ICSE Solutions for Class 7 History and Civics – Making of Composite Culture – Sufi and Bhakti Movements
ICSE SolutionsSelina ICSE SolutionsML Aggarwal Solutions
APlusTopper.com provides step by step solutions for ICSE Solutions for Class 7 History and Civics. You can download the History and Civics ICSE Solutions for Class 7 with Free PDF download option. History and Civics for Class 7 ICSE Solutions all questions are solved and explained by expert teachers as per ICSE board guidelines.
ICSE Solutions Class 7 History & CivicsGeographyMathsPhysicsChemistryBiology
Important Words
- Silsilas were the the monastic organizations of the Sufis. Two of these organizations, the chishti and Suhrawardi orders, became popular in India.
- Monotheism is the belief that there is only one God.
- Dohas were the simple, beautiful Hindi verses through which Kabir spread his message.
- Gurumat means the guru’s doctrine and Sikhism is also known by this name.
- Guru Granth Sahib is the holy scripture of the Sikhs. It is also known as the AdiGranth.
- Khalsa was a disciplined military order of sikh soldier-saints created by Guru Gobind Singh, who transformed the Sikhs into a martial race.
Time To Learn
I. Fill in the blanks:
- The Sufi saints were organised into various orders or Silsilahs.
- The Chishti order was established in India by Moin-ud-din Chishti.
- Kabir’s couplets were known as Kabirpanthis.
- Guru Nanak was bom in 1469 AD.
- Chaitanya Mahaprabhu believed in kirtan as the most important means of expressing devotion to God.
- Meerabai worshipped Krishna.
- Ramanand preached the worship of Rama.
- Sant Jnaneshwar wrote a commentary on the Gita, known as Dhyaneshwari.
- Sant Tukaram composed devotional songs in praise of Vithoba (Lord Krishna).
- The Bhakti and Sufi movements brought about an understanding among the Hindus and Muslims.
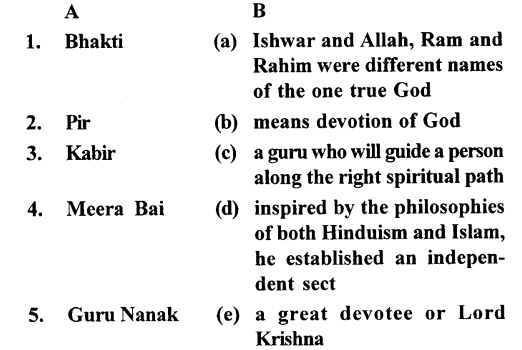
II. Match the contents of Column A with those of Column B:


Answer:

III. State whether the following statements are Ture or False:
- Early Sufis came from Central Asia.
False. - Sufis believed in caste distinctions.
False. - Meerabai was an ardent devotee of Lord Krishna.
True - Kabir was a weaver by profession.
True. - The Marathi devotional songs are known as kirtans.
False
- Sant Tukaram was a contemporary of Shivaji.
True.
IV. Answer the following questions:
Question 1.
Who were the Sufis? What were their teachings? Name some famous Sufi saints.
Answer:
The Sufis were a group of Muslim mystics who started a religious reform movement in West Asia.
Teachings of Sufism:
- There is only one god and all people are his children.
- All human beings are equal.
- Different religions are different natK leading to one God. Therefore, all religions must …cted.
- It is necessary to follow the path shown by a pir, who will guide a person along the right spiritual path.
Famous Sufis saints: Moin-ud-din Chishti, Baba Farid and Nizam-ud-din Auliya.
Question 2.
What do you understand by Bhakti? What were the teachings of the Bhakti reformers?
Answer:
The word ‘Bhakti’ means devotion or love to God. Ramananda, Kabir, Guru Nanak, Mira Bai, Chaitanya were important reformers of Bhakti Movement.
They preached that with love or devotion one could get salvation. They taught all are the children of same God. That is why distinctions of caste, creed or sect and condemned useless rites and false practices. They laid importance on good deeds and purity of conduct. They believed that God could be attained by leading a normal household life and not by renouncing the world. All the Bhakti saints emphasised on the oneness of God and universal brotherhood.
Question 3.
Who was Kabir? What were his teachings?
Answer:
Kabir was one of the great reformers of the Bhakti movement. He taught Hindu Muslim unity. He believed that God is one and Tshwar’ and ‘Allah’ are different names of one God.He taught devotion to God and also preached brotherhood of man. He was against caste distinctions because he firmly believed that salvation could be attained only through good deeds. That is why he condemned useless rites, false practices as well as idol worship.
Question 4.
How were the Bhakti and Sufi movements similar?
Answer:
The similarities between the Bhakti and Sufi movements are:
- Both believe in one Supreme God.
- Both the communities sternly opposed the discrimination of castes, religions and divisions.
- They stressed the same before the people that basically there are no differences between the Hindus and Muslims,
- They are both the children of God. They told that the simple route to the attainment of Godlihood lies in the love for humanity.
Question 5.
Who was the founder of the Sikh religion? What are his main teachings?
Answer:
Guru Nanak Dev was the founder of Sikh religion. He preached:
- Oneness of god.
- God is truth.
- He discarded caste distinctions which divided human beings.
- He advocated ‘Langar’ or community kitchen which brought all castes together.
- He condemned useless rites and practices.
- He preached true devotion to God.
- He did not believe in renouncing the world to attain I salvation.
Additional Questions
(Making of Composite Culture – Sufi and Bhakti Movements)
A. Fill in the blanks:
- As the spirit of tolerance and understanding developed between the Hindus and the Muslims, two liberal religious reform movements took shape in the Medieval Period. They were the sufi and Bhakti movements.
- The Sufis came to India with the Turks in the 12th century ce. Over the years, they absorbed Buddhist and Hindu influences and were greatly respected by the Muslims as well as the Hindu.
- The Bhakti Movement began in South India in the 7th century ce and became a popular movement before the arrival of the Turks.
- There were 10 Sikh gurus.
- The holy book of the Sikhs is known as the Shri Guru Granth Sahibji.
- The Sikhs worship in a Gurdwara which means door of the guru
B. Match the following
Answer:

C. Choose the correct answer:
- 1. The Sufis were a group of Hindu/Buddhist/Muslim mystics.
Ans. The Sufis were a group of Muslim mystics. - The word ‘bhakti’ means fear of God/following rituals/ devotion to God.
Ans. The word ‘bhakti’ means devotion to God. - The Bhakti saints drew their inspiration from the Bhagwad Gita and the Vedas/Puranas/Upanishads.
Ans. The Bhakti saints drew their inspiration from the Bhagwad Gita and the Upanishads. - Guru Nanak/Guru Tegh Bahadur/Guru Gobind Singh was the founder of the Sikh religion.
Ans.Guru Nanak was the founder of the Sikh religion. - The word ‘Sikh’ is derived from a word which means teacher/disciple/warrior.
Ans. The word Sikh’ is derived from a word which means disciple.
D. State whether the following are true or false:
- The organization of the Sufis was known as the sangha.
False. Correct: The organization of the Sufis was known as the silsilas. - Bhakti saints believed in monotheism.
True. - Ramananda taught his message through dohas.
False. Correct: Kabir taught his message through dohas. - Chaitanya Mahaprabhu was a believer in the importance of following rituals.
False. Correct: Chaitanya Mahaprabhu was a believer in the existence of God. - Guru Tegh Bahadur was executed by Aurangzeb.
True.
E. Answer the following questions in one or two words/ sentences:
1. Who were the Sufis?
Ans. The Sufis were a group of Muslim mystics who started a religious reform movement in West Asia.
2. What are silsilas?
Ans. Silsilas were the monsastic organizations of the Buddhist sangha and the Sufis.
3. Name the two popular Sufi orders in India.
Ans. Chishti and the Suhrawardi orders, became popular in India.
4. What is the importance of qawwali in Sufism?
Ans. One could come closer to God through devotional music qawwali.
5. Mention any one positive effect of the Bhakti Movement on Hindu-Muslim unity.
Ans. People were attracted to the principles of monotheism, equality and ritual-free worship. By propagating its principles of one God, universal brotherhood and respect for all religions, the Bhakti Movement created conditions conducive to the harmonious and peaceful coexistence of Hindus and Muslims.
6. What are dohas?
Ans. Dohas were the simple, beautiful Hindi verses (poems) through which Kabir spread his message.
7. How did Meera Bai spread the message of Bhakti among the people.
Ans. Meera Bai spread the message of devotion and love for’ od through devotional songs called Meera’s bhajans.
8. Name the five sacred symbols of Sikhism.
Ans. The five sacred symbols of Sikhism are:
- Kesh,
- Kanga,
- Kaccha,
- Kirpan,
- Kara
9.Who transformed the Sikhs into a martial race?
Ans. Guru Gobind Singh transformed the peace-loving Sikhs into a martial race.
10. How did the Sufi and Bhakti movements lead to the development of local languages?
Ans. The Bhakti and Sufi saints preached in the language of the common people and this led to the development of local language.
F. Answer the following questions briefly:
Question 1.
What are the important teachings of the Sufi saints? Explain the impact of Sufism on the people and their rulers?
Answer:
Teachings of Sufism:
- There is only one god and all people are his children.
- All human beings are equal.
- Different religions are different paths leading to one God. Therefore, all religions must be respected.
- It is necessary to follow the path shown by a pir, who will guide a person along the right spiritual path.
The liberal ideas and rational principles of sufism, had great impact on the people and their rulers. It encouraged religious tolerance promoted the idea of universal brotherhood and brought the Hindus and Muslims closer to one another.
Question 2.
Explain the origin of the Bhakti Movement in India. Why did the teaching of the Bhakti saints appeal to the people?
Answer:
The word ‘bhakti’ means devotion to God. The Bhakti Movement was a reform movement within Hinduism. It began in South India in the 7th century ce and became a popular movement before the arrival of the Turks. The Bhakti saints drew their inspiration from the Upanishads and the Bhagavad Gita. People were attracted to the principles of monotheism, equality and ritual-free worship. By propagating its principles of one God, universal brotherhood and respect for all religions, the Bhakti Movement created conditions conducive to the harmonious and peaceful coexistence of Hindus and Muslims.
Teachings of the Bhakti saints:
- There is only one God. Everyone is equal in the eyes of God.
- God can be reached through love and devotion and total surrender to his will and not through rites rituals and idol worship.
- Everyone should lead a pure life.
Question 3.
Mention the chief teachings of the Bhakti saints.
Answer:
Teachings of the Bhakti saints:
- There is only one God. Everyone is equal in the eyes of God.
- God can be reached through love and devotion and total surrender to his will and not through rites rituals and idol worship.
- Everyone should lead a pure life.
Question 4.
Mention the important teachings of Sant Kabir.
Answer:
Sant Kabir stressed the idea of one God. He taught that Ishwar, Allah, Ram and Rahim were different names of one God. He spread the message of Hindu-Muslim unity, Universal brotherhood, tolerance and banned idol worship, caste system and rituals. Kabir preached his message through simple beautiful Hindi poems called Dohas.
Question 5.
What are the main teachings of Guru Nanak? Why is the holy book of the Sikhs known as the Guru Granth Sahib?
Answer:
The important teachings of Guru Nanak are as follows:
- There is only one God and He is the creator of this universe.
- All human beings are equal. The caste system must be rejected and the principle of universal brotherhood must be followed.
- Everyone should lead a good and pure life based’on truth and kindness, and discard idol worship and ritualism.
- True spiritual knowledge can be gained under the guidance of a guru.
The last Guru Gobind Singh Ji, transferred the authority of the Guru to the holy scriptures called the ‘Adi Granth’ which came to be known as the Guru Granth Sahib. The teachings of all the Gurus are contained in it and it serves as a guide or Guru.
Question 6.
What effect did the Bhakti and Sufi movements have on Indian society?
Answer:
The Bhakti and Sufi movements brought a new era in Indian society which was based on tolerance and brotherhood among the human beings. Following are the impact of the movements:
- The Bhakti and Sufi movement preached in the language v/; the common man which gave rise to development of common languages.
- The common man came to know about great truths of Hindu philosophy which helped in slowing down conversions during this period.
- These movements helped in reducing the superiority of the brahman as.
- They also brought feeling of universal brotherhood and created an environment of tolerance and mutual respect.
G Picture study:
This is the picture of a monument associated with the founder of a religious reform movement in India.

Question 1.
Name the reformer and the movement he started in India.
Answer:
Religious reformer was Moinuddin Chishti. He started Sufi- Movements
Question 2.
Identify the monument.
Answer:
Dargah of Moinuddin Chisti.
Question 3.
Why is this monument famous?
Answer:
This monument is famous for its teachings
- All human beings are equal and God is only one.
- All religions must be respected.
- Fasts and other rituals are not necessary.
- There is no need to convert to another religion.
Question 4.
Mention any four important religious principles of that movement, which are common to the principles of the Bhakti Movement.
Answer:
(a) There is only one God.
(b) Everyone is equal in the eyes of God.
(c) God can be reached through love and devotion and total surrender to His will and not through rites, rituals and idol worship.
(d) Eveyone should lead a pure life.
Question 5.
Name any two religious reformers of the Bhakti Movement.
Answer:
Ramananda, Guru Nanak Dev ji.