ICSE Commercial Studies Previous Year Question Paper 2014 Solved for Class 10
ICSE Paper 2014
COMMERCIAL STUDIES
(Two Hours)
Answers to this Paper must be written on the paper provided separately.
You will not be allowed to write during the first 15 minutes.
This time is to be spent in reading the Question Paper.
The time given at the head of this Paper is the time allowed for writing the answers.
Attempt all questions from Section A and any four questions from Section B.
The intended marks for questions or parts of questions are given in brackets [ ].
Section-A (40 Marks)
(Attempt all questions from this Section)
Question 1:
Distinguish between:
(a) Formal Communication and Informal Communication. [2]
(b) A Product and a Service. [2]
(c) Standardisation and Grading. [2]
(d) Direct Labour Cost and Indirect Labour Cost. [2]
(e) A Warehouse Receipt and Warehouse Warrant. [2]
Answer:
(a)
Formal Communication | Informal Communication |
1. Formal communication is authorised and well-planned. | 1. Informal communication is unauthorised and unplanned. |
2. Formal communication is generally written. | 2. The informal communication is generally verbal. |
| 3. Formal communication refers to the flow of information through the chain of command. | 3. Informal communication refers to the inter-change of information between people through informal and unofficial channels. |
(b)
Product | Service |
1. Fully tangible can be touched and standardized. | 1. Intangible cannot be touched and standardized. |
2. Can be stored for use in future. | 2. Cannot be stored for use in future. |
| 3. Can be transferred. | 3. Cannot be transferred. |
4. Fully separable remote transactions are possible. | 4. Not separable, remote transactions usually not possible. |
(c)
Standardization | Grading |
Standardisation is the process of making goods perfectly identical to the model product. In this case, the product contains certain desirable qualities like durability, safety, utility and special features such as design, weight, colour and size. | In case of Grading, a product is classified into identical lots and groups on the basis of predetermined standards. Grading divides products into different classes of uniform characteristics. |
(d)
Direct Labour Costs | Indirect Labour Costs |
Labour which is directly consumed in the process of production. It is also known as productive or operating labour. e.g. — Wages | Labour which indirectly helps in the production process, which cannot be easily traced. e.g.—Salesman’s Salary. |
(e)
Warehouse Receipt | Warehouse Warrant |
1. Warehouse receipt is a only acknowledgement receipt of the goods. | 1. Warehouse warrant is a warrant in favour of owner of goods. |
| 2. Warehouse receipts is not transferred. | 2. Warehouse warrant can be transferred by simple endorsement and delivery. |
Question 2:
(a) State any two advantages of branding. [2]
(b) How do group discussions help in the selection process of suitable candidates for employment? [2]
(c) State two limitations of a budget. [2]
(d) What is meant by an ‘Overdraft’ facility given by a Commercial Bank? [2]
(e) Mention any two objectives of Training. [2]
Answer:
(a) Advantages of Branding:
- It saves time and efforts of consumers as they can identify and recognise the product to be purchased.
- Branding is the basis of advertising and other techniques of mass selling.
- Branding helps to minimise selling cost by reducing dependence on middlemen.
- Branding insures uniform standards of quality and designs to consumers.
- Branded products are invariable packed which prevents adulteration and helps to prevent adulteration and helps to preserve the quality of the product. (any two)
(b) The two uses of group discussions in selecting employees for a concern are as follows:
- In an interview, the candidate gets no opportunity to participate and show his leadership ability.
- Group discussion is widely used to screen candidates for admission into management schools.
(c) Two limitations of a budget:
- Budget estimates are generally based on the price level at a particular point of time. These estimates may become meaningless when there is either inflation or depression in the market.
- In order to keep with in budget limits, they may overlook the goals of the organisation. In such cases, budgetary goals supersede enterprise goals and budgets obstruct the attainment of objectives.
(d) Overdraft means an arrangement under which a current account holder is allowed to withdraw more than the balance to his credit upto the specified limit. Overdraft is allowed for a short period and interest is charged on it. Commercial Banks provide overdraft facility on the security of some assets or on the personal security of the account holder.
(e) The main objectives of training are as follows:
- To prepare employees for the right jobs by imparting the required knowledge and skills.
- To enable employees to work more efficiently on their present jobs by exposing them to the latest concepts and techniques.
Question 3:
(a) State any two disadvantages of Rail Transport. [2]
(b) State any two characteristics of an Ideal Warehouse. [2]
(c) What is a Provident Fund Scheme? [2]
(d) What is meant by the term ‘Revenue Expenditure’? [2]
(e) How does a ‘Status barrier’ affect Effective Communication? [2]
Answer:
(a) Two disadvantages of Rail Transport:
- Door-to-door service is not possible. Its services are available only between certain definite points.
- Railway transport is not suitable for carrying perishable and fragile goods due to frequent and careless handling of goods.
(b) Two characteristics of an Ideal Warehouse:
- It must be centrally located so that loading, unloading and transportation of goods takes minimum time and cost.
- Goods should be protected from heat, cold, water, insects, corrosion, fire and theft of goods.
(c) Provident Fund Scheme: Under this schemes the employee and the employer contribute every month ten per cent of the basic wages. The total contributions are invested in specified investments. The accumulated amount of standing credit to an employee is payable on retirement, death or at the time of leaving service. An employee can get advances and permanent withdrawals for construction of house, marriage of dependents and other specified purposes, like serious illness.
(d) Revenue Expenditure: This expenditure relates to normal functioning of the government departments and provision of various government services. The main examples of such expenditures are salaries, pensions, interest, subsidies, grants to the state governments etc., are known as Revenue Expenditure. These expenditures are incurred to maintain the general services of the government like defence, law and order, administration and to provide-various social services (education, health, etc.) and economic services (agriculture, industry, power, transport and communications etc.)
(e) Status Barriers: Superior-subordinate relationship in the formal organisation structure may obstruct free flow of information. A manager may convey only selected information to his subordinates so as to maintain status difference. He may feel that if he communicates problems or results which reflect his ability and judgment his position as a superior would be undermined. Similarly, subordinates tend to convey only those things which the superiors would appreciate. Thus, status creates filtering and distorts downward and upward communications.
Question 4:
(a) Briefly explain any two elements of a Promotion Mix. [2]
(b) Give two reasons for workers joining a Trade Union. [2]
(c) What is meant by Orientation or Induction Training? [2]
(d) What is ‘Discounting of Bill of Exchange’? [2]
(e) Explain ‘contribution’ as a principle of an Insurance contract. [2]
Answer:
(a) Two elements of a Promotion Mix:
- Advertising: It is non-personal communication, which is paid for by an identified sponsor. It is aimed at promoting ideas (no smoking), products (BPL-television) or services (Dolphin mobile).
- Publicity: It is non-paid form of non-personal communication. This is like advertising except that advertising is paid for and it is not. Publicity takes place when media in the form of news, covers some event and information is disseminated about something free of cost.
(b)
- Protection: Trade unions safeguard workers against all sorts of exploitation by the employer and political parties. A union provides protection from unfair labour practices and atrocities of management. It also tries to revise the status of workers in industry and society. Trade unions resist retrenchment of their members and help to ensure steady employment for workers. Unions serve as a check on arbitrary action by employers.
- Economic Security: Unions protect their members from various economic hazards such as illness, accidental injuries, unemployment. They secure compensation from employers. Unions also provide financial assistance to workers during distress.
(c) Orientation or induction training refers to the training given to new employees to familiarise them with the policies, rules and regulations of the organisation and the conditions of the job. A systematic orientation programme enables the new employees to adjust quickly to new surroundings and people.
(d) Bank purchases bills of exchange at the face value and less the interest at current rate till its due date. This is called discounting of bills. The owner of the bills can get cash immediately and need not to wait for payment until the bills fall due.
(e) Contribution: The principle of contribution is another corollary of the doctrine of indemnity. It implies that when property is insured for the same risk with two or more insurers, the different insurers will contribute to the total payment in proportion to the amount assured by each. In case one insurer has paid the full compensation for loss, he is entitled to receive proportionate contribution from other insurers.
Section – B (40 Marks)
(Answer any four questions from this section)
Question 5:
(a) Write any five expectations of the General Public or Society from a Business Enterprise. [5]
(b) State any five objectives of marketing. [5]
Answer:
(a) The expectations of the General Public or society from a business enterprise are as follows:
- To protect the environment from all types of pollution.
- To Produce socially desirable products in accordance with national interest and priorities.
- To help weaker sections of the society by giving them preference in employment and other fields.
- To preserve social and cultural values.
- To respect human rights including rights of women and children.
(b) Five Objectives of Marketing: Refer Ans. 5. (a) 2015.
Question 6:
(a) State five benefits of Advertising to manufactures dealers. [5]
(b) What is meant by ‘Sustainable Development’? Explain any two examples of sustainable use of resources. [5]
Answer:
(a) Benefits of Advertising to Manufacturers: Advertising is beneficial to the manufacturers in the following ways:
- Steady Demand: Advertising creates regular demand by smoothening out seasonal and other fluctuations. It helps in increasing and maintaining steady demand for a particular article and ensures continuity of production on a large-scale.
- Increases Sales: Advertising acts as an aid to selling. It increases sale of all products and services. Goods produced on a large scale are sold by the methods of mass presentation through advertising.
- Support to Dealers and Salesmen: Advertising prepares the necessary ground for the success of the efforts of the dealers or salesmen for selling the goods because it creates awareness, interest and demand for the product. It makes it easier for the salesman to approach the potential customers as they have already been familiarized with the product through the advertisement. It improves the moral of the employees and encourages them for better performance.
- Helps in Introducing New Products: Advertising helps in the replacement of old habits and traditions by new and better goods and methods of use. It introduces new products or old products to new customers. Repeated advertisement through proper media helps the manufacturer in creating awareness and gaining acceptance of their products by the consumers. It may educate the consumer about the use of the new products or the new uses of the old products.
- Market Expansion: Advertising enables the manufacturer to expand the markets for his products. It helps him not only in retaining the old markets but also in entering and capturing the new markets. Repeat advertising carries a very forceful sales message to the prospective customers residing in remote and inaccessible areas.
(b) Sustainable development means the development that meets the needs of present generations without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs. For development to be sustainable, it must take into account social and ecological factors in addition to economic aspects of the living and non-living base both in the long run as well as the short term. Three main elements of sustainable development are well-being of the human society, well being of the environment, and sustainability over time.
Any component of nature which human beings need and value is called a resource. A country uses natural resources in order to develop. But development leads to over-exploitation and depletion of natural resources. No development can be sustained for a long period if it upsets the balance of nature. Therefore, development must include protection of our environment.
Two examples of Sustainable Use of resources: Refer Ans. 4. (d), 2015.
Question 7:
(a) Explain the benefits of taking an Insurance Policy. [5]
(b) Explain any five objectives of Industrial Relations. [5]
Answer:
(a) Insurance offers the following benefits:
- Protection: Insurance provides protection against several types of risks. Life insurance provides financial assistance to family in the untimely death of the policyholder.
- Savings: Life insurance encourages the habit of thrift and savings. After taking an insurance policy, a person saves money to pay regular premium. On the maturity of the life policy, the insured receives a lump sum. This amount can be utilised for higher education/marriage of children or construction of a residential house. Thus, life insurance serves as a means of protection as well as a means of savings.
- Financial aid: In case of financial need the policyholder can take a loan against the policy. Ute loan can be repaid in easy instalments.
- Provision for old-age: People can make financial provision for old-age by taking life insurance policies. They can lead their retired life happily and without depending upon their families for money.
- Tax relief: Under the Income Tax Act, an income tax payer can reduce his tax liability by taking life insurance policy.
(b) The main objectives of industrial relations are as follows:
- To develop and maintain harmonious relations between management and labour so essential for higher productivity of labour and industrial progress in the country.
- To safeguard the interests of labour as well as management by securing the highest level of mutual understanding and goodwill between all sections in industry.
- To establish and maintain industrial democracy based on the participation of labour in the management and gains of industry, so that the personality of every individual is fully recognised and developed.
- To avoid all forms of industrial conflict so as to ensure industrial peace by providing better working and living standards to workers.
- To ensure a healthy and balanced social order through recognition of human rights in industry and adaptation of complex social relationships to the advancements in technology.
Question 8:
(a) Explain any two types of deposit accounts. [5]
(b) Explain five main characteristics of Communication. [5]
Answer:
(a)
- Savings bank account: For savings deposits an account is opened with the bank which is called savings account. This account is opened for non-trading customers with small amounts, say Rs. 300 without cheque facility, Rs. 500 with cheque facility. The main aim of these accounts is to develop the saving habit among common people. Such an account can also be opened by two persons in joint names. The account holders are allowed to withdraw money by cheque or by withdrawal form subject to the condition that they maintain a minimum balance in their accounts. Interest is paid on minimum monthly balances and credited to the respective accounts yearly or half yearly.
- Recurring deposit account: This deposit has been started to encourage those people to save who cannot give large deposit in lumpsum. Recurring deposit can be opened with small amount over a specified period. The depositor keeps on depositing a certain sum of money every month. The number of monthly installments may be 12, 24, 36, 48, 60 and so on. After the expiry of the period, the depositor gets back his money along with interest thereon. Cheques cannot be drawn to withdraw money from a recurring deposit account.
(b) Five main characteristics of communication are:
- Continuous process: Communication is an on-going process. Group activity requires regular flow of information and ideas among the members of the group.
- Pervasive function: Communication is essential in all organisations and at all levels of authority. It is all pervading.
- Circular process: Communication involves a circular flow of messages. The response to the message, called feedback, requires another message to be transmitted by the receiver of the original message. The response indicates the impact of communication.
- Influencing human behaviour: The main purpose of communication is to influence human behaviour. It is a means of creating interpersonal relations. A manager creates motivation and loyalty among his subordinates by sharing information, opinions and feelings with them.
- Mutual understanding: The basic purpose of communication is to create mutual understanding. Managers communicate to influence human behaviour and to obtain the desired response from employees. Communication is a means and not an end itself.
Question 9:
(a) Briefly explain any five utilities of a budget. [5]
(b) State any five tools or techniques of Brand Promotion. [5]
Answer:
(a) Utilities of a budget are:
- Operationalise plans: Budget makes business plans operational. They serve as a means of implementary different plans, goals of an organisation and its basic plans cannot be concerted into performance without budgets and other operational plans.
- Higher efficiency: Budget bring efficiency and economy in the working of a business firm. They help management in obtaining the most profitable combination of different factors of production.
- Sense of responsibility: Budget puts a sense of responsibility on the shoulders of management. Budget motivates them to act responsibly and escape from extravagance.
- Source of motivation: The projected cost cuts results into the profit expansion. This acts as the motivation and leads an enterprise to stick to the budget.
- Co-ordination: The various budgets made in the organisation are to be co-ordinated and should follow the same objectives. Hence it makes co-ordination mandatory.
- Delegation of authority: The budget is prepared by the management but the responsibility to carry on the budget is vested to the respective department. Thus the budget helps to delegate the authority and fix the responsibility.
- Effective control: Management keeps effective control and help the various departments in the organisation to keep an effective control and check on extravagance.
- Sound planning: The good budget helps to have sound planning. This is also necessary for the organisation to have a sound planning structure. (any five)
(b) Tools or techniques of Brand Promotion are:
- Advertising: It is non-personal communication, which is paid for by an identified sponsor. It is aimed at promoting ideas (no smoking), products (BPL-television) or services (Dolphin mobile).
- Personal Selling: It involves direct face to face personal interactions ‘between the sales person and potential customer. For instance, when Eureka Forbes salesman demonstrates, provides information, answers the questions and book orders. In this way he does personal selling.
- Sales promotion: It includes a variety of non recurrent activities like coupons, samples, special discount offers etc. These stimulate trial or purchase immediately.
- Publicity: It is non-paid form of non-personal communication. This is like advertising except that advertising is paid for and it is not. Publicity takes place when media in the form of news, covers some event and information is disseminated about something free of cost.
- Quality Control: Brands become popular and continue to enjoy confidence of buyers only when quality of the brand is maintained.
Question 10:
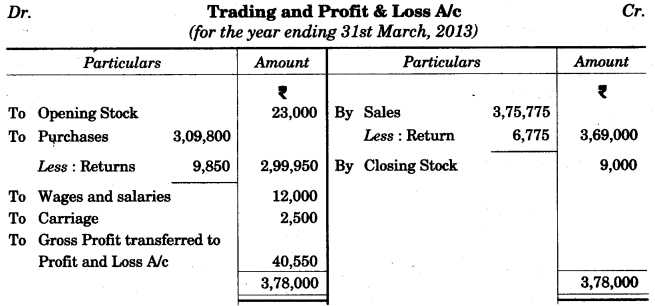
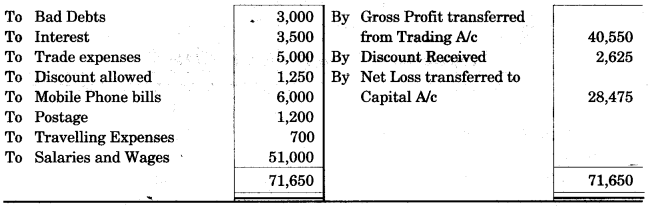
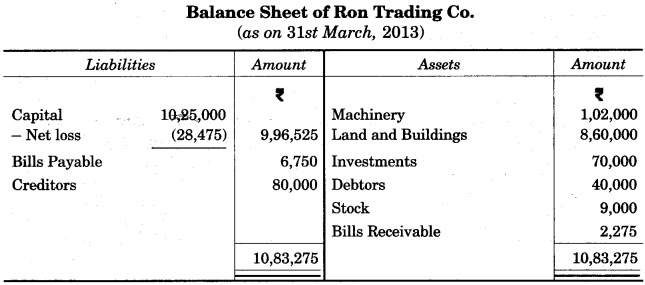
The following is the Trial Balance of Ron Trading Co. on 31st March 2013. [10]
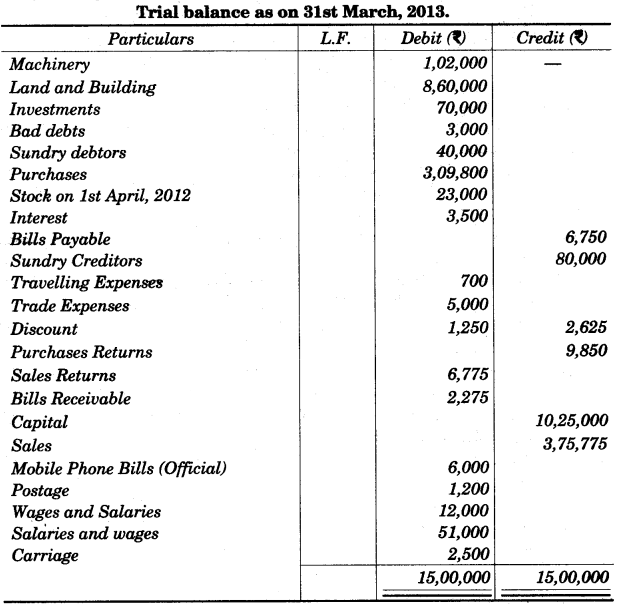
The closing stock was valued at Rs. 9,000. Prepare a Trading and Profit and Loss Account and the Balance Sheet as on 31st March, 2013.
Answer: