ||m, AF || BE, FC ⊥ m and ED ⊥ m
∵ ||gm ABEF and rectangle CDEF are on the same base EF and between the same parallel
∴ area ||gm ABEF = area rect. CDEF (a)
Question 2.
Two parallelograms are on equal bases and between the same parallels. The ratio of their areas is
(a) 1 : 2
(b) 1 : 1
(c) 2 : 1
(d) 3 : 1
Solution:
A triangle and a parallelogram are on the same base and between same parallel, then
∴ They are equal in area
∴ Their ratio 1:1 (b)
Question 3.
If a triangle and a parallelogram are on the same base and between same parallels, then the ratio of area of the triangle to the area of parallelogram is
(a) 1 : 3
(b) 1 : 2
(c) 3 : 1
(d) 1 : 4
Solution:
A triangle and a parallelogram are on the same base and between same parallel, then area of
triangle = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) area ||gm
∴ Their ratio 1 : 2 (b)
Question 4.
A median of a triangle divides it into two
(a) triangles of equal area
(b) congruent triangles
(c) right triangles
(d) isosceles triangles
Solution:
A median of a triangle divides it into two triangle equal in area. (a)
Question 5.
In the given figure, area of parallelogram ABCD is
(a) AB x BM
(b) BC x BN
(c) DC x DL
(d) AD x DL
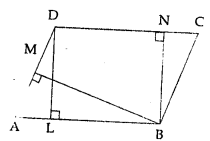
Solution:
In the given figure,
Area of ||gm ABCD = AB x DL or DC x DL (∵ AB = DC) (c)
Question 6.
The mid-points of the sides of a triangle along with any of the vertices as the fourth point make a parallelogram of area equal to
(a) \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) area of ∆ABC
(b) \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 }\) area of ∆ABC
(c) \(\frac { 1 }{ 4 }\) area of ∆ABC
(d) area of ∆ABC
Solution:
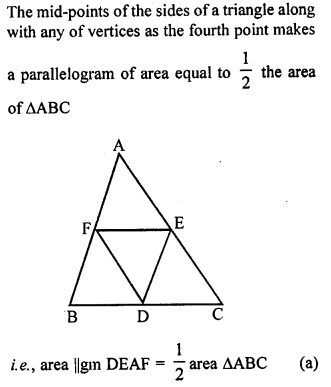
Question 7.
In the given figure, ABCD is a trapezium with parallel sides AB = a cm and DC = b cm. E and F are mid-points of the non parallel sides. The ratio of area of ABEF and area of EFCD is
(a) a : b
(b) (3a + b) : (a + 3b)
(c) (a + 3b) : (3a + b)
(d) (2a + b) : (3a + b)
Solution:

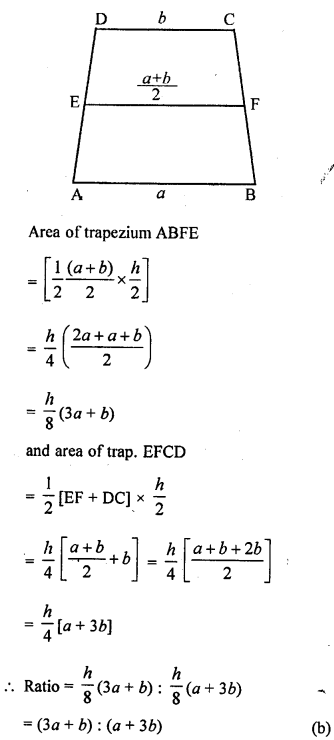
Question 8.
In the given figure, AB || DC and AB ≠ DC. If the diagonals AC and BD of the trapezium ABCD intersect at O, then which of the following statements is not true?
(a) area of ∆ABC = area of ∆ABD
(b) area of ∆ACD = area of ∆BCD
(c) area of ∆OAB = area of ∆OCD
(d) area of ∆OAD = area of ∆OBC
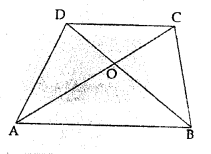
Solution:

Chapter test
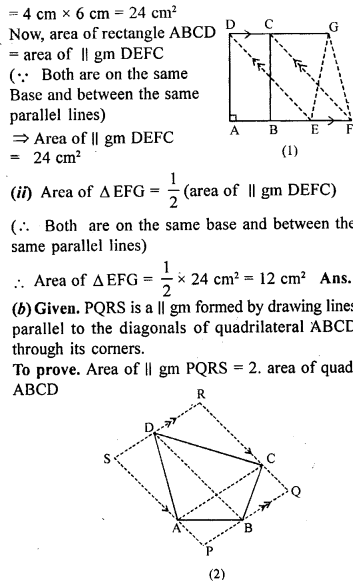
Question 1.
(a) In the figure (1) given below, ABCD is a rectangle (not drawn to scale ) with side AB = 4 cm and AD = 6 cm. Find :
(i) the area of parallelogram DEFC
(ii) area of ∆EFG.
(b) In the figure (2) given below, PQRS is a parallelogram formed by drawing lines parallel to the diagonals of a quadrilateral ABCD through its corners. Prove that area of || gm PQRS = 2 x area of quad. ABCD.
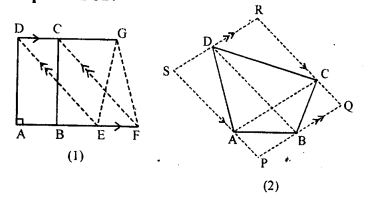
Solution:


Question P.Q.
In the adjoining figure, ABCD and ABEF are parallelogram and P is any point on DC. If area of || gm ABCD = 90 cm2, find:
(i) area of || gm ABEF
(ii) area of ∆ABP.
(iii) area of ∆BEF.
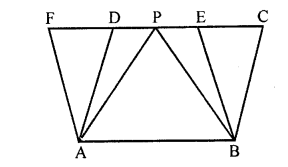
Solution:

Question 2.
In the parallelogram ABCD, P is a point on the side AB and Q is a point on the side BC. Prove that
(i) area of ∆CPD = area of ∆AQD
(ii)area of ∆ADQ = area of ∆APD + area of ∆CPB.
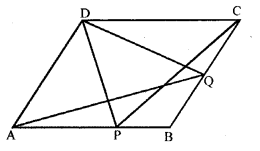
Solution:

Question 3.
In the adjoining figure, X and Y are points on the side LN of triangle LMN. Through X, a line is drawn parallel to LM to meet MN at Z. Prove that area of ∆LZY = area of quad. MZYX.
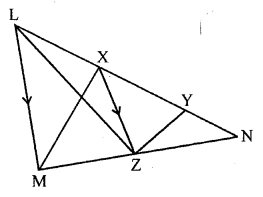
Solution:

Question P.Q.
If D is a point on the base BC of a triangle ABC such that 2BD = DC, prove that area of ∆ABD= \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 }\) area of ∆ ABC.
Solution:
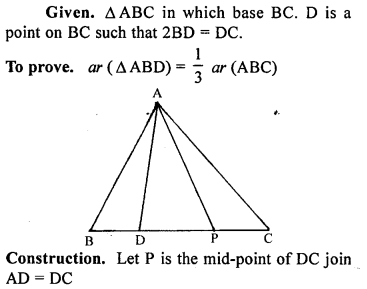

Question 4.
Perpendiculars are drawn from a point within an equilateral triangle to the three sides. Prove that the sum of the three perpendiculars is equal to the altitude of the triangle.
Solution:
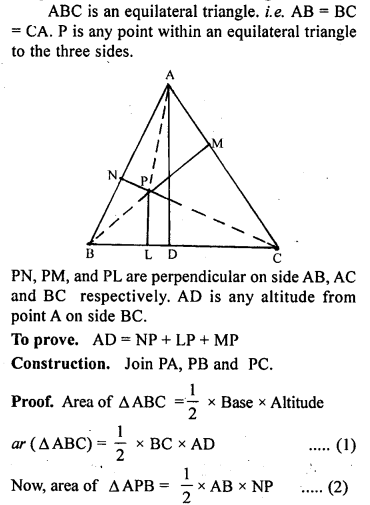

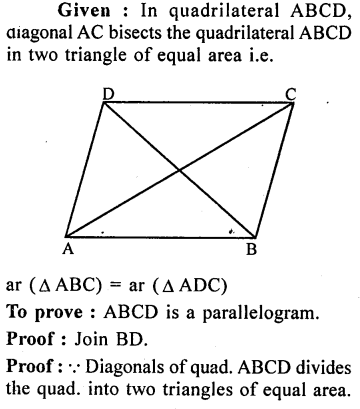
Question 5.
If each diagonal of a quadrilateral’ divides it into two triangles of equal areas, then prove that the quadrilateral is a parallelogram.
Solution:

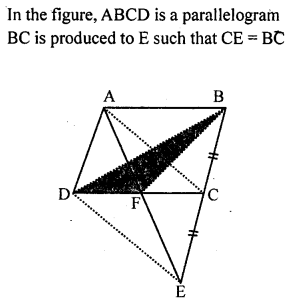
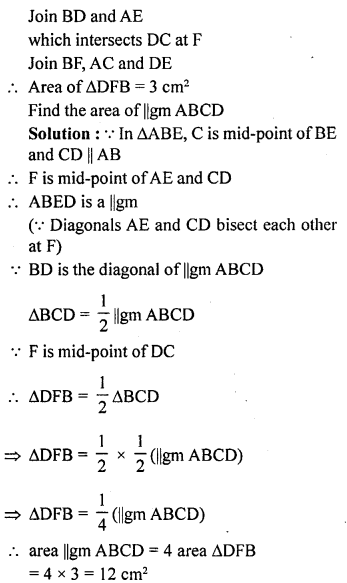
Question 6.
In the given figure, ABCD is a parallelogram in which BC is produced to E such that CE = BC. AE intersects CD at F. If area of ∆DFB = 3 cm², find the area of parallelogram ABCD.
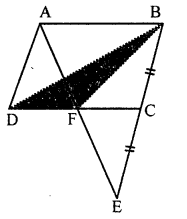
Solution:
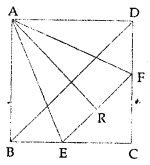
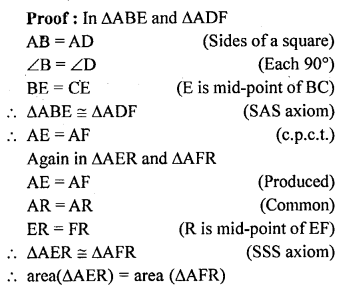
Question 7.
In the given figure, ABCD is a square. E and F are mid-points of sides BC and CD respectively. If R is mid-point of EF, prove that: area of ∆AER = area of ∆AFR.
Solution:

Question 8.
In the given figure, X and Y are mid-points of the sides AC and AB respectively of ∆ABC. QP || BC and CYQ and BXP are straight lines. Prove that area of ∆ABP = area of ∆ACQ.
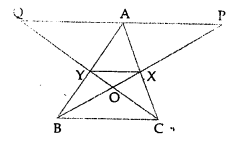
Solution:
