Algebraic Identities Of Polynomials
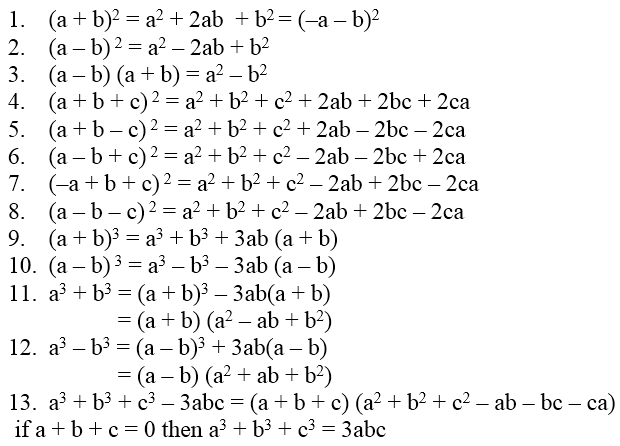
You can also read https://cbselibrary.com/ncert-solutions-for-class-10-maths-chapter-2/ for more solved examples.
People also ask
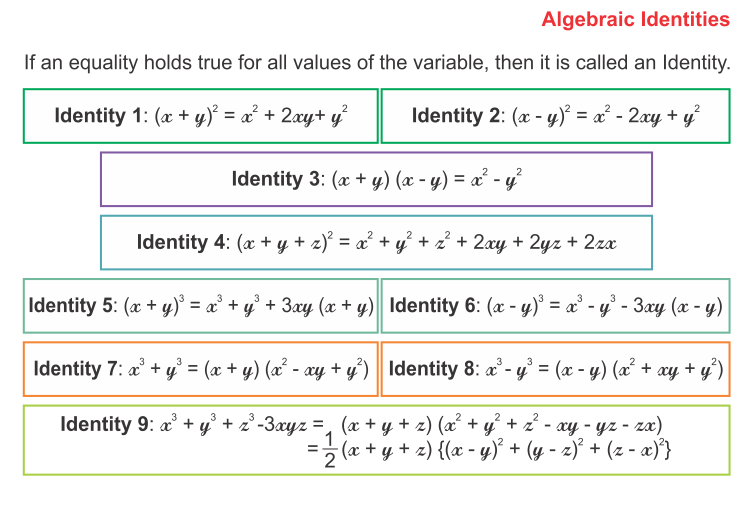
Algebraic Identities Of Polynomials Example Problems With Solutions
Example 1: Expand each of the following
\(\left( \text{i} \right)\text{ }{{\left( \text{3x — 4y} \right)}^{\text{2}}}\text{ }\!\!~\!\!\text{ }\!\!~\!\!\text{ }\!\!~\!\!\text{ }\!\!~\!\!\text{ }\!\!~\!\!\text{ }\!\!~\!\!\text{ }\!\!~\!\!\text{ }\!\!~\!\!\text{ }\!\!~\!\!\text{ }\!\!~\!\!\text{ }\left( \text{ii} \right)\text{ }\!\!~\!\!\text{ }{{\left( \frac{x}{2}+\frac{y}{3} \right)}^{2}}\)
Solution: (i) We have,
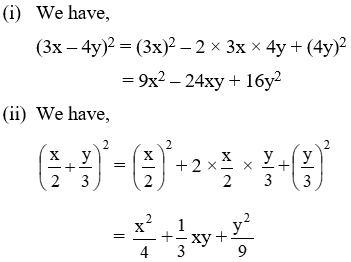
Example 2: Find the products
(i) (2x + 3y) (2x – 3y)
\(\left( \text{ii} \right)\text{ }\left( x-\frac{1}{x} \right)\left( x+\frac{1}{x} \right)\left( {{x}^{2}}+\frac{1}{{{x}^{2}}} \right)\left( {{x}^{4}}+\frac{1}{{{x}^{4}}} \right)\)
Solution: (i) We have,
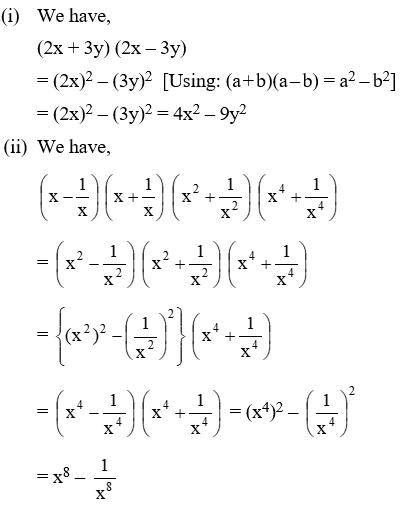
Example 3: Evaluate each of the following by using identities
(i) 103 × 97 (ii) 103 × 103
(iii) (97)2 (iv) 185 × 185 – 115 × 115
Solution: (i) We have,
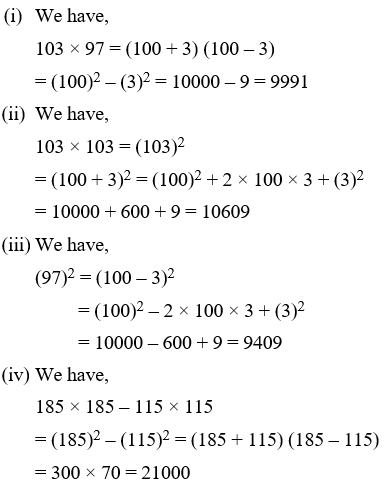
Example 4: \(\text{If }x+\frac{1}{x}=6,\text{ find }{{x}^{4}}+\frac{1}{{{x}^{4}}}\)
Solution: We have,
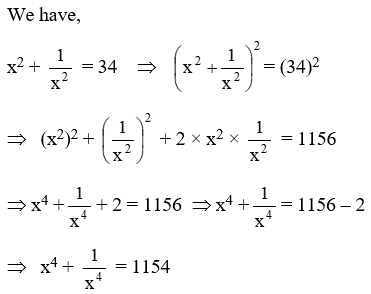
Example 5: \(\text{If }{{x}^{2}}+\frac{1}{{{x}^{2}}}=27,\text{ find the value of the }x-\frac{1}{x}\)
Solution: We have,
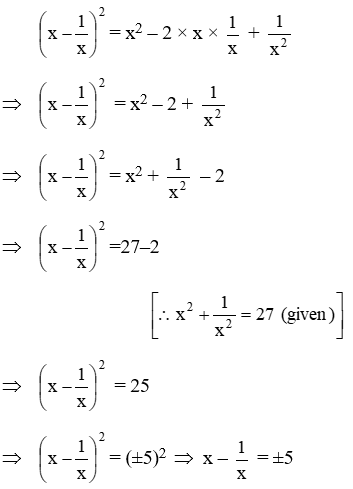
Example 6: If x + y = 12 and xy = 32, find the value of x2 + y2
Solution: We have,
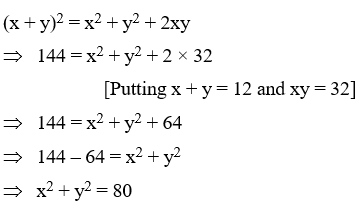
Example 7: Prove that:
2a2 + 2b2 + 2c2 – 2ab – 2bc – 2ca = [(a – b)2 + (b – c)2 + (c – a)2]
Solution: We have,
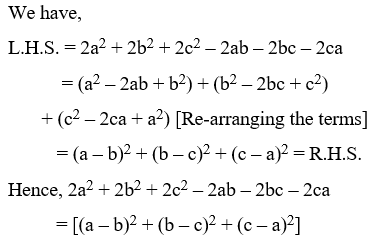
Example 8: If a2 + b2 + c2 – ab – bc – ca = 0, prove that a = b = c.
Solution: We have,
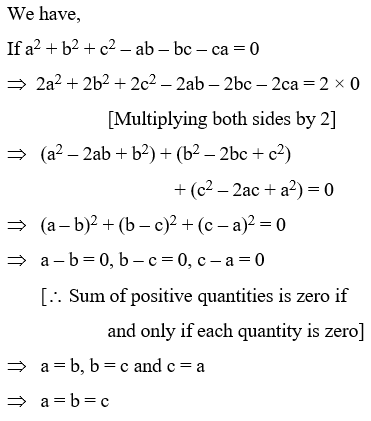
Example 9: Write the following in expanded form :
(i) (9x + 2y + z)2 (ii) (3x + 2y – z)2
(iii) (x – 2y – 3z)2 (iv) (–x + 2y + z)2
Solution: Using the identity
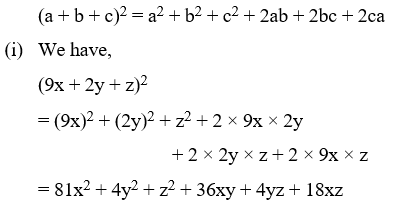
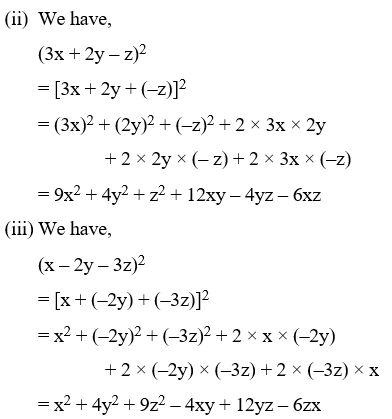
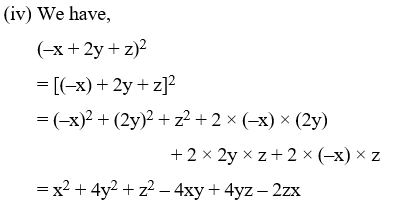
Example 10: If a2 + b2 + c2 = 20 and a + b + c = 0, find ab + bc + ca.
Solution:
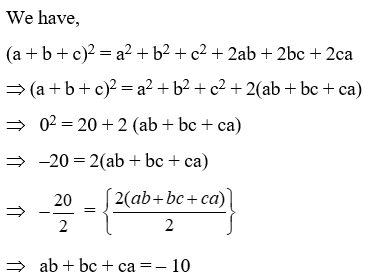
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Z5g3kl8JGYc
Example 11: If a + b + c = 9 and ab + bc + ca = 40, find a2 + b2 + c2.
Solution: We know that
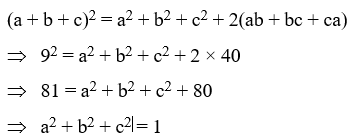
Example 12: If a2 + b2 + c2 = 250 and ab + bc + ca = 3, find a + b + c.
Solution: We know that
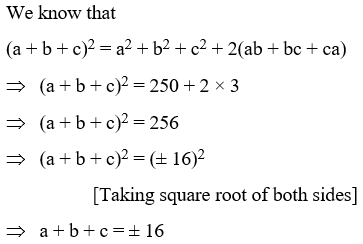
Example 13: Write each of the following in expanded form:
(i) (2x + 3y)3 (ii) (3x – 2y)3
Solution:
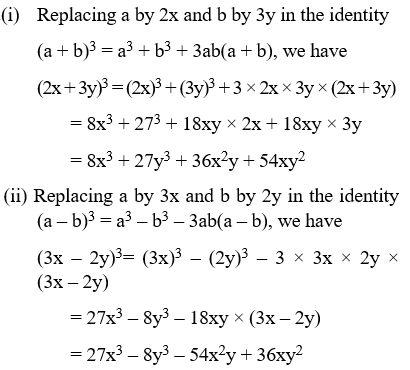
Example 14: If x + y = 12 and xy = 27, find the value of x3 + y3.
Solution: We know that
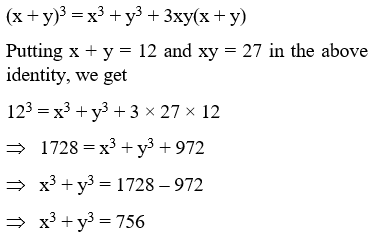
Example 15: If x – y = 4 and xy = 21, find the value of x3 – y3.
Solution: We know that
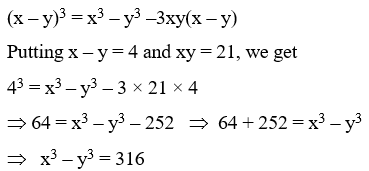
Example 16: \(\text{If }x+\frac{1}{x}=7,\text{ find the value of }{{x}^{3}}+\frac{1}{{{x}^{3}}}\)
Solution: We have,
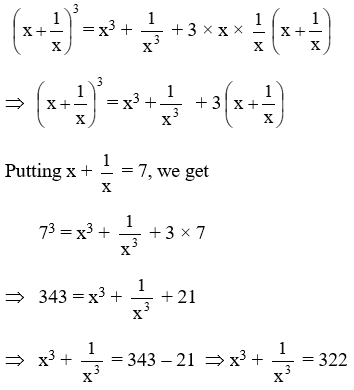
Example 17: If a + b = 10 and a2 + b2 = 58, find the value of a3 + b3.
Solution: We know that

Example 18: \(\text{If }{{x}^{2}}+\frac{1}{{{x}^{2}}}=7,\text{ find the value of }{{x}^{3}}+\frac{1}{{{x}^{3}}}\)
Solution: We have,
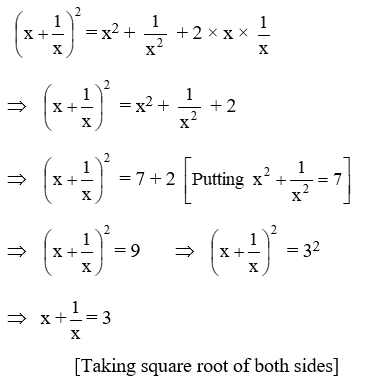
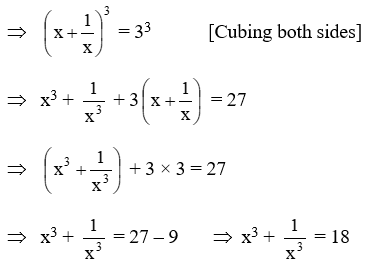
Example 19: \(\text{If }{{x}^{4}}+\frac{1}{{{x}^{4}}}=47,\text{ find the value of }{{x}^{3}}+\frac{1}{{{x}^{3}}}\)
Solution: We know that
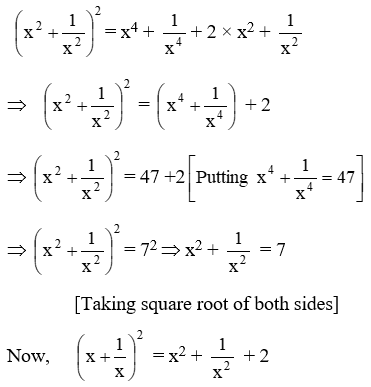
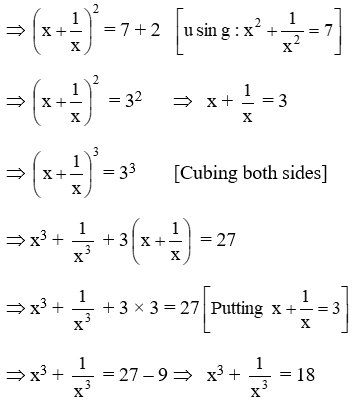
Example 20: If a + b = 10 and ab = 21, find the value of a3 + b3.
Solution: We know that
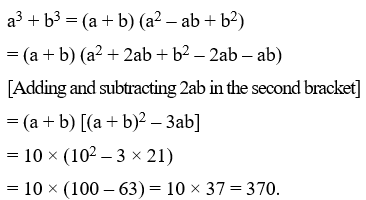
Example 21: If a – b = 4 and ab = 45, find the value of a3 – b3.
Solution: We have,
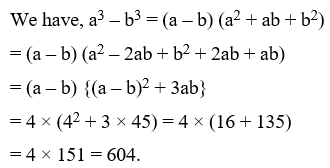
Example 22: If a + b + c = 0, then prove that a3 + b3 + c3 = 3abc
Solution: We know that
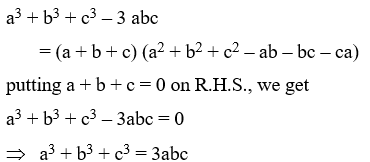
Example 23: Find the following product:
(x + y + 2z) (x2 + y2 + 4z2 – xy – 2yz – 2zx)
Solution: We have,
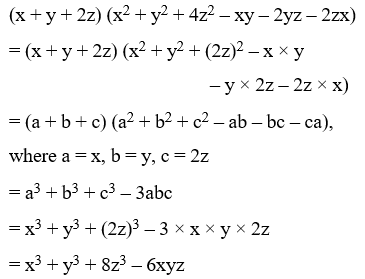
Example 24: If a + b + c = 6 and ab + bc + ca = 11, find the value of a3 + b3 + c3 – 3abc.
Solution:
We know that
a3 + b3 + c3 – 3abc
= (a + b + c) (a2 + b2 + c2 – ab – bc – ca)
⇒ a3 + b3 + c3 – 3abc =
(a + b + c) {(a2 + b2 + c2) – (ab + bc + ca)}…(i)
Clearly, we require the values of a + b + c,
a2 + b2 + c2 and ab + bc + ca to obtain the value of a3 + b3 + c3 – 3abc. We are given the values of a + b + c and ab + bc + ca. So, let us first obtain the value of a2 + b2 + c2.
We know that
(a + b + c)2 = a2 + b2 + c2 + 2ab + 2bc + 2ca
⇒ (a + b + c)2 = (a2 + b2 + c2) + 2(ab + bc + ca)
⇒ 62 = a2 + b2 + c2 + 2 × 11
[Putting the values of a + b + c and ab + bc + ca]
⇒ 36 = a2 + b2 + c2 + 22
⇒ a2 + b2 + c2 = 36 – 22
⇒ a2 + b2 + c2 = 14
Now, putting a + b + c = 6, ab + bc + ca = 1 and a2 + b2 + c2 = 14 in (i), we get
a3 + b33 + c3 – 3abc = 6 × (14 – 11)
= 6 × 3 = 18.
Example 25: If x + y + z = 1, xy + yz + zx = –1 and xyz = –1, find the value of x3 + y3 + z3.
Solution:
We know that :
x3 + y3 + z3 – 3xyz
= (x + y + z) (x2 + y2 + z2 – xy – yz – zx)
⇒ x3 + y3 + z3 – 3xyz
= (x + y + z) (x2 + y2 + z2 + 2xy + 2yz + 2zx – 3xy – 3yz – 3zx)
[Adding and subtracting 2xy + 2yz + 2zx]
⇒ x3 + y3 + z3 – 3xyz
= (x + y + z) {(x + y + z)2 – 3(xy + yz + zx)}
⇒ x3 + y3 + z3 – 3 × –1 = 1 × {(1)2 – 3 × –1}
[Putting the values of x + y + z, xy + yz + zx and xyz]
⇒ x3 + y3 + z3 + 3 = 4
⇒ x3 + y3 + z3 = 4 – 3
⇒ x3 + y3 + z3 = 1