New Simplified Chemistry Class 7 ICSE Solutions – Matter and Its Composition
ICSE SolutionsSelina ICSE SolutionsML Aggarwal Solutions
Simplified ChemistryChemistryPhysicsBiologyMathsGeographyHistory & Civics
Points to Remember:
- Matter has mass and occupies space.
- Matter is made up of atoms and molecules.
- Atoms are the smallest particles of matter which may or may not have independent existence.
- 4. Molecules are capable of independent existence. They are
- made up of atoms of same kind or different kinds.
- The atoms and molecules are in random motion.
- There are gaps between the molecules of matter called as intermolecular space.
- There exists a force of attraction between the molecules
- known as intermolecular force of attraction.
- Matter exists in three states : solids, liquid and gas.
- Matter can change from one state to another on changing temperature and pressure.
- The change of state of a matter from one form into another I is called inter conversion of states of matter.
EXERCISE
Question 1.
Explain the meaning of the term matter with special reference to the term ‘substance’.
Answer:
Matter is the basic substance of which all materials, living or non-living are made of.
Question 2.
Name the three states of matter. On what basis are the three states classified.
Answer:
Three states of matter are:
- Solid
- Liquid
- Gases
Basis of the classification are:
Physical properties like:
- Mass
- Volume
- Shape
- Rigidity
- Density
- Arrangement of particles.
Question 3.
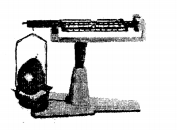
Each of the three states of matter has mass. Explain with the help simple experiments – that each state of matter has mass.
Answer:
Matter i.e. solids, liquids and Gases have mass explained by the following experiments.
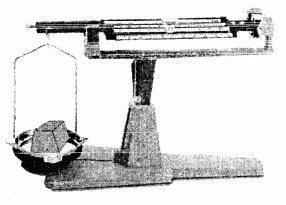
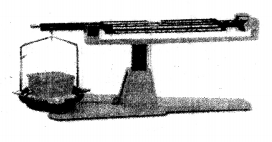
(1) Solid
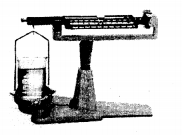
Experiment: A solid placed on one side of the scale, causes the scale to tilt towards one side.
Conclusion: The scale tilts due to the mass of the solid, hence all solids have mass.
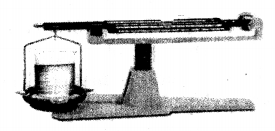
(2) Liquid:
Experiment: A liquid placed on one side of the scale, causes the scale to tilt towards one side.
Conclusion: The scale tilts due to the mass of the liquid, hence all liquids have mass.
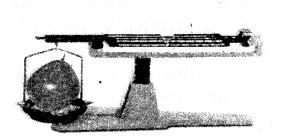
(3) Gas:
Experiment: An inflated balloon placed on one side of the scale causes it to tilt towards one side.
Conclusion: The scale tilts due to the mass of the gas, hence all gases have mass.
Question 4.
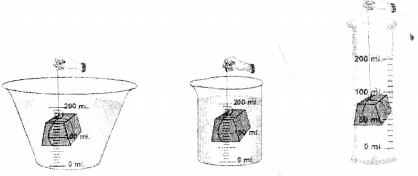
A measuring cylinder is filled with water to a particular mark. A piece of solid is immersed inside the measuring cylinder. State why the level of water in the measuring cylinder will rise up. If the solid is removed, what will be the new level of the water in the measuring cylinder. Give a reason for your answer.
Answer:
When a piece of solid stone is immersed inside the measuring cylinder. The water level rises up.
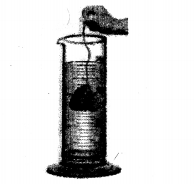
On removal of solid stone the water level in the measuring cylinder falls down back to the mark ‘A’.

Hence, It show that the stone occupies the space of the water and thus pushes the water level up. This experiment or procedure also proves that all solids occupy space.
Question 5.
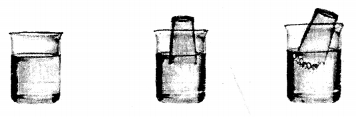
A glass beaker is half filled with water and an empty glass tumbler is inverted & lowered inside the glass beaker. State your observations on tilting the tumbler below the level of the water in the glass beaker. Give a reason for your answer.
Answer:
(1) Take a glass beaker half-filled with water as shown in diagram.

(2) Take an empty glass tumbler which contains air is inverted and lowered inside the glass beaker.

(3) On tilting the tumbler the air inside the tumbler is displaced and bubbles of air are seen coming out. The air is pushed out by the water on tilting the tumbler inside the beaker of water.This experiment or procedure also proves that air or gases occupy space

Question 6.
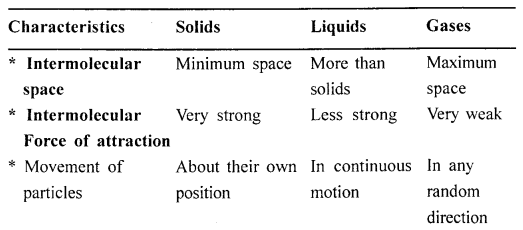
Differentiate the general properties of solids, liquids and gases in the form of a table — with reference to
(a) mass (b) space (c) volume (d) shape (e) compressibility (f) density (g) free surfaces (h) diffusion.
Answer:
(a)
Solids— They have mass
Liquid — They have mass
Gases— They have mass
(b)
Solids— They Occupies space
Liquid— They Occupies space
Gases— They Occupies space
(c)
Solids-They have a definite volume
Liquid-They have a definite volume
Gases-They have no definite volume
(d)
Solids-They have a definite shape
Liquid-They have no shape
Gases-They have no shape
(e)
Solids-They have a no compressibility
Liquid-They have slight compressibility
Gases-They have high compressibility
(f)
Solids-They have high density
Liquid-They have less density
Gases-They have least density
(g)
Solids-They have any number(of free surfaces)
Liquid-They have one free surfaces
Gases-They have no free surfaces
(f)
Solids-They have no diffusibility
Liquid-They have slight diffusibility
Gases-They have high proper diffusibility
Question 7.
State in which of the three states of matter-
(a) Are the atoms or particles far apart
(b) The space between the particles is minimum.
(c) The force of attraction between the particles is very weak.
(d) The movement of the particles are neither about their own positions nor in any random direction.
Answer:
(a) Gas (b) Solid (c) Gas (d) Gas
Question 8.
Give a reason why –
(a) Solids have a definite volume & a definite shape.
(b) Liquids have a definite volume but no definite shape.
(c) Gases have no definite volume and no definite shape.
Answer:
(a)
Any matter that is a solid has a definite shape and a definite volume. The molecules in a solid are in fixed positions and are dose together. Although the molecules can still vibrate, they cannot move from one part of the solid to another part. As a result, a solid does not easily change its shape or its volume.
(b)
Any matter that is a liquid has a definite volume but no definite shape. The molecules in a liquid are less closely packed and they have space between them as compared to solids. Although the molecules can easily move. The inter molecular forces of attraction between the particles are less strong as compared to solids. Hence liquid does have fixed shape and takes the shape of the container in which it is placed e. It has definite volume.
(c)
Any matter that is a gas has no definite volume and no definite shape. The molecules in a gas are least closely packed and inter molecular space between them is very large when compared to solids & liquids. The inter molecular force of attraction between the particles are negligible. As a result a liquid does not easily change its shape nor they have fixed volume.
Question 9.
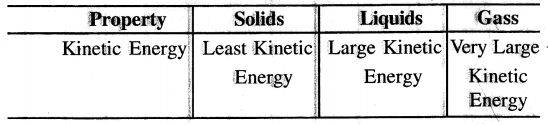
Particles of matter possess energy due to their random motion. Compare the particles in a solid, -liquid & in a gas with reference to the amount of kinetic energy possessed by each.
Answer:
Particles of matter possess energy due to random motion is called kinetic energy.
Comparison of particles in a solid, liquid and gas with reference to kinetic energy are given in the following:
Question 10.
Describe simple experiments to show that –
(a) particles of matter have inter molecular attraction
(b) particles of matter are closely packed in solids and less in liquids.
Answer:
(a) Experiment – To show that particles off matter have inter molecular attraction

Procedure:
- Globules of mercury are placed in a petri dish and kept at – a distance.
- The petri dish is shaken slowly and the mercury globules come together forming a big globule.
Conclusion — The above experiment concludes that a force of attraction exist between particles of matter.
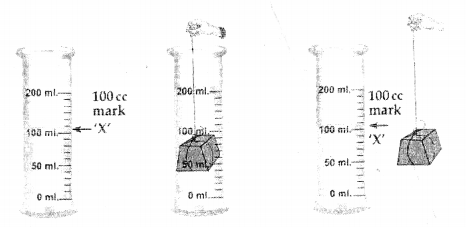
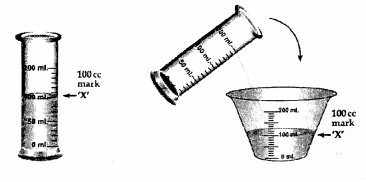
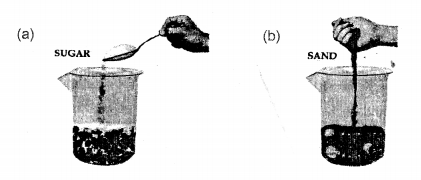
(b) Experiment – To show that particles are closely packed in solids and less in liquids
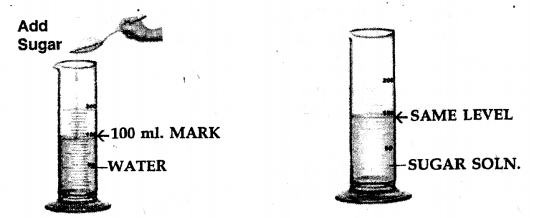
Procedure:
- Take a measuring cylinder and add 100 ml. of water to it.
- Add crystals of sugar [solid] to the water and stir carefully to obtain a sugar solution.
- The volume of water after addition of sugar remains the
same i.e. at the 100 ml. mark.
Conclusion
- Particles of a liquid [e.g. water] are less closely packed.
- Particles of a solid [e.g. sugar] are closely packed.
- The sugar particles fill the inter molecular spaces, which must be existing between the water molecules and hence the level of water in the measuring cylinder does not rise.
Question 11.
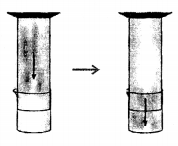
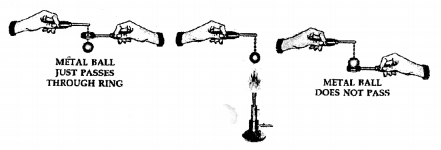
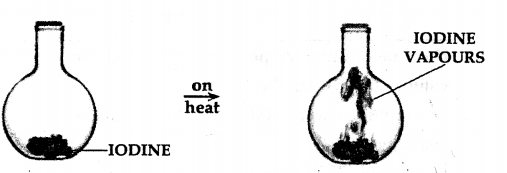
A crystal of iodine is placed in a closed flat bottom flask and heated. State how you would conclude from the observations seen, that inter particle space is minimum in solids and maximum in gases.
Answer:
Procedure:
- 40 A crystal of iodine is heated in a closed flask. The crystal containing ‘X’ no. of particles turns into vapours, which also contain ‘X’ no. of particles and fills the complete flask.
Conclusion
- Particles of a solid [e.g. crystal of iodine] are more closely packed.
- Particles of a gas [e.g. vapours of iodine] are least closely packed and fill the flask completely.
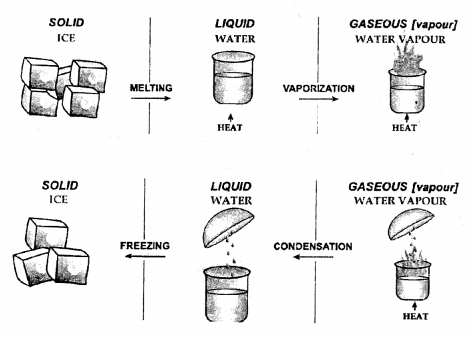
Question 12.
Explain the term ‘inter conversion of matter’ – with ice as a starting material. State the term which refers to the conversion of a substance on heating from.
(a) solid state to liquid state
(b) liquid state to vapour state
(c) vapour state to liquid state
(d) liquid state to solid state.
Answer:
The phenomenon of change from one state to the other and then back to the original state without any change in its chemical composition is called ‘inter conversion of matter.’
The terms which refers to the conversion of a substance are:
(a) Melting
(b) Vaporisation
(c) Liquefaction
(d) Solidification
Question 13.
Give a reason why solids and liquids co-exist at their melting points.
Answer:
A substance exists in the solid state below its melting point and in the liquid state above its melting point. Hence, solids and liquids co-exist at their melting point.
Objective Type Questions
Matter and its composition
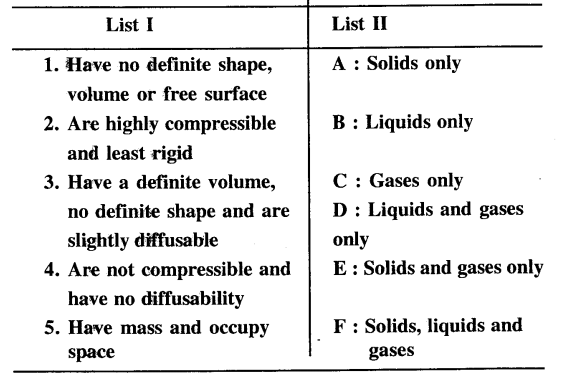
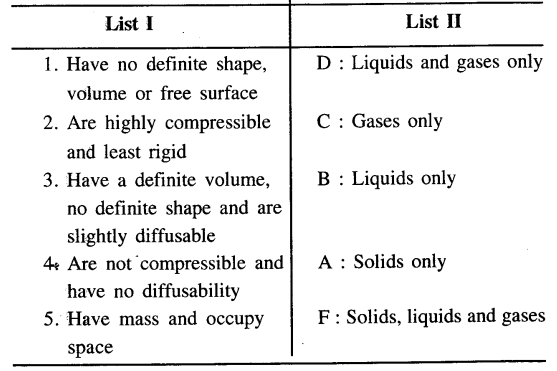
Question 1.
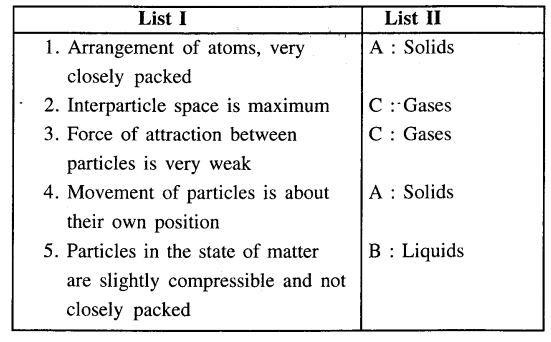
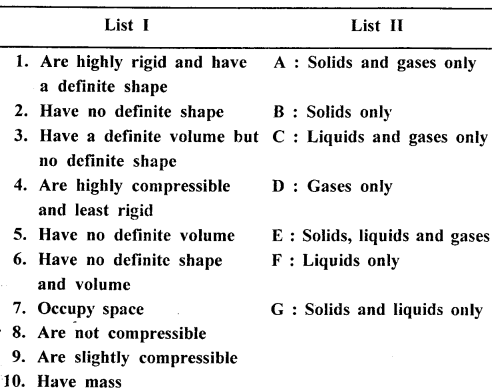
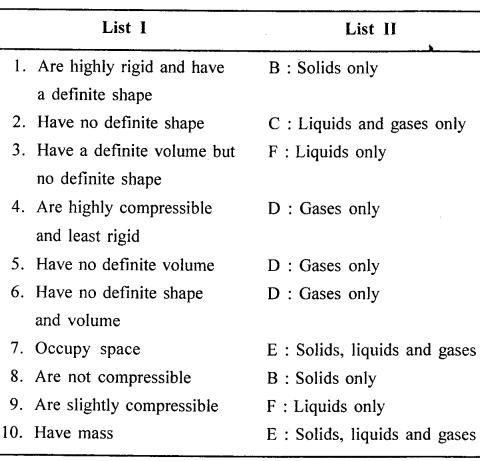
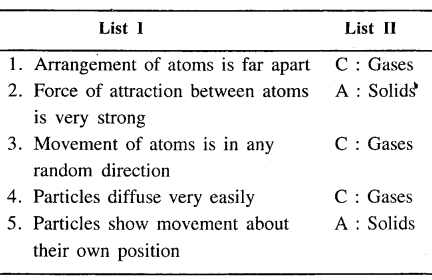
Match the characteristics of the three states of matter in List I with their correct answer from List II.
Answer:
Question 2.
Select the correct answer from the choice in bracket to complete each sentence:
- Matter is defined as anything that occupies space and has mass
- The three states of matter are classified on the basis of differences of certain physical.
- Matter made up of one kind of particles is said to be homogeneous.
- Particles in a gas possess very large kinetic energy.
- The inter molecular force of attraction is maximum in solids.
Question 3.
Give reasons for the following.
- Gases have no definite shape or volume.
- Liquids have one free upper surface only.
- Globules of mercury kept in a petri dish, which is shaken slowly, come together forming a big globule.
- A crystal of iodine on slow heating in a closed flask, turns into vapours and fills the complete flask.
- An empty tumbler lowered into a glass beaker containing water, on tilting shows bubbles of air coming out, but when not tilted, no bubbles are seen.
Answer:
- Any matter that is a gas has no definite volume and no definite shape. The molecules in a gas are least closely packed and inter molecular space between them is very large when compared to solids & liquids. The inter molecular force of attraction between the particles are negligible. As a result a liquid does not easily change its shape nor they have fixed volume.
- Liquids have one free upper surface only because as liquids have a definite volume but no shape and while liquids are bounded by the container, they are placed in and have only one free surface, the upper surface.
- This is because the air is being pushed out by the water on tilting the tumbler inside the beaker of water. Air or gases occupy space.
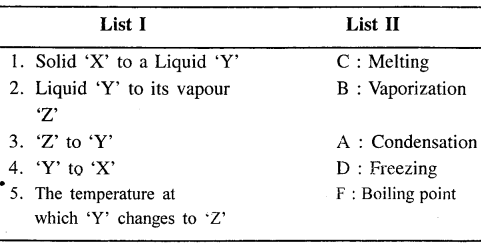
Question 4.
State the correct term from A, B, C, D, E or F in List II which represents the – change of state of matter or its relevant property from List I
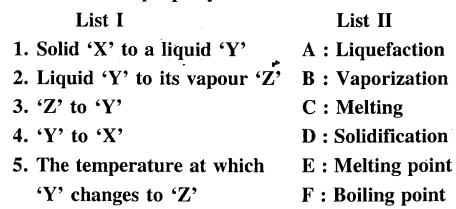
Answer:

Question 5.
Match the arrangement of atoms in the three states of matter in List I with the correct state in List II.
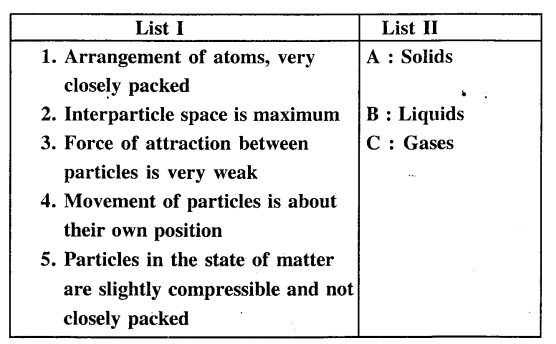
Answer: