What is the Law of Reflection of Light?
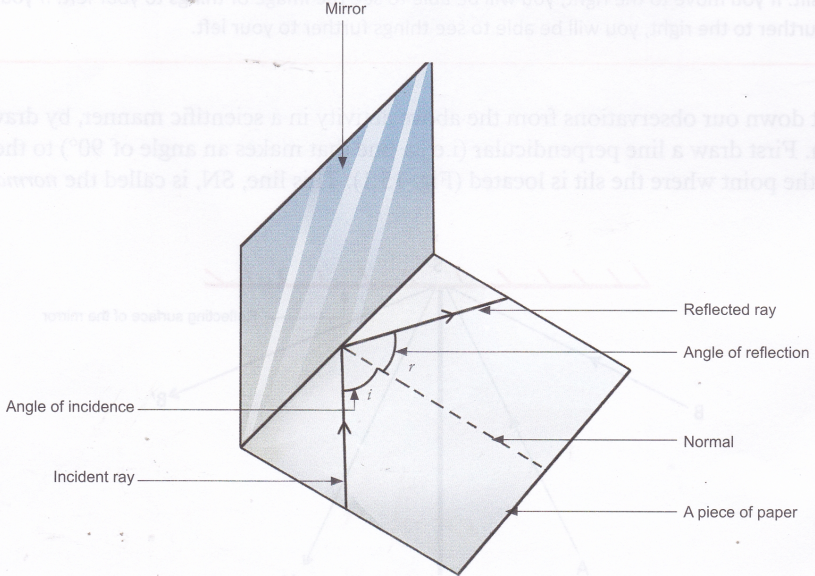
First law : The incident ray, the reflected ray and the normal at the point of incidence, all lie in the same plane.
Second law : The angle of reflection (∠r) is always equal to the angle of incidence (∠i).
i.e., ∠r = ∠i
(For normal incidence, i = 0, r = 0. The ray is reflected back along normal).
In figure the image of an object at A could be seen at A’ and the image of an object at B could be seen at B’, What conclusions can you draw from this observation? Look closely at the angle of incidence and the corresponding angles of reflection in figure. You will see that in each case, the angle of incidence (∠i) equals the angle of reflection (∠r). Also, the incident ray, the reflected ray, and the normal at the point of incidence lie on the same plane.
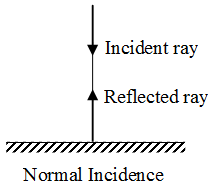
- A ray of light striking the surface normally retraces its path.
When a ray of light strikes a surface normally, then angle of incidence is zero i.e., ∠i = 0. According to the law of reflection,
∠r = ∠i, ∴ ∠r = 0 i.e. the reflected ray is also perpendicular to the surface. Thus, an incident ray normal to the surface (i.e. perpendicular to the surface) retraces its path as shown in figure.
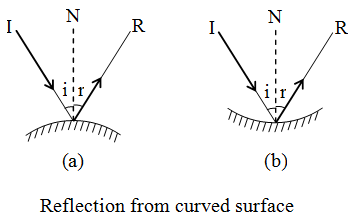
- Laws of reflection are also obeyed when light is reflected from the spherical or curved surfaces as shown in figure (a) and (b).
People also ask
- What is Reflection of Light?
- Analysing Reflection of Waves
- Application of Reflection of Light in Daily Life
- What do you mean by Total Internal Reflection?
- Applications of Total Internal Reflection
- Image Reflection by a Plane Mirror
- Which Type of Image is Formed by a Plane Mirror?
- Is an Image formed by Reflection Real or Virtual
- Reflection of Light from Spherical Mirror
- What are Concave and Convex Mirrors?
- How is Focal Length related to Radius of Curvature?
- How is the Image Formed by a Spherical Mirror?