ML Aggarwal Class 6 Solutions for ICSE Maths Chapter 2 Whole Numbers Objective Type Questions
Mental Maths
Question 1.
Fill in the blanks:
(i) A whole number is less than all those whole numbers that lie to its on the number line.
(ii) One more than a given whole is called its
(iii) There is atleast one whole number between two whole numbers.
(iv) 738 × 335 = 738 x (300 + 30 + ……..)
(v) If a is a non-zero whole number and a × a = a, then a = ……..
(vi) …….. is the only whole number which is not a natural number.
(vii) The additive identity in whole numbers is …….
Solution:
(i) A whole number is less than all those whole numbers that lie to its right on the number line.
(ii) One more than a given whole is called its successor.
(iii) There is atleast one whole number between two non-consecutive whole numbers.
(iv) 738 × 335 = 738 × (300 + 30 + 5)
(v) If a is a non-zero whole number and a × a = a, then a = 1.
(vi) 0 is the only whole number which is not a natural number.
(vii) The additive identity in whole numbers is 0.
Question 2.
State whether the following statements are true (T) or false (F):
(i) The predecessor of a 3-digit number is always a 3-digit number.
(ii) The successor of a 3-digit number is always a 3-digit number.
(iii) If a is any whole number, then a + a = 1.
(iv) If a is any non-zero whole number, then 0 ÷ a = 0.
(v) On adding two different whole numbers, we always get a natural number.
(vi) Between two whole numbers there is a whole number.
(vii) There is a natural number which when added to a natural number, gives that number.
(viii)If the product of two whole numbers is zero, then atleast one of them is zero.
Solution:
(i) The predecessor of a 3-digit number is always a 3-digit number. False
(ii) The successor of a 3-digit number is always a 3-digit number. False
(iii) If a is any whole number, then a ÷ a = 1. False
(iv) If a is any non-zero whole number, then 0 ÷ a = 0. True
(v) On adding two different whole numbers, we always get a natural number. True
(vi) Between two whole numbers there is a whole number. False
(vii) There is a natural number which when added to a natural number, gives that number. False
(viii)If the product of two whole numbers is zero, then atleast one of them is zero. True
Multiple Choice Questions
Choose the correct answer from the given four options (3 to 16):
Question 3.
The whole number which does not have a predecessor in whole number system is
(a) 0
(b) 1
(c) 2
(d) none of these
Solution:
0
Question 4.
The predecessor of the smallest 4-digit number is
(a) 99
(b) 999
(c) 1000
(d) 1001
Solution:
The smallest 4-digit number = 1000
The predecessor of the given number
= 1000 – 1 =999 (b)
Question 5.
The predecessor of 1 million is
(a) 9999
(b) 99999
(c) 999999
(d) 1000001
Solution:
Predecessor is 1 less than the given number
= 1000000 – 1 = 999999 (c)
Question 6.
The product of the predecessor and the successor of the greatest 2-digit number is
(a) 9900
(b) 9800
(c) 9700
(d) none of these
Solution:
Greatest 2-digit number = 99
Successor = 99 + 1 = 100
Predecessor = 99 – 1 = 98
∴ Product = 98 + 1 × 99 – 1
= 100 × 98 = 9800 (b)
Question 7.
The sum of the successor of the greatest 3-digit number and the predecessor of the smallest 3-digit number is
(a) 1000
(b) 1100
(c) 1101
(d) 1099
Solution:
Greatest 3-digit number = 999
Successor = 999 + 1 = 1000
Smallest 3-digit number = 100
Predecessor = 100 – 1 = 99
∴ Their Sum = 1000 + 99 = 1099 (d)
Question 8.
The number of whole numbers between 22 and 54 is
(a) 30
(b) 31
(c) 32
(d) 42
Solution:
The whole numbers between 22 and 54 are 23, 24, 25, 26, 27, ……, 53
Number of these numbers = 53 – 22 = 31 (b)
Question 9.
The number of whole numbers between the smallest whole number and the greatest 2-digit number is
(a) 100
(b) 99
(b) 98
(d) 88
Solution:
98 (Between 0 and 99) (c)
Question 10.
If a is a whole number such that a + a = a, then a is equal to
(a) 0
(b) 1
(c) 2
(d) none of these
Solution:
0 (a)
Question 11.
The value of (93 × 63 + 93 × 37) is
(a) 930
(b) 9300
(c) 93000
(d) none of these
Solution:
(93 × 63 + 93 × 37)
= 93 (63 + 37)
= 93 × 100 = 9300 (b)
Question 12.
Which of the following is not equal to zero?
(a) 0 × 5
(b) 0 = 5
(c) (10 – 10) + 5
(d) (5 – 0) + 5
Solution:
(5 – 0) + 5 = 1 (d)
Question 13.
Which of the following statement is true?
(a) 21 – (13 – 5) = (21 – 13) – 5
(b) 21 – 13 is not a whole number
(c) 21 × 1 = 21 × 0
(d) 13 – 21 is not a whole number
Solution:
13 – 21 is not a whole number (d)
Question 14.
Which of the following statement is not true?
(a) Zero is the identity for multiplication of whole numbers.
(b) Addition and multiplication both are commutative for whole numbers.
(c) Addition and multiplication both are associative for whole numbers.
(d) Multiplication is distributive over addition for whole numbers.
Solution:
Zero is the identity for multiplication of whole numbers. (a)
Question 15.
On dividing a number by 9 we get 47 as quotient and 5 as remainder. The number is
(a) 418
(b) 428
(c) 429
(d) none of these
Solution:
428 (b)
Question 16.
By using dot (•) pattern, which of the following numbers can be arranged in two ways namely a triangle and a rectangle?
(a) 12
(b) 11
(c) 10
(d) 9
Solution:
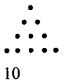
(c)
Higher Order Thinking Skills (HOTS)
Question 1.
The height of a slippery pole is 10 m and an insect is trying to climb the pole. The insect climbs 5 m in one minute and then slips down by 4 m. In how much time will insect reach the top?
Solution:
In first 1 min, insect climbs 5 metres, then slips down 4 metres.
So it climbs 1 metres every 1 mins, except the last minute.
In the last minute, it would cover all 5 metres and reach the top.
So keeping 1 min aside for last 5 metres. Total distance to be covered is 10 m, in which we subtract the last 5 m for last climb. So, to cover first 5m:
Time required = 5m × 1min = 5 min Adding that last 1 min, it takes 6 mins to reach the top of a pole.
Question 2.
Which is greater, the sum of first twenty whole numbers or the product of first twenty whole numbers?
Solution:
Sum of first 20 whole numbers :
0 + 1 + 2 + 3 + 4 + ………… + 19 = 190
Product of first 20 whole numbers :
0 × 1 × 2 × 3 × 4 × ………. × 19 = 0
Hence, sum of first 20 whole numbers is greater than its product.
Question 3.
If a whole number is divisible by 2 and 4, is it divisible by 8 also?
Solution:
May or may not.
Example:
(i) 12, 20, 28 are the whole number which is divided by both 2 and 4, but is not divisible by 8.
(ii) 8, 16, 24 are the whole numbers which are divided by 2, 4 and 8.