Frank ICSE Solutions for Class 9 Biology – The Skeletal System
PAGE NO:162
Solution 1:
Bones of skull, vertebral column, sternum and ribs.
Solution 2:
Longest bone – Femur
Smallest bone – Stapes of middle ear.
Solution 3:
There are seven cervical vertebrae. First vertebra is called atlas, second is axis while the rest are called typical cervical vertebrae.
Solution 4:
The skeletal system performs the following functions in an animal:
- It provides a framework to support the body and gives a definite shape and form to the body.
- It helps to protect some of the vital organs like heart, lungs, brain and spinal cord.
- It provides the base for attachment of muscles and several bones so as to make body movements possible.
- Bones act as storehouse of some minerals like calcium and phosphorus.
- Red bone marrow of long bones of limbs produces red blood cells and granulated white blood cells in their hollow cavities.
Solution 5:
- Axial skeleton
- Appendicular skeleton
Solution 6:
The various parts of a human skeleton are:
- Axial skeleton: This consists of skull, vertebral column, sternum and ribs
- Appendicular skeleton: It consists of pectoral and pelvic girdles and bones of limbs.
Solution 7:
Solution 8:
On the basis of position, endoskeleton is divided into two main parts:
Axial skeleton: This consists of skull, vertebral column, sternum and ribs. Human skull has 22 bones of which 8 are present in the cranium and 14 on the face. Brain is present in the cavity called cranium. In the occipital region is an opening called foramen magnum through which spinal cord passes. Cranium has 8 bones which covers the brain from all sides.
Facial bones: These bones form the face and protect the sensory organs present in the head. It has 14 bones.
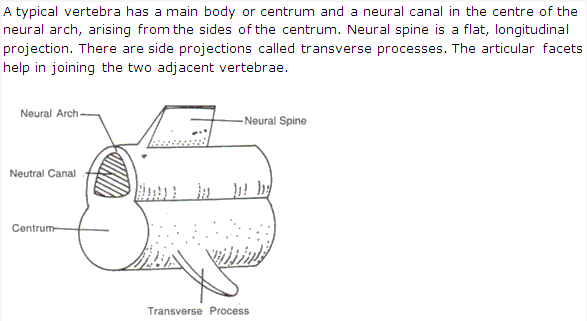
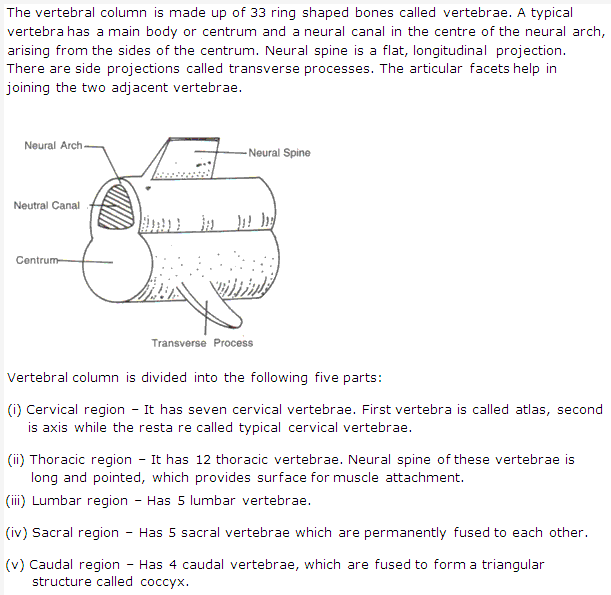
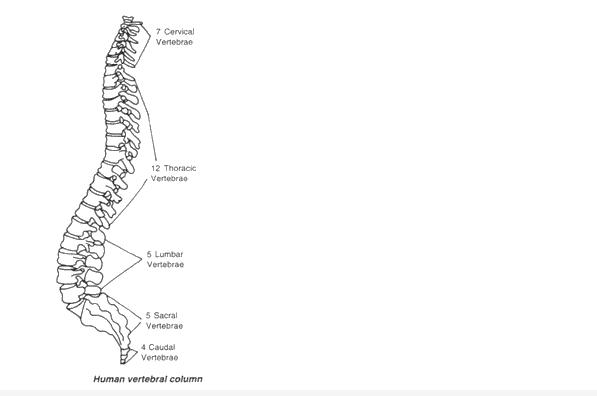
Vertebral Column:
It makes the axis of the body and provides support like a pillar. Vertebral column is divided into following five parts:
- Cervical Region. It has 7 cervical vertebrae. First vertebra is called atlas, second is axis and rest are called typical cervical vertebrae.
- Thoracic Region. It has 12 thoracic vertebrae. Neural spine of these vertebrae is long and pointed, which provdes surface for muscle and attachment.
- Lumber Region. It has 5 lumber vertebrae.
- Sacral Region. It has 5 sacral vertebrae which are permanently fused to each other. These are situated on both halves of pelvic and form a joint with pelvic girdle.
- Caudal Region. It has 4 caudal vertebrae. These are also fused to form a triangular structure which is called coccyx.
Sternum and Ribs
Sternum is the bone at the mid-ventral line of the thorax to which most of the ribs are attached at their ventral ends. Ribs are formed by vertebral and sterna part. First seven pairs of ribs are called true ribs. These are joined on one side with sternum and on second side with thorax.
Appendicular skeleton: It consists of limbs, shoulder or pectoral girdle and hip or pelvic girdles and bones of limbs.
- Bones of the fore arm: Humerus, radius, Ulna, Carpals, Metacarpals, finger bones, etc.
- Bones of hind limb: Femur, Tibia, Fibula, Tarsal, Metatarsal, etc.
- Pectoral Girdle: In mammals, two halves of pectoral girdle are situated at equal distance from the ribs on the dorsal plane. Each of it is called shoulder bones. Each half of it made up of a triangular flat bone called scapula. From its outer side a projection arises called acromion and has a cavity called glenoid cavity.
- Pelvic Girdle: It consists of two similar halves. In each, three bones are found, ilium, ischium and pubis. Pubis bones of both halves are joined and are called pubic sysmphysis. Ilium and ischium form acetabulum cavity in which head of femur articulates by forming ball and socket joint. A hollow space is found between pubis and ischium, which is called obdurate foramen, which provides passage for obturatry artery, vein and nerve.
Solution 9:
Solution 10:
Solution 11:
Importance of pectoral girdle:
- It provides support to the anterior portion of the body.
- Provides surface articulation of fore arms.
- Provides surface for muscle attachment.
- Provides protection to vital organs like heart and lungs.
Importance of pelvic girdle:
- Provides surface articulation of hind limbs.
- Provides surface for joining of muscles.
- Provides protection to the uterus.
- Protects from shocks.
Solution 12:
The place of joining of two or more than two bones is called joint.
Solution 13:
Flexor is a muscle that causes bending of a limb or other part e.g. thigh muscle.
Extensor is the muscle that causes the straightening of a limb or other part. E.g. for extending the foot
Levator is the muscle that raises any part of the body.
Rotator is a muscle that rotates one part on another.
Solution 14:
Axial skeleton: This consists of skull, vertebral column, sternum and ribs. Human skull has 22 bones of which 8 are present in the cranium and 14 on the face. Brain is present in the cavity called cranium. In the occipital region is an opening called foramen magnum through which spinal cord passes. Cranium has 8 bones which covers the brain from all sides.
Facial bones: These bones form the face and protect the sensory organs present in the head. It has 14 bones.
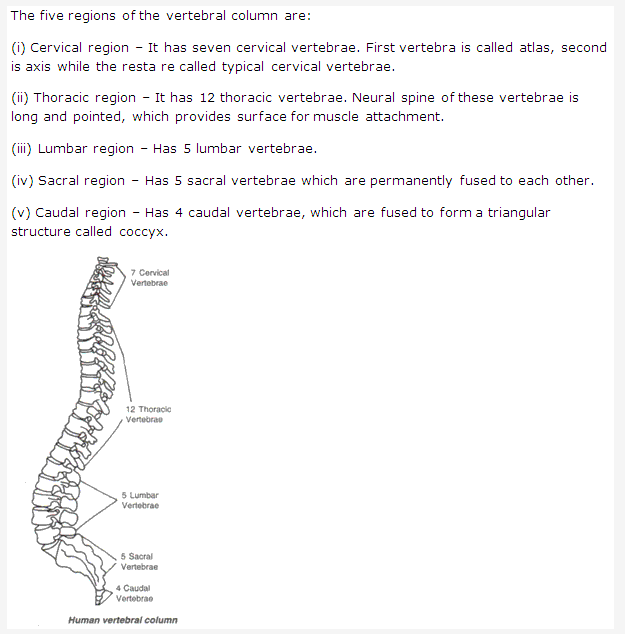
Vertebral Column:
It makes the axis of the body and provides support like a pillar. Vertebral column is divided into following five parts:
- Cervical Region. It has 7 cervical vertebrae. First vertebra is called atlas, second is axis and rest are called typical cervical vertebrae.
- Thoracic Region. It has 12 thoracic vertebrae. Neural spine of these vertebrae is long and pointed, which provdes surface for muscle and attachment.
- Lumber Region. It has 5 lumber vertebrae.
- Sacral Region. It has 5 sacral vertebrae which are permanently fused to each other. These are situated on both halves of pelvic and form a joint with pelvic girdle.
- Caudal Region. It has 4 caudal vertebrae. These are also fused to form a triangular structure which is called coccyx.
Sternum and Ribs:
Sternum is the bone at the mid-ventral line of the thorax to which most of the ribs are attached at their ventral ends. Ribs are formed by vertebral and sterna part. First seven pairs of ribs are called true ribs. These are joined on one side with sternum and on second side with thorax.
Appendicular skeleton: It consists of limbs, shoulder or pectoral girdle and hip or pelvic girdles and bones of limbs.
- Bones of the fore arm: Humerus, radius, Ulna, Carpals, Metacarpals, finger bones, etc.
- Bones of hind limb: Femur, Tibia, Fibula, Tarsal, Metatarsal, etc.
- Pectoral Girdle: In mammals, two halves of pectoral girdle are situated at equal distance from the ribs on the dorsal plane. Each of it is called shoulder bones. Each half of it made up of a triangular flat bone called scapula. From its outer side a projection arises called acromion and has a cavity called glenoid cavity.
- Pelvic Girdle: It consists of two similar halves. In each, three bones are found, ilium, ischium and pubis. Pubis bones of both halves are joined and are called pubic sysmphysis. Ilium and ischium form acetabulum cavity in which head of femur articulates by forming ball and socket joint. A hollow space is found between pubis and ischium, which is called obdurate foramen, which provides passage for obturatry artery, vein and nerve.
Solution 15:
Forelimbs consists of one humerus (anterior arm bone), one radius and one ulna (posterior arm bones), 8 carpals (wrist bones), 5 metacarpals ( palm bones) and 14 phalanges (finger bones).
Hindlimb consists of one femur bone or thigh bone, one tibia and fibula which are bones of the leg, 8 tarsals (bones of ankle), 5 metatarsals (bones of feet), and 14 phalanges (bones of fingers).
Solution 16:
The three levers found in the human skeleton are:
- First order levers
- Second order levers
- Third order levers
Solution 17:
- Ball and socket joint
- Pivot joint
Solution 18:
In a ball and socket joint, the ball of one bone is fitted into the socket of another bone such that the ball can move in the socket. Such a joint always involves a long bone, which can move in all planes. This type of joint is found in pectoral girdle, glenoid cavity, femur and acetabulum of pelvic girdle.
Solution 19:
Forelimbs consists of one humerus (anterior arm bone), one radius and one ulna (posterior arm bones), 8 carpals (wrist bones), 5 metacarpals (palm bones) and 14 phalanges (finger bones).
Hind limb consists of one femur bone or thigh bone, one tibia and fibula which are bones of the leg, 8 tarsal (bones of ankle), 5 metatarsals (bones of feet), and 14 phalanges (bones of fingers).
Solution 20:
Biceps muscles first contract to bend the arm, following which the triceps muscles act to straighten the arm. Thus act in opposite ways and are antagonistic muscles, since they counteract each other’s action. The muscles of biceps are called flexor muscle while that of the triceps is the extensor muscle. This whole coordination of muscular action is under the nerve impulse and brain control.
Solution 21:
Muscles which counteract each other’s actions are known as antagonistic muscles. Biceps and triceps are two such muscles.
Solution 22:
Biceps cause bending of a limb or other part. Triceps cause straightening of a limb or other part.
Solution 23:
Striped, Unstriped and cardiac muscles.
Solution 24:
- Synovial joint is a movable joint present between the adjoining bones which can move independently. The articulating surfaces of the two bones are covered with articular cartilage. The joint is covered with a synovial membrane which secretes synovial fluid for lubrication.
- These are found in elbow joint, knee joint, femur and pelvic girdle, etc.
- The cartilages cover the ends of the adjoining bones. They function to absorb shock and reduce friction during movement.
- 1 and 5 -epiphyseal bone
2- synovial cavity
3- synovial fluid
4- synovial membrane
Solution 25:
- (a) Scapula;
- Shoulder joint;
- Humerus;
- Bicep;
- Tricep;
- Radius;
- Tricep
- Elbow Joint;
- Ulna.
(b) Bicep muscles and triceps are antagonistic muscles.
(c) Bicep muscles.
(d) Shoulder bones.
(e) Ball and socket joint.
PAGE NO:163
Solution 26:
- (d) all the above
- (c) 24
- (b) 7
- (a) Parietals of skull
- (d) stapes
- (b) Cranium
- (c) It allows movement in all directions.
BiologyChemistryPhysicsMaths