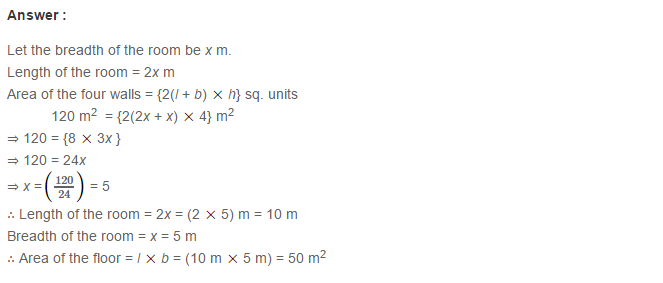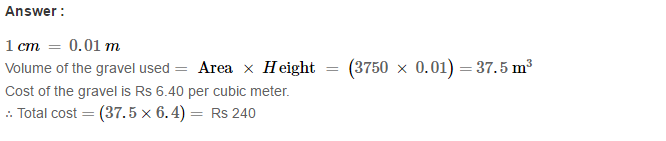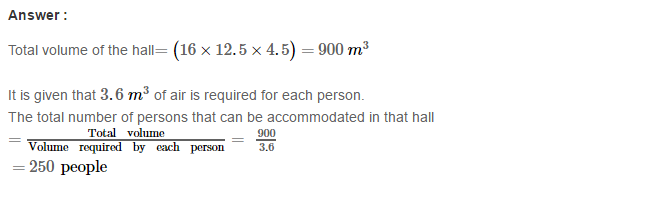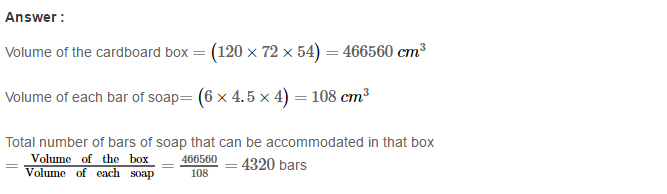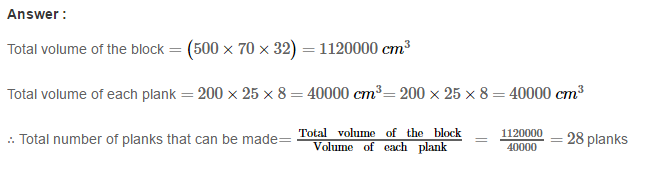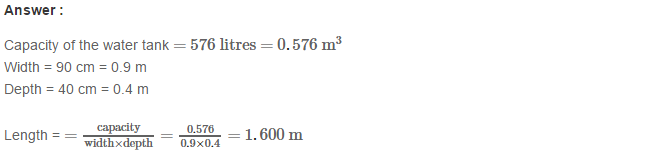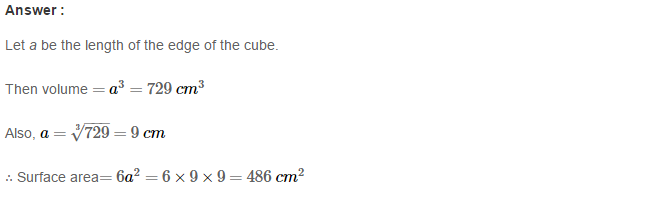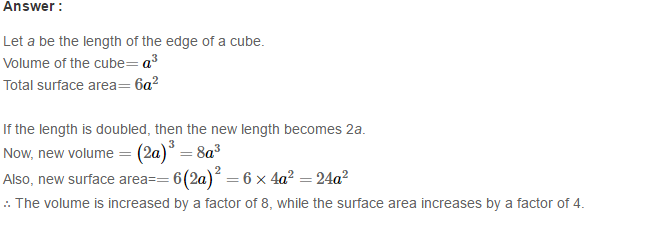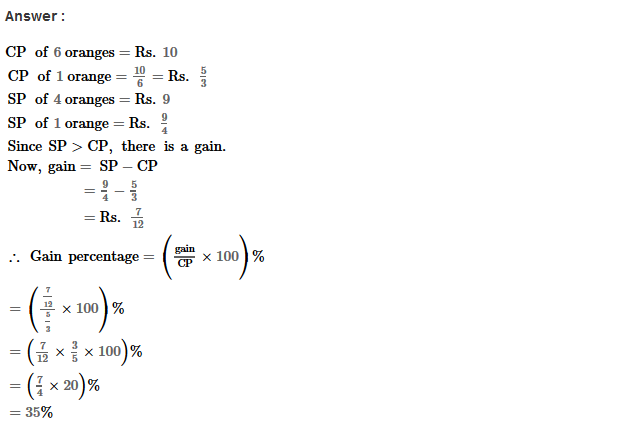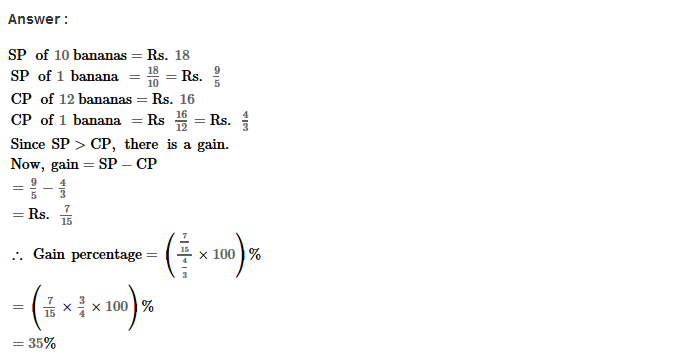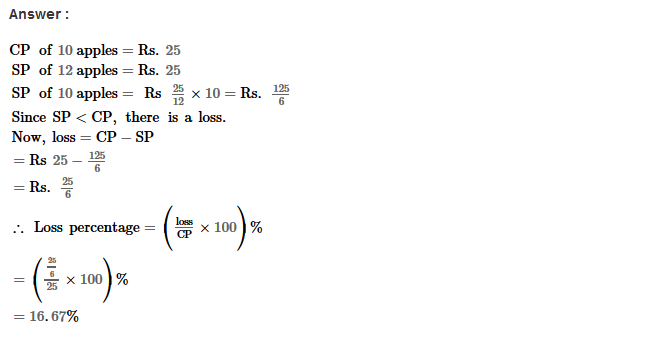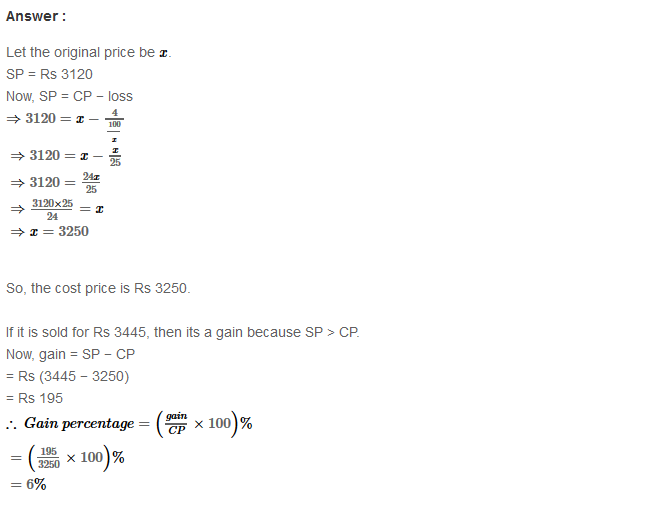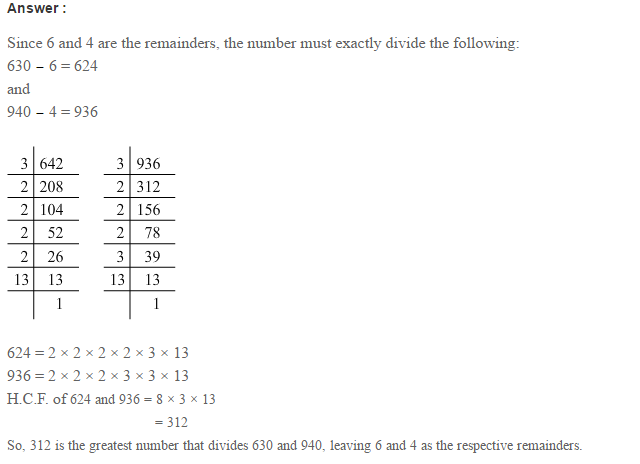What is Euclid Division Algorithm

Euclid’s Division Lemma:
For any two positive integers a and b, there exist unique integers q and r satisfying a = bq + r, where 0 ≤ r < b.
For Example
(i) Consider number 23 and 5, then:
23 = 5 × 4 + 3
Comparing with a = bq + r; we get:
a = 23, b = 5, q = 4, r = 3
and 0 ≤ r < b (as 0 ≤ 3 < 5).
(ii) Consider positive integers 18 and 4.
18 = 4 × 4 + 2
⇒ For 18 (= a) and 4(= b) we have q = 4,
r = 2 and 0 ≤ r < b.
In the relation a = bq + r, where 0 ≤ r < b is nothing but a statement of the long division of number a by number b in which q is the quotient obtained and r is the remainder.
Thus, dividend = divisor × quotient + remainder ⇒ a = bq + r
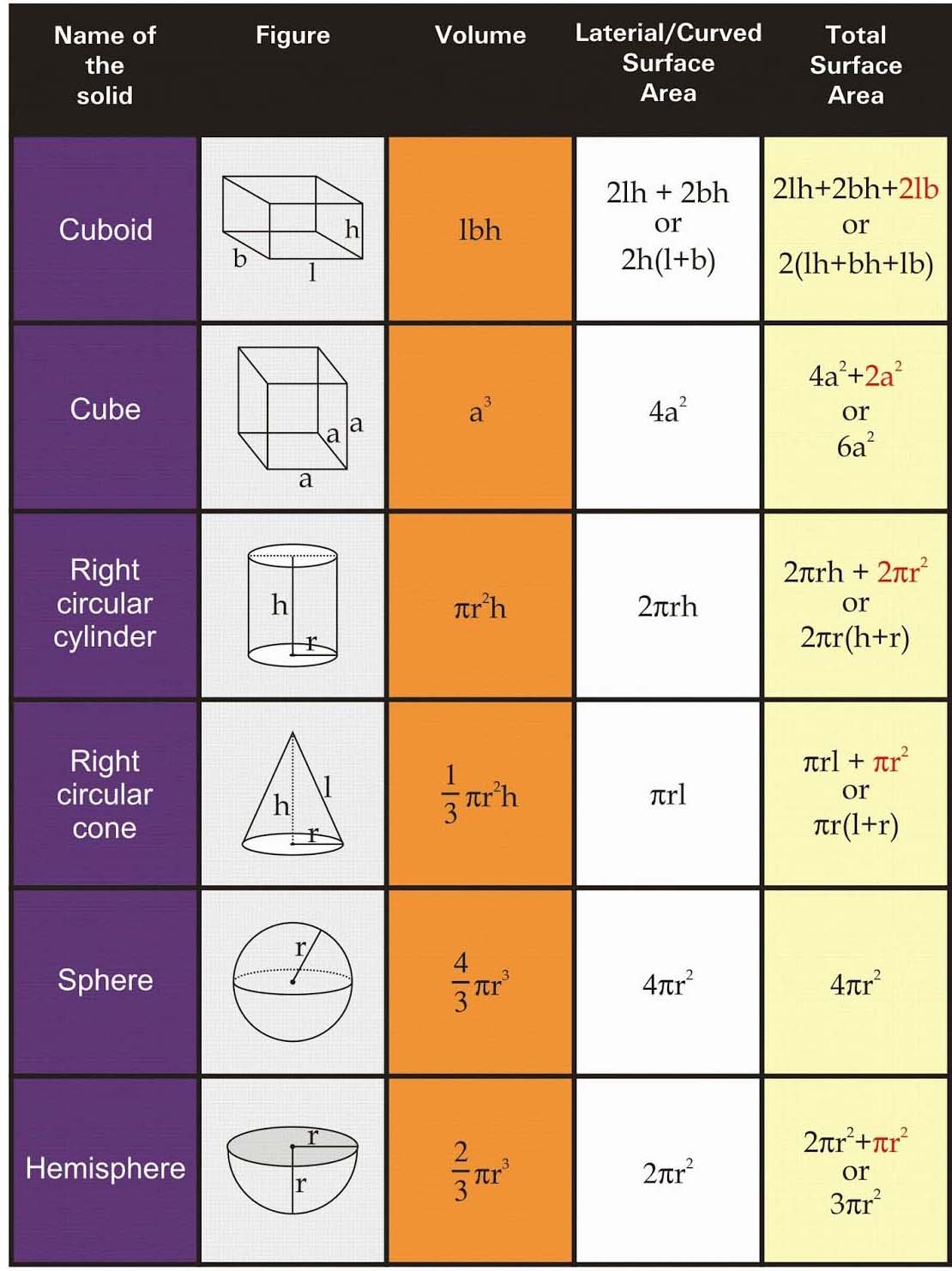
H.C.F. (Highest Common Factor)
The H.C.F. of two or more positive integers is the largest positive integer that divides each given positive number completely.
i.e., if positive integer d divides two positive integers a and b then the H.C.F. of a and b is d.
For Example
(i) 14 is the largest positive integer that divides 28 and 70 completely; therefore H.C.F. of 28 and 70 is 14.
(ii) H.C.F. of 75, 125 and 200 is 25 as 25 divides each of 75, 125 and 200 completely and so on.
Using Euclid’s Division Lemma For Finding H.C.F.
Consider positive integers 418 and 33.
Step-1
Taking bigger number (418) as a and smaller number (33) as b
express the numbers as a = bq + r
⇒ 418 = 33 × 12 + 22
Step-2
Now taking the divisor 33 and remainder 22; apply the Euclid’s division algorithm to get:
33 = 22 × 1 + 11 [Expressing as a = bq + r]
Step-3
Again with new divisor 22 and new remainder 11; apply the Euclid’s division algorithm to get:
22 = 11 × 2 + 0
Step-4
Since, the remainder = 0 so we cannot proceed further.
Step-5
The last divisor is 11 and we say H.C.F. of 418 and 33 = 11
Verification :
(i) Using factor method:
∴ Factors of 418 = 1, 2, 11, 19, 22, 38, 209 and 418 and,
Factor of 33 = 1, 3, 11 and 33.
Common factors = 1 and 11
⇒ Highest common factor = 11 i.e., H.C.F. = 11
(ii) Using prime factor method:
Prime factors of 418 = 2, 11 and 19.
Prime factors of 33 = 3 and 11.
∴ H.C.F. = Product of all common prime factors = 11.
For any two positive integers a and b which can be expressed as a = bq + r, where 0 ≤ r < b, the, H.C.F. of (a, b) = H.C.F. of (q, r) and so on. For number 418 and 33
418 = 33 × 12 + 22
33 = 22 × 1 + 11
and 22 = 11 × 2 + 0
⇒ H.C.F. of (418, 33) = H.C.F. of (33, 22)
⇒ H.C.F. of (22, 11) = 11.
Euclid Division Algorithm Example Problems With Solutions
Example 1: Using Euclid’s division algorithm, find the H.C.F. of 135 and 225
Sol. Starting with the larger number i.e., 225, we get:
225 = 135 × 1 + 90
Now taking divisor 135 and remainder 90, we get
135 = 90 × 1 + 45
Further taking divisor 90 and remainder 45, we get
90 = 45 × 2 + 0
∴ Required H.C.F. = 45
Example 2: Using Euclid’s division algorithm, find the H.C.F. of 196 and 38220
Sol. Starting with larger number 38220, we get:
38220 = 196 × 195 + 0
Since, the remainder is 0
∴ H.C.F. = 196
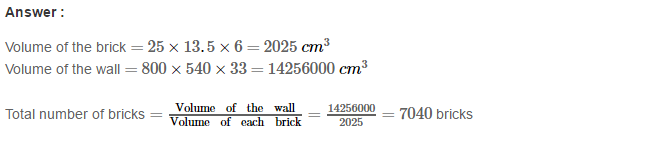
Example 3: Using Euclid’s division algorithm, find the H.C.F. of (iii) 867 and 255
Sol. Given number are 867 and 255
867 = 255 × 3 + 102 (Step-1)
255 = 102 × 2 + 51 (Step-2)
102 = 51 × 2 + 0 (Step-3)
∴ H.C.F. = 51
Example 4: Show that every positive integer is of the form 2q and that every positive odd integer is of the from 2q + 1, where q is some integer.
Sol. According to Euclid’s division lemma, if a and b are two positive integers such that a is greater than b; then these two integers can be expressed as
a = bq + r; where 0 ≤ r < b
Now consider
b = 2; then a = bq + r will reduce to
a = 2q + r; where 0 ≤ r < 2,
i.e., r = 0 or r = 1
If r = 0, a = 2q + r ⇒ a = 2q
i.e., a is even
and, if r = 1, a = 2q + r ⇒ a = 2q + 1
i.e., a is add;
as if the integer is not even; it will be odd.
Since, a is taken to be any positive integer so it is applicable to the every positive integer that when it can be expressed as
a = 2q
∴ a is even and when it can expressed as
a = 2q + 1; a is odd.
Hence the required result.
Example 5: Show that any positive odd integer is of the form 4q + 1 or 4q + 3, where q is some integer.
Sol. Let a is b be two positive integers in which a is greater than b. According to Euclid’s division algorithm; a and b can be expressed as
a = bq + r, where q is quotient and r is remainder and 0 ≤ r < b.
Taking b = 4, we get: a = 4q + r,
where 0 ≤ r < 4 i.e., r = 0, 1, 2 or 3
r = 0 ⇒ a = 4q, which is divisible by 2 and so is even.
r = 1 ⇒ a = 4q + 1, which is not divisible by 2 and so is odd.
r = 2 ⇒ q = 4q + 2, which is divisible by 2 and so is even.
and r = 3 Þ q = 4q + 3, which is not divisible by 2 and so is odd.
Any positive odd integer is of the form
4q + 1 or 4q + 3; where q is an integer.
Hence the required result.
Example 6: Show that one and only one out of n; n + 2 or n + 4 is divisible by 3, where n is any positive integer.
Sol. Consider any two positive integers a and b such that a is greater than b, then according to Euclid’s division algorithm:
a = bq + r; where q and r are positive integers and 0 ≤ r < b
Let a = n and b = 3, then
a = bq + r ⇒ n = 3q + r; where 0 ≤ r < 3.
r = 0 ⇒ n = 3q + 0 = 3q
r = 1 ⇒ n = 3q + 1 and r = 2 ⇒ n = 3q + 2
If n = 3q; n is divisible by 3
If n = 3q + 1; then n + 2 = 3q + 1 + 2
= 3q + 3; which is divisible by 3
⇒ n + 2 is divisible by 3
If n = 3q + 2; then n + 4 = 3q + 2 + 4
= 3q + 6; which is divisible by 3
⇒ n + 4 is divisible by 3
Hence, if n is any positive integer, then one and only one out of n, n + 2 or n + 4 is divisible by 3.
Hence the required result.
Example 7: Show that any positive integer which is of the form 6q + 1 or 6q + 3 or 6q + 5 is odd, where q is some integer.
Sol. If a and b are two positive integers such that a is greater than b; then according to Euclid’s division algorithm; we have
a = bq + r; where q and r are positive integers and 0 ≤ r < b.
Let b = 6, then
a = bq + r ⇒ a = 6q + r; where 0 ≤ r < 6.
When r = 0 ⇒ a = 6q + 0 = 6q;
which is even integer
When r = 1 ⇒ a = 6q + 1
which is odd integer
When r = 2 ⇒ a = 6q + 2 which is even.
When r = 3 ⇒ a = 6q + 3 which is odd.
When r = 4 ⇒ a = 6q + 4 which is even.
When r = 5 ⇒ a = 6q + 5 which is odd.
This verifies that when r = 1 or 3 or 5; the integer obtained is 6q + 1 or 6q + 3 or 6q + 5 and each of these integers is a positive odd number.
Hence the required result.
Example 8: Use Euclid’s Division Algorithm to show that the square of any positive integer is either of the form 3m or 3m + 1 for some integer m.
Sol. Let a and b are two positive integers such that a is greater than b; then:
a = bq + r; where q and r are also positive integers and 0 ≤ r < b
Taking b = 3, we get:
a = 3q + r; where 0 ≤ r < 3
⇒ The value of positive integer a will be
3q + 0, 3q + 1 or 3q + 2
i.e., 3q, 3q + 1 or 3q + 2.
Now we have to show that the squares of positive integers 3q, 3q + 1 and 3q + 2 can be expressed as 3m, or 3m + 1 for some integer m.
Square of 3q = (3q)2
= 9q2 = 3(3q2) = 3m; 3 where m is some integer.
Square of 3q + 1 = (3q + 1)2
= 9q2 + 6q + 1
= 3(3q2 + 2q) + 1 = 3m + 1 for some integer m.
Square of 3q + 2 = (3q + 2)2
= 9q2 + 12q + 4
= 9q2 + 12q + 3 + 1
= 3(3q2 + 4q + 1) + 1 = 3m + 1 for some integer m.
The square of any positive integer is either of the form 3m or 3m + 1 for some integer m.
Hence the required result.
Example 9: Use Euclid’s Division Algorithm to show that the cube of any positive integer is either of the 9m, 9m + 1 or 9m + 8 for some integer m.
Sol. Let a and b be two positive integers such that a is greater than b; then:
a = bq + r; where q and r are positive integers and 0 ≤ r < b.
Taking b = 3, we get:
a = 3q + r; where 0 ≤ r < 3
⇒ Different values of integer a are
3q, 3q + 1 or 3q + 2.
Cube of 3q = (3q)3 = 27q3 = 9(3q3) = 9m; where m is some integer.
Cube of 3q + 1 = (3q + 1)3
= (3q)3 + 3(3q)2 ×1 + 3(3q) × 12 + 13
[Q (q + b)3 = a3 + 3a2b + 3ab2 + 1]
= 27q3 + 27q2 + 9q + 1
= 9(3q3 + 3q2 + q) + 1
= 9m + 1; where m is some integer.
Cube of 3q + 2 = (3q + 2)3
= (3q)3 + 3(3q)2 × 2 + 3 × 3q × 22 + 23
= 27q3 + 54q2 + 36q + 8
= 9(3q3 + 6q2 + 4q) + 8
= 9m + 8; where m is some integer.
Cube of any positive integer is of the form 9m or 9m + 1 or 9m + 8.
Hence the required result.