ML Aggarwal Class 8 Solutions for ICSE Maths Chapter 12 Linear Equations and Inequalities in one Variable Objective Type Questions
Mental Maths
Question 1.
Fill in the blanks:
(i) An equation of the type ax + b = 0 where a ≠ 0 is called a …………. in variable x.
(ii) Any value of the variable which satisfies the equation is called a …………. of the equation.
(iii) The process of finding all the solutions of an equation is called ………….
(iv) We can add the …………. to both sides of an equation.
(v) We can divide both sides of an equation by the same …………. number.
(vi) The solution set of the inequality 3x ≤ 10, x ϵ N is ………….
Solution:
(i) An equation of the type ax + b = 0
where a ≠ 0 is called a linear equation in variable x.
(ii) Any value of the variable which satisfies
the equation is called a solution of the equation.
(iii) The process of finding all the solutions of
an equation is called solving the equation.
(iv) We can add the same number to both sides of an equation.
(v) We can divide both sides of an equation
by the same non-zero number.
(vi) The solution set of the inequality 3x ≤ 10, x ϵ N is (1, 2, 3).
Question 2.
State whether the following statements are true (T) or false (F):
(i) An equation is a statement that two expressions are equal.
(ii) A term may be transposed from-one side of the equation to the other side, but its sign will not change.
(iii) We cannot subtract the same number from both sides of an equation.
(iv) 3x + 2 = 4(x + 7) + 9 is a linear equation in variable x.
(v) x = 1 is the solution of equation 4(x + 5) = 24.
Solution:
(i) An equation is a statement that two expressions are equal. True
(ii) A term may be transposed from one side of
the equation to the other side, but its sign will not change. False
Correct:
The sign will change.
(iii) We cannot subtract the same number from
both sides of an equation. False
Correct:
We can subtract.
(iv) 3x + 2 = 4(x + 7) + 9 is a linear equation in variable x. True
(v) x = 1 is the solution of equation 4(x + 5) = 24. True
4(1 + 5) = 24 ⇒ 4 × 6 = 24
Multiple Choice Questions
Choose the correct answer from the given four options (3 to 16):
Question 3.
Which of the following is not a linear equation in one variable?
(a) 3x + 2 = 0
(b) 2y – 4 = y
(c) x + 2y = 7
(d) 2(x – 3) + 7 = 0
Solution:
x + 2y = 7 is not a linear equation in one variable
as there are two variables x and y. (c)
Question 4.
The solution of the equation \(\frac{2}{3} x+1=\frac{15}{9}\) is
(a) 1
(b) \(\frac{3}{2}\)
(c) 2
(d) \(\frac{2}{3}\)
Solution:
The solution of the equation
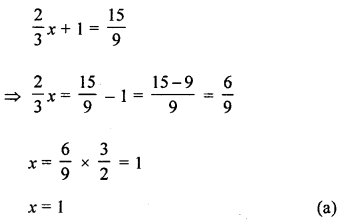
Question 5.
The solution of the equation 4z + 3 = 6 + 2z is
(a) 1
(b) \(\frac{3}{2}\)
(c) 2
(d) 3
Solution:
Solution of equation 4z + 3 = 6 + 2z
⇒ 4z – 2z = 6 – 3 ⇒ 2z = 3 ⇒ z = \(\frac{3}{2}\) (b)
Question 6.
The solution of the equation \(\frac{3 x}{5}+1=\frac{4 x}{15}\) is +7 is
(a) 12
(b) 14
(c) 16
(d) 18
Solution:
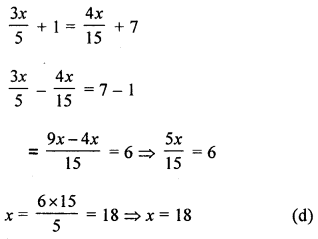
Question 7.
The solution of the equation \(\frac{x}{2}-\frac{1}{5}=\frac{x}{3}+\)\(\frac{1}{4}\) is
(a) 2.7
(b) 1.8
(c) 2.9
(d) 1.7
Solution:
The solution of the equation
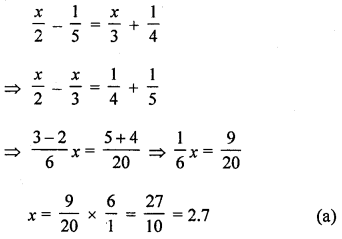
Question 8.
The solution of the equation \(\frac{8 x-3}{3 x}=2\) is


Solution:
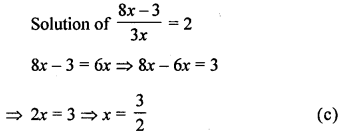
Question 9.
If we subtract \(\frac{1}{2}\) from a number and multiply the result by \(\frac{1}{2}\), we get \(\frac{1}{8}\), then the number is
Solution:
Let number be x, then
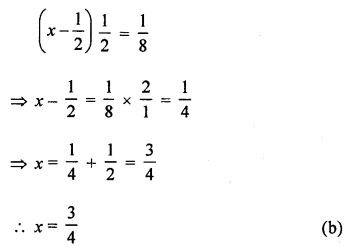
Question 10.
Fifteen years from now Ravi’s age will be four times his present age. What is Ravi’s present age?
(a) 4 years
(b) 5 years
(c) 6 years
(d) 3 years
Solution:
Let present age of Ravi = x years
After 15 years, his age will be = (x + 5) years
∴ x + 15 = 4x
⇒ 15 = 4x – x = 3x
⇒ x = \(\frac{15}{3}\) = 5
∴ His present age = 5 years (b)
Question 11.
If the sum of three consecutive integers is 51, then the largest integer is
(a) 16
(b) 17
(c) 18
(d) 19
Solution:
Let first integers = x
Then next two integers = x + 1, x + 2
∴ x + x + 1 + x + 2 = 51
⇒ 3x + 3 = 51
⇒ 3x = 51 – 3 = 48
⇒ x = \(\frac{48}{3}\) = 16
∴ First integer = 16
and other two integer = 17, 18
Largest integers =18 (c)
Question 12.
If the perimeter of a rectangle is 13 cm and its Width is \(2 \frac{3}{4}\) cm, then its length is

Solution:
Perimeter of a rectangle = 13 cm
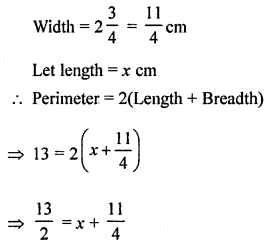
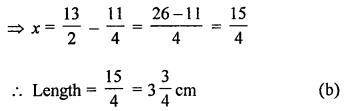
Question 13.
What should be added to twice the rational number \(\frac{-7}{3}\) to get \(\frac{3}{7}\) ?

Solution:
Let x be added
According to the condition,
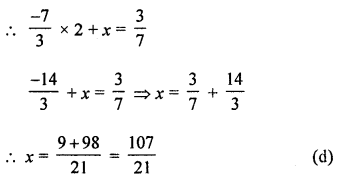
Question 14.
Sum of digits of a two digit number is 8. If the number obtained by reversing the digits is 18 more than the original number, then the original number is
(a) 35
(b) 53
(c) 26
(d) 62
Solution:
Sum of digits of a two digit number = 8
Let unit digit = x
Then tens digit = 8 – x
∴ Number = x + 10(8 – x) = x + 80 – 10x = 80 – 9x
By reversing the digits,
Unit digit = 8 – x
and tens digit = x
∴ Number = 8 – x + 10x = 8 + 9x
∴ 8 + 9x = 80 – 9x + 18
⇒ 9x + 9x = 80 + 18 – 8
⇒ 18x = 90
⇒ x = \(\frac{90}{18}\) =5
∴ Number = 80 – 9x = 80 – 9 × 5 = 80 – 45 = 35 (a)
Question 15.
Arjun is twice as old as Shriya. If five years ago his age was three times Shriya’s age, then Arjun’s present age is
(a) 10 years
(b) 15 years
(c) 20 years
(d) 25 years
Solution:
Let Shriya’s age = x years
Then Arjun’s age = 2x
5 years ago,
Age of Shriya was = (x – 5) years
and age of Arjun’s = (2x – 5) years
∴ 2x – 5 = 3(x – 5)
⇒ 2x – 5 = 3x – 15
⇒ 3x – 2x = 15 – 5 = 10
⇒ x = 10
∴ Arjun’s present age = 2x = 2 × 10 = 20 years (c)
Question 16.
If the replacement set is {-5, -3, -1,0, 1, 3}, then the solution set of the inequation -3 < x < 3 is
(a) {-2,-1, 0, 1, 2}
(b) {-1, 0, 1, 2}
(c) {-3,-1, 0, 1, 3}
(d) {-1,0, 1}
Solution:
Replacement set = {-5, -3, -1, 0, 1,3}
-3 < x < 3
∴ x = {-2, -1, 0, 1, 2} from the replacement set,
Solution set x = {-1, 0, 1} (d)
Value Based Questions
Question 1.
Seema is habitual of saving her pocket money. She collected some 50 paise and 25 paise coins in her piggy bank. If she collected ₹25 and number of 50 paise coins is double the number of 25 paise coins. How many coins of each type did she collect? What values are being promoted? Is saving a good habit?
Solution:
Seema has 50 paise and 25 paise coins in his piggy bank.
Total amount = ₹25
Let 25 paise coins = x
Then 50 paise coins = 2x
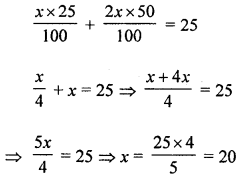
∴ 25-paise coins = 20
and 50 paise coins = 20 × 2 = 40
This is a good habit to save some money,
we can solve any financial problem with its help at any time.
Question 2.
Ramesh gave one-fourth of his property to his two sons in equal shares and rest to his wife Sunita. Sunita gave one-third of her share to an orphanage. If the amount given by Sunita to the orphanage was ₹20000, find the total value of the Ramesh’s property and the amount each person got? What value is shown by the Sunita?
Solution:
Let Ramesh’s property = x
\(\frac{1}{4}\)th part of property was given to two sons equally = \(\frac{x}{4}\)
So, each son’s share = \(\frac{x}{4} \times \frac{1}{2}=\frac{x}{8}\)
Rest to his wife Sunita = \(x-\frac{1}{4} x=\frac{3}{4} x\)
Sunita gave one third of her share to orphanages
Property given to orphanage
\(\frac{1}{3} \text { of } \frac{3}{4} x=\frac{1}{4} x\)
∴ \(\frac{1}{4}\)x = ₹20000
∴ Total value of Ramesh property = ₹20000 × \(\frac{4}{1}\) = ₹80000
Each son will get = ₹\(\frac{x}{8}\) × 80000 = ₹ 10000
and wife will get = ₹80000 × \(\frac{3}{4}\) = ₹60000
Sunita done a good deed to help the orphanage
where needy person are living and they need your help and support.
Higher Order Thinking Skills (Hots)
Question 1.
A man covers a distance of 24 km in \(3 \frac{1}{2}\) hours partly on foot at the speed of 4.5 km/h and partly on bicycle at the speed of 10 km/h. Find the distance covered on foot.
Solution:
Total distance = 24 km
Time taken = \(3 \frac{1}{2}\) hours = \(\frac{7}{2}\) hours
Let a man travels x km on foot at the speed of 4.5 km
and (24 – x) km on bicycle at the speed of 10 km/hr
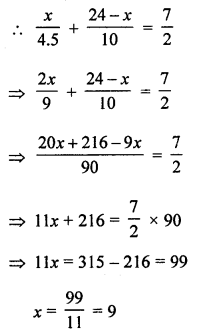
∴ He travelled 9 km on foot.
Question 2.
The perimeter of a rectangle is 240 cm. If its length is decreased by 10% and breadth is increased by 20% we get the same perimeter. Find the original length and breadth of the rectangle.
Solution:
Perimeter of a rectangle = 240 cm
∴ Length + breadth = \(\frac{240}{2}\) = 120 cm
Let length = x cm
Then breadth = (120 – x) cm
By decreasing length by 10%
and increasing breadth by 20%, we get

According to the condition,
Length + Breadth =120
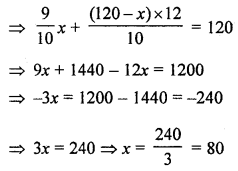
∴ Length = 80 cm
and breadth = 120 – 80 = 40 cm
Question 3.
A person preparing a medicine wants to convert 15% alcohol solution into 32% alcohol solution. Find how much pure alcohol he should mix in 400 mL of 15% alcohol solution to obtain required solution?
Solution:
15% of alcohol mixture = 400 mL
∴ Alcohol = \(\frac{15}{100}\) × 400 = 60 mL
and other solution = 400 – 60 = 340 mL
In new mixture alcohol = 32%
Other solution = 100 – 32 = 68%
In 86 mL, alcohol = 32
and in 340 mL, alcohol will be = \(\frac{32 \times 340}{68}\) = 160 mL
Already alcohol = 60 mL
∴ More alcohol required = 160 – 60 = 100 mL
Question 4.
Rahul covers a distance from P to Q on bicycle at 10 km/h and returns back at 9 km/h. Anuj covers the distance from P to Q and Q to P both at 12 km/h. On calculating we find that Anuj took 10 minutes less than Rahul. Find the distance between P and Q.
Solution:
Let distance between P and Q = x km
Speed of Rahul from P to Q = 10 km/h
and back Q to P = 9 km/h
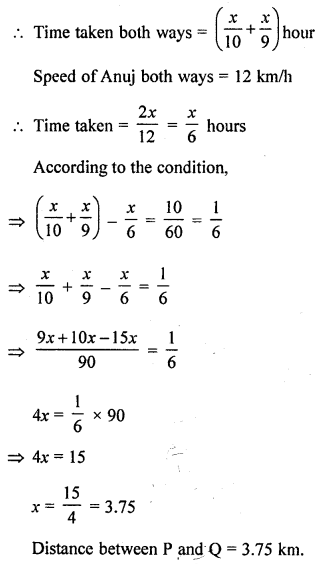
Question 5.
Solve:
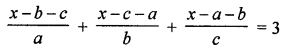
Solution: