ICSE Solutions for Class 8 History and Civics – Great Reformers and Reform Movements
ICSE SolutionsSelina ICSE SolutionsML Aggarwal Solutions
APlusTopper.com provides step by step solutions for ICSE Solutions for Class 8 History and Civics. You can download the History and Civics ICSE Solutions for Class 8 with Free PDF download option. History and Civics for Class 8 ICSE Solutions all questions are solved and explained by expert teachers as per ICSE board guidelines.
ICSE Solutions Class 8 History & Civics GeographyBiologyChemistryPhysicsMaths
Time To Learn
I. Fill in the blanks:
- The impact of western education led to a great awakening in India.
- It was due to Raja Rammohan Roy’s efforts that Lord William Bentinck, the Governor General of India, banned Sati in 1829.
- Ishwar Chandra Vidyasagar made a remarkable contribution to the education of girls and uplift of women.
- Ramakrishna Paramhansa believed that all religions were just different paths to reach one goal salvation or realisation of God.
- Swami Vivekananda wanted people of India to be fearless, self confident and self-reliant.
- Swami Dayanand’s slogan was back to the Vedas.
- Sir syed Ahmad Khan founded the Mohammedan Anglo-Oriental College at Aligarh in 1875.
- Jyotiba Phule was given the title of Mahatma for his work for uplift of the oppressed classes.
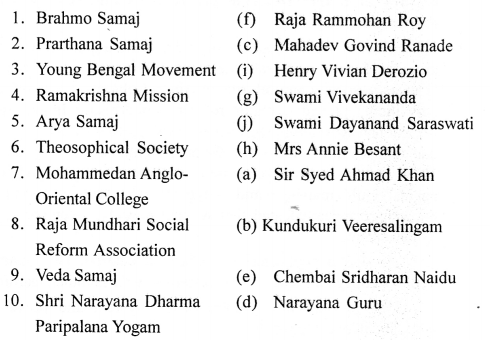
II. Match the contents of Column A and Column B:
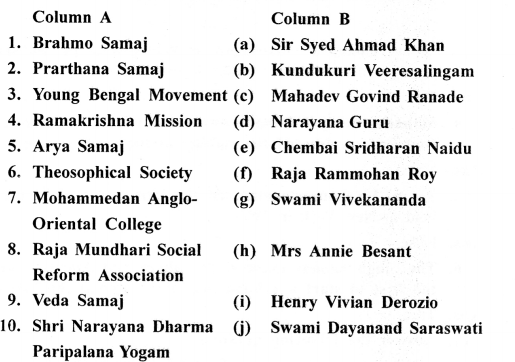
Answer:
III. State whether the following statements are True or False:
- The reform movements took place in Bengal only.
False. - Raja Rammohan Roy’s religious beliefs were based on the Bible.
False. - Ishwar Chandra Vidyasagar, as Principal of the Sanskrit College, allowed lower castes to join his college.
True. - Mahadev Govind Ranade advocated worship of Supreme God and condemned the rigidity of the caste system.
True. - Swami Vivekananda attended the Parliament of Religions held at New York in 1980.
False. - The Singh Sabhas founded at Lahore and Amritsar were the first to start a reform movement among the Sikhs.
True.
IV. Answer the following questions:
Question 1.
What were the main aims of the reformers of the nineteenth century in India? Describe the reforms initiated by Raja Rammohan Roy.
Answer:
The impact of Western culture on India led to a great awakening in India. Many social reformers came forward and advocated changes in society and reforms in Hindu Religion. These reform movements played a major role in modernising India. Raja Rammohan Roy fought against the evil custom of Sati. It was due to his efforts that Lord William Bentinck banned Sati in 1829. He was a strong champion of Women’s Rights and was against child marriage and polygamy. He advocated widow remarriage and advocated that women must be given the right to inheritance.
He was a supporter of western education. He founded Vedanta college for teaching of western as well as Indian learning. He opposed Idol worship, caste system and preached worship of one God only
Additional Questions
EXERCISES
A. Fill in the blanks:
- Sati was banned by Lord William Bentinck with the support of progressive Indians like Bruhmo samaj.
- The first Indian school for girl was established in Calcutta in 1849 by Drinkwater Bethune with the support of Vidyasagar.
- Vidyasagar was a great champion of widow remarriage, which was legalized by Lord Dalhousie.
- The most ardent follower of Ramakrishna Paramahansa was Narendranath Datta, later known as Swami Vivekananda.
- Annie Besant started the Home Rule Movement in India.
- The Prarthana Samaj was founded by R. G Bhandarkar and Mahadev Govind Ranade
B. Match the following:

Answer:
![]()
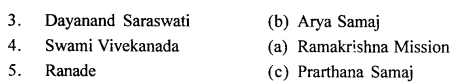
C. Choose the correct answer:
- Swami Dayanand/Ishwar Chandra Vidyasagar/Raja Ram Mohan Roy founded the Arya Samaj in 1875.
Ans. Swami Dayanand founded the Arya Samaj in 1875. - Veeresalingam/Sri Narayan Guru/R. G Bhandarkar was referred to as the ‘Vidyasagar of South India’
Ans. Veeresalingam was referred to as the ‘Vidyasagar of South India’. - Dadabhai Naoroji/Mahadev Govind Ranade/Syed Ahmed Khan was an outstanding social reformer in Parsee society.
Ans. Dadabhai Naoroji was an outstanding social reformer in Parsee society. - Swami Dayanand/Syed Ahmed Khan/Dadabhai Naoroji founded the Mohammedan Anglo-Oriental College at Aligarh in 1875.
Ans. Syed Ahmed Khan founded the Mohammedan Anglo-Oriental College at Aligarh in 1875. - The Sikh reformers launched the A kali Movement/Aligarh Movement/Arya Samaj against the corrupt management of the gurudwaras.
Ans. The Sikh reformers launched the Akali Movement against the corrupt management of the gurudwaras.
D. State whether the following are true or false:
- Raja Ram Mohan Roy propagated widow remarriage.
True. - Ishwar Chandra Vidyasagar supported Lord William Bentinck to banning sati.
False
Correct : Ishwar Chandra Vidyasagar supported Lord William Bentinck on Hindu widow Remarriage Act. - Dayanand Saraswati believed that the Vedas were the fountainhead of all knowledge and truth.
True. - Ramakrishna Paramahansa was a priest in the temple of Goddess Lakshmi at Calcutta.
True. - Swami Vivekananda believed that the regeneration of the society is the responsibility of every Indian.
True.
- Jyotiba Phule was a social reformer in Maharashtra.
True.
E. Answer the following questions in one or two words/ sentences:
Question 1.
Mention any two evil social practices against which the Brahmo Samaj launched a relentless struggle.
Answer:
The Brahmo Samaj launched a relentless struggle against the following evil social practices:
- Sati Practice
- Caste distinctions and untouchability
- Child Marriage
- Poloygamy
Question 2.
What effect would the social regeneration that took place in the 19th century have on India’s future?Answer:
Due to social regeneration there was rise of nationalism and the growth of the national movement.
Question 3.
Who established the Ramakrishna Mission and why?
Answer:
Ramakrishna Mission was founded by Swami Vivekananda to propagate the teachings and ideals of Ramakrishana Paramahansa. The main ideas of this Mission are
- Selfless social service
- Spread of
- Removal of ignorance
- Social inequalities
Question 4.
Mention any two social reforms advocated by Syed Ahmed Khan.
Answer:
To introduce social reforms Syed Ahmed Khan focused on the backward condition of the women. He advocated the removal of education for women and opposed polygamy.
Question 5.
Why was the Singh Sabha set up in Punjab ?
Answer:
The Singh Sabha was set up in Amritsar and Lahore for religious and social reforms among the Sikhs.
F. Answer the following questions briefly:
Question 1.
The central figure in the Indian Renaissance was Raja Ram Mohan Roy-the pioneer of the Modern Age in India. In this context answer the following questions:
- Discuss briefly Raja Ram Mohan’s views and ideas on religious reform within Hindu society.
- What was the programme of the Brahmo Samaj?
- Explain Raja Ram Mohan’s views on education.
Answer:
(a)
To reform society, it was important to first reform religion.
He propagated the following religious ideas based on rationalism and the philosophy of the Vedas.
- There is only one God who is the creator and preserver of the universe.
- All men are children of the one god of all human beings and therefore equal.
- It was not necessary to worship idols and perform rituals and sacrifices. God could be reached through prayer and devotion.
Raja Ram Mohan Roy condemned the domination of the priests who were responsible for misleading the people and perpetuating ritualism and socio-religious practices like sati.
He published Bengali translations of the Vedas and the Upanishads to prove that all the ancient religious texts preached monotheism.
(b)
The Brahmo Samaj launched a relentless struggle against the following evil social practices:
- Sati Practice
- Caste distinctions and untouchability
- Child Marriage
- Poloygamy
The Brahmo Samaj supported:
- Education of women
- Widow remarriage
(c)
Raja Mohan Roy was a great champion of Modem Western education. He believed it would serve as an instrument for the spread of progressive ideas and accelerate the pace of social change. He believed that the salvation of India lay in adopting western principles of reason and humanism and acquiring the knowledge of Modem science.
Question 2.
With reference to Ishwar Chandra Vidyasagar, an outstanding social and religious reformer, discuss his contribution in the following fields:
- Education in Sanskrit College
- Women’s education
- Widow remarriage
Answer:
(a) Education in Sanskrit College:
Vidyasagar denounced caste discrimination and as the principal of the Sanskrit College he admitted non-brahmana students. He was strongly opposed to the monopoly of the brahmanas on the study of Sanskrit and the ancient Vedic texts.
(b) Women’s education:
Vidyasagar was a staunch supporter of women’s education and helped Drinkwater Bethune to establish the first Indian school for girl in Calcutta in 1849. As inspector of school he opened thirty five schools for girls.
(c) Widow remarriage:
The great misery and sufferings of the Hindu widows in Bengal pained him deeply. He started a bold movement advocating the remarriage of widows. His efforts bore fruit. Lord Dalhousie passed the widow Remarriage Act in 1856. The first legal Hindu Widow remarriage was celebrated in Calcutta in December 1857, with the support of Vidyasagar.
Question 3.
Many great humanists and social reformers propagated their ideas in an effort to arrest the stagnation of Indian society. In this context, discuss:
(a) The Arya Samaj
(b) Vivekananda’s belief and achievements
(C) The Prarthana Samaj
Answer:
(a)
Swami Dayanand founded a society known as Arya Samaj in 1875.
The Social reforms advocated by Arya Samaj are on the following practices
- Caste system and untouchability
- Child marriage
The Samaj supported and encouraged
- Education for Women
- Widow remarriage
(b)
Swamiji proclaimed the essential unity of all religions and emphasized the importance of religious tolerance, brotherhood, peace and harmony among Indians. He condenmed the caste system social and economic inequalities, superstitions and ritualism and urged Indians to act responsibly
(c)
It was founded in Bombay Under the supervision of R.G. Bhandarkar and Mahadev Govind Ranade. It worked on the same lines as the Brahmo Samaj and worked for the abolition of caste system, polygamy, child marriage.
Question 4.
Write short notes on the following:
(a) Ram Mohan Roy’s achievements in the field of education
(b) Jyotiba Phule
(c) Reforms among Parsees
Answer:
(a)
Raja Mohan Roy opened an English medium school which combined traditional Indian learning with Western knowledge. He assisted David Hare, a Scottish watchmaker, to establish the Hindu College in Calcutta. He also founded the Vedanta College which offered courses of study in Indian learning and Western sciences.
(b)
Jyotirao Govindrao Phule and his wife, Savitribai Phule, were dedicated social reformers in Maharashtra. Jyotirao was popularly known as Mahatma Phule. He challenged the superiority of the brahmanas and the authority of the scriptures. He took up the cause of the low-caste members of society. He organized Satyashodhak Samaj in 1873 to mobilize the low-caste members and oppressed sections of society in a movement for equality. He also pressed for the education of girls.
(c)
In reform movement among the Parsees an association was set up and it started a movement against religious orthodoxy. Modem ideas and changes were introduced to elevate the position of the Parsee women. Education of woman, raising the marriageable age of girls and widow remarriage were some of the major concerns of the reforms.
Question 5.
With reference to the reform movements in various parts of India, discuss:
- Reform movement in South India
- The Aligarh Movement
- Reforms among the Sikhs
Answer:
(a)
Veeresalingam, a prominent social reformer in South India, was deeply disturbed by the deplorable condition of Women in general and widow remarriage and education for women in particular .Sri Narayan Gum carried on a lifelong struggle against the caste system. His crusade was based on the principle of one caste, one religion, one god for mankind.
(b)
Sir Syed Ahmed Khan started a reform movement called the Aligarh Movement. He had a significant role in awakening the Muslims to the need to change with the times. He believed that only through Western education and knowledge of English, the Muslim community could progress and scientific temper be developed. His greatest achievement was the foundation of Mohammedan Anglo-Oriental College at Aligarh in 1875. This College later on grew into the Aligarh Muslim University.
(c)
The Singh Sabha was set up in Amritsar and Lahore for the religious and social reforms among Sikhs. It set up the Khalsa college in Amritsar and opened many schools and promoted the Gurumukhi script and Punjabi literature.
G Picture Study
This is the painting of the Indian social reformer considered to be the ‘Father of Indian Renaissance.’

Question 1.
Name the person.
Answer:
Raja Ram Mohan Roy
Question 2.
What were his views on religion?
Answer:
A comparative study of the Vedas, the Koran and the Bible (the old Testament and New Testament) convinced Raja Ram Mohan Roy about the basic unity in the fundamental truths of ail religions. According to him religion was central to an individual’s life. Every aspect of social life revolved around religious beliefs. He propagated the religious ideas based on the philosophy of the Vedas.
- There is only one God who is the creater and preserver of the universe/monotheism)
- All men are children of the ‘one God of all human beings’ and therefore equal (brotherhood of man)
- It was not necessary to worship, idols and perform rituals and sacrifices. God could be reached through prayer and devotion.
Question 3.
Name the society established by him in 1828.
Answer:
Raja Ram Mohan Roy founded a society’ called the Sabha Brahmo (1828) which later became Brahmo Samaj.
Question 4.
Mention the social practices against which this society- launched a relentless struggle.
Answer:
Brahmo Samaj launched a relentless struggle against the following social practices Sati. Caste distinctions and untouchability. Child marriage Polygamy
Question 5.
Mention two important social reforms supported by this society.
Answer:
Education of Women, Widow Remarriage.