ML Aggarwal Class 6 Solutions for ICSE Maths Chapter 13 Practical Geometry Check Your Progress
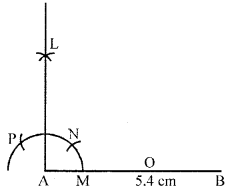
Question 1.
Draw a line segment AB = 5.4 cm. Construct a perpendicular at A by using ruler and compass.
Solution:
Steps of construction:
- Draw AB = 5.4 cm.
- With any radius draw an arc which cuts AB at M.
- With M as centre and the same radius
cut the previous arc at N and P. - With N and P as centres draw arcs which intersect at L.
Join AL. - AL is required perpendicular.
Question 2.
Draw a line segment PQ = 6.8 cm. Draw a perpendicular to it from a point A outside PQ by using ruler and compass.
Solution:
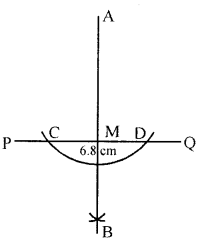
Steps of construction:
- Draw a line segment PQ = 6.8 cm
and take a point A outside PQ. - With A as centre and any suitable radius,
draw an arc to cut line PQ at point C and D. - With C and D as centres,
draw two arcs of equal radius cutting each other
at B on the other side of line PQ. - Join AB to meet the line PQ at M.
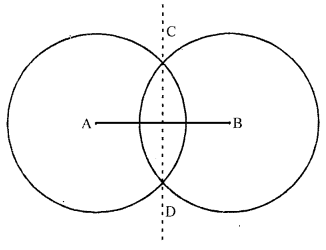
Question 3.
Draw a line segment of length 6.5 cm and construct its axis of symmetry.
Solution:
Steps of construction:
- Draw a line segment \(\overline{\mathrm{AB}}\) of length 6.5 cm.
- With A as centre, using a compass, draw a circle.
The radius of this circle should be more than half of the length of \(\overline{\mathrm{AB}}\). - With the same radius and with B as centre,
draw another circle using a compass.
Let it cut the previous circle at C and D. - Join CD. Then, \(\overline{\mathrm{CD}}\) is the axis of symmetry of \(\overline{\mathrm{AB}}\).
Question 4.
Draw ∠AOB = 76° with help of a protractor. Bisect this angle by using ruler and compass. Measure the two parts by your protractor and see how accurate you are.
Solution:
Steps of construction:
- Draw a line segment OB.
- Construct ∠AOB with the help of protector = 76°.
- With the help of compass and O as centre
draw an arc meeting OB and OA at P and Q respectively.
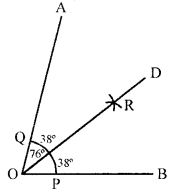
- With P and Q as centre and radius more than \(\frac{1}{2}\) PQ
draw two arcs meeting each other at R. - OD is the bisector of ∠AOB.
- On measuring ∠AOD = ∠DOB = 38°.
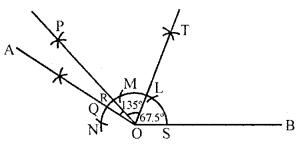
Question 5.
By using and compass, construct an angle of 135° and bisect it. Measure any one part by protractor and see how accurate you are.
Solution:
Steps of construction:
- Draw a line OB with help of ruler.
- With O as a centre and any suitable radius
draw an arc to meet OB at S. - With S as a centre and same radius
draw an arc to meet the previous arc at L.
With L as centre and same radius draw another arc M.
Again M as centre draws another arc to meet the first arc at N. - With M and N as centres draw two arcs of
equal radius \(\left(>\frac{1}{2} \mathrm{SL}\right)\) cutting each other at A. - Join OA intersecting the radius at point Q.
- Now taking Q and M as a centres
draw two arcs of equal radius cutting each other at P. - Join PO.
- Measuring the ∠POB with protractor we get ∠POB equal to 135°.
- Taking S and R as a centres draw two arcs cutting each other at T.
Join TO. - ∠TOB is the bisector of ∠POB. ∠TOB = ∠TOP = 67.5°.