ML Aggarwal Class 6 Solutions for ICSE Maths Chapter 6 Fractions Objective Type Questions
Mental Maths
Question 1.
Fill in the blanks:
(i) A fraction is a number which represent a ………… of whole.
(ii) A proper fraction lies between 0 and …………
(iii) A mixed fraction can be converted into ………… fraction.
(iv) Fractions having different denominations are called …………
(v) In two like fractions, the fraction having smaller numerator is …………
(vi) \(\frac{144}{180}\) reduced to simplest form is …………..
(vii) \(7 \frac{2}{5}\) + ………… = 12
(viii) \(\frac{42}{56}=\frac{6}{\dots . .}\)
Solution:
(i) A fraction is a number which represent a part of whole.
(ii) A proper fraction lies between 0 and 1.
(iii) A mixed fraction can be converted into an improper fraction.
(iv) Fractions having different denominations are called unlike fractions.
(v) In two like fractions, the fraction having smaller numerator is smaller.
(vi) \(\frac{144}{180}\) reduced to simplest form is \(\frac{4}{5}\)
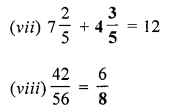
Question 2.
State whether the following statements are true (T) or false (F):
(i) Two fractions with same numerator are called like fractions.
(ii) A fraction in which the numerator is greater than is denominator is called an improper fraction.
(iii) Every improper fract on can be converted into a mixed fraction.
(iv) Every fraction can be represented by a point on a number line.
(v) In two unlike fractions with same numerator, the fraction having greater denominator is greater.
(vi) \(\frac{1}{2}, \frac{1}{3} \text { and } \frac{1}{4}\) are like fractions.
(vii) \(5-1 \frac{3}{4}=4 \frac{1}{4}\)
Solution:
(i) Two fractions with same numerator are called like fractions. False
(ii) A fraction in which the numerator is greater than is denominator is called an improper fraction. True
(iii) Every improper fraction can be converted into a mixed fraction. True
(iv) Every fraction can be represented by a point on a number line. True
(v) In two unlike fractions with same numerator, the fraction having greater denominator is greater. False
(vi) \(\frac{1}{2}, \frac{1}{3} \text { and } \frac{1}{4}\) are like fractions. False
(vii) \(5-1 \frac{3}{4}=4 \frac{1}{4}\). False
Multiple Choice Questions
Choose the correct answer from the given four options (3 to 17):
Question 3.
In the given figure, the shaded part is represented by the fraction :
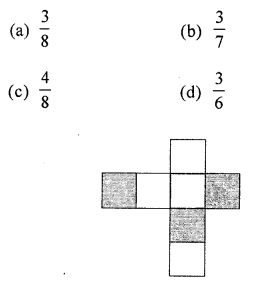
Solution:
\(\frac{3}{7}\)
Question 4.
In the given figure, the shaded region is represented by the fraction :
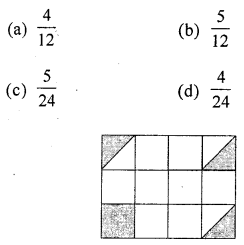
Solution:
\(\frac{5}{24}\)
Question 5.
The two consecutive integers between which the fraction \(\frac{5}{7}\) lies are
(a) 5 and 7
(b) 5 and 6
(c) 6 and 7
(d) 0 and 1
Solution:
0 and 1 (d)
Question 6.
Which of the following pairs of fractions are not equivalent?
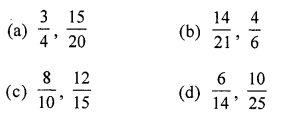
Solution:
\(\frac{6}{14}, \frac{10}{25}\)
∵ \(\frac{3}{7}, \frac{2}{5}\) not same. (d)
Question 7.
The fraction equivalent to \(\frac{45}{81}\) is
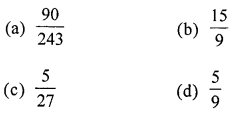
Solution:
\(\frac{45,9}{81,9}=\frac{5}{9}\) (d)
(Dividing numerator and denominator by 9)
Question 8.
The fraction which is not equal to \(\frac{4}{5}\) is

Solution:
\(\frac{9}{15}\) is not equal to \(\frac{4}{5}\). (b)
∴ \(\frac{9}{15}=\frac{3}{5}\)
Question 9.
Which of the following fractions is not in the lowest form?

Solution:
The lowest form of this can be written as
\(\frac{39}{87}=\frac{13}{29}\)
Question 10.
A pair of like fraction is
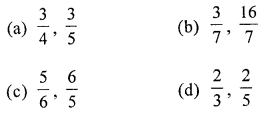
Solution:
\(\frac{3}{7}, \frac{16}{7}\)
Like fractions are those fractions who have same denominator. (b)
Question 11.
Which of the following fractions is the greatest?
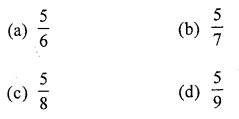
Solution:
\(\frac{5}{6}\) (a)
Question 12.
Which of the following fractions is the smallest?

Solution:
\(\frac{11}{10}\) (c)
Question 13.
Which of the following is a false statement?
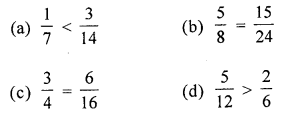
Solution:
\(\frac{3}{4}=\frac{6}{16}\)
Because, if we multiply and divide the fraction with 4, we get
\(\frac{3}{4} \times \frac{4}{4}=\frac{12}{16}\) (c)
Question 14.
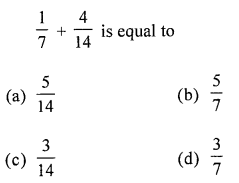
Solution:
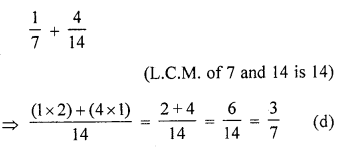
Question 15.
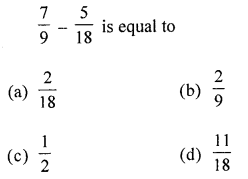
Solution:
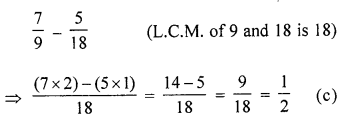
Question 16.
Anshul eats \(\frac{4}{7}\) of a pizza. The fraction of the pizza left is

Solution:
Let the total size of pizza be 1
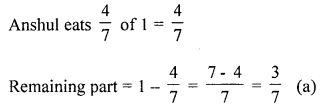
Question 17.
The fraction whose numerator is the smallest odd prime number and denominator is the smallest composite number is

Solution:
\(\frac{3}{4}\)
Higher Order Thinking Skills (Hots)
Question 1.
Write all proper fractions whose sum of numerator and denominator is 12.
Solution:
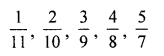
⇒ 1 + 11 = 12
⇒ 2 + 10 = 12
⇒ 3 + 9 = 12
⇒ 4 + 8 = 12
⇒ 5 + 7=12
Question 2.
The given figure represents the preferences of the students during breakfast in a hostel mess. If the total number of students in the mess is 540, then with reference to the given figure, answer the following questions:
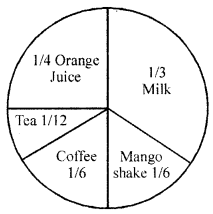
(i) What is the number of students who prefer coffee?
(ii) Whose number is greater, milk drinkers or orange juice drinkers and by what number?
(iii) What is the total number of students who drink mango shake or coffee? Is it equal to milk drinker?
(iv) Is the sum of all fractions in the given figure equal to 1 ?
Solution:
(i) Total number of students = 540
Ratio of students who prefer coffee = \(\frac{1}{6}\)
∴ Number of student prefer coffee
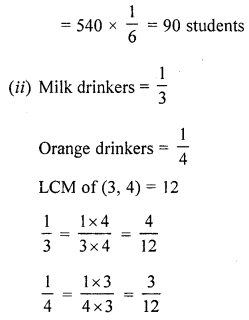
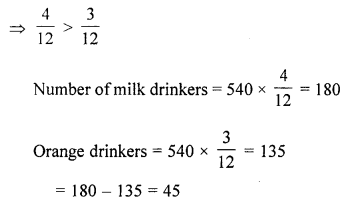
∴ Milk drinkers are more than orange drinkers by number = 45.
(iii) Number of Mango shake drinkers
\(=540 \times \frac{1}{6}=90\)
Number of coffee drinkers
\(=540 \times \frac{1}{6}=90\)
Total number of mango shake and coffee drinkers = 90 + 90 = 180
Milk drinkers = 180
Yes, it is equal to milk drinkers.
(iv) Sum of all fraction are:
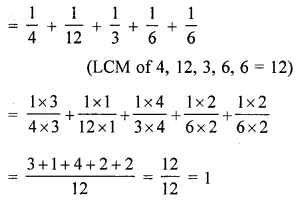
Yes, the sum of all the fractions are equal to 1.