A New Approach to ICSE Physics Part 2 Class 10 Solutions Model Test Paper -2
These Solutions are part of A New Approach to ICSE Physics Part 2 Class 10 Solutions. Here we have given A New Approach to ICSE Physics Part 2 Class 10 Solutions Model Test Paper -2 .
SECTION I (40 MARKS)
Attempt all questions from this section
Question 1.
(a)
1. State the principle of conservation .of energy.
2. Name the form of energy which a body possess even when it is not in motion.- [2]
(b) Where does the position of center of gravity lie for
1. a circular lamina
2. a triangular lamina ? [2]
(c) A man can open a nut by applying a force of 150 N by using a lever handle of length 0.4 m. What should be the length of the handle if he is able to open it by applying a force of 60 N ? [2]
(d) Name a machine which can be used to
1. multiple force
2. change the direction of force applied. [2]
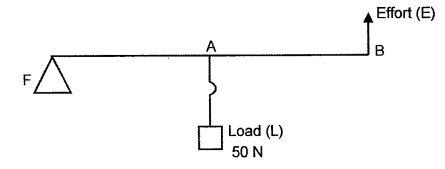
(e) The given diagram shows a lever in use.
1. To which class of lever does it belong ?
2. If FA = 40 cm, AB = 60 cm, then find the mechanical advantages of the lever. [2]
Answer:
(a)
(1) Principle of conservation of energy : Energy can neither be created, nor destroyed. It may be transformed from one form to another form, but the total energy of the system remains constant.
(2) Form of mechanical energy which a body possess even when not in motion : Potential energy.
(b)
(1) Center of the circle or the point of intersection of diameters.
(2) Centroid or the point of intersection of the medians.
(c)
Equating the torque in both the cases :
150 x 0.4 = x x 60
x=150 x 0.4/60=1.0 m
(d)
(1) Inclined plane
(2) Pulley
(e)
(1) II nd class
(2)
Question 2.
(a) A ball of mass 200 g falls from a height of 5 m. What will be its kinetic energy when it just reaches the ground? (g = 9.8 m s-1) [2]
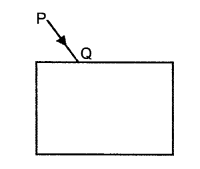
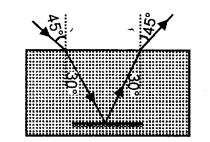
(b) In the diagram below, PQ is a ray of light incident on a rectangular glass block.
1. Copy the diagram and complete the path of the ray of light through the glass block. In your diagram, mark the angle of incidence by letter ‘f and the angle of emergence by the letter ‘e’
2. How are the angles T and V related to each other?
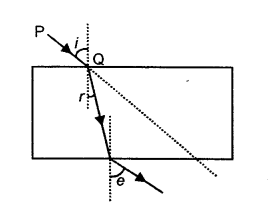
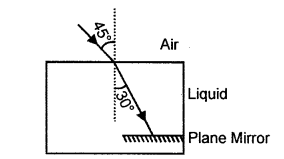
(c) A ray of monochromatic light enters a liquid from air as shown in the given diagram.
(1) Copy the diagram and show in the diagram the path of the ray of light after it strikes the mirror and re-enters the medium of air.
(2) Mark in your diagram the two angles on the surface of separation when the ray of light moves out from the liquid to air. [2]
(d)
(1) When does a ray of light falling on a lens pass through it undeviated ?
(2) Which lens can produce a real and inverted image of an object ? [2]
(e)
(1) How is the refractive index of a medium related to its real depth the apparent depth ?
(2) Which characteristic property of light is responsible for the blue colour of the sky ? [2]
Answer:
(a)
(1) K.E. at the lowest point = P.E. at the highest point
P.E. at the highest point = mgh
= 200/1000 x 9.8×5 = 9.8J 1000
K.E. when it just reaches the ground = 9.8 J
(b)
(1)
(2) ∠i = ∠e
(c)
(d)
(1) When the ray is directed towards the optical center.
(2) Convex lens.
(e)
(1)
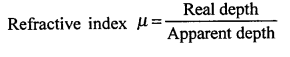
(2) Dispersion
Question 3.
(a) When acoustic resonance takes place, a loud sound is heard. Why does this happen ? Explain. [2]
(b)
(1) Three musical instruments give out notes at the frequencies listed below. Flute : 400 Hz ; Guitar : 200 Hz ; Trumpet : 500 Hz. Which one of these has the highest pitch ?
(2) With which of the following frequencies does a tuning fork of 256 Hz resonate ? 288 Hz. 314 Hz, 333 Hz, 512 Hz. [2]
(c) Two bulbs are marked 100 W, 220 V and 60 W, 110 V. Calculate the ratio of their resistances. [2]
(d)
(1) What is the colour code for the insulation on the earth wire ?
(2) Write an expression for calculating electrical power in terms of current and resistance. [2]
(e) Calculate the equivalent resistance between A and B from the given diagram. [2]
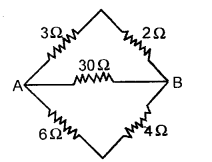
Answer:
(a) These are vibrations of the largest possible amplitude. Since loudness a Amplitude2.
(b)
(1) Trumpet :500 Hz (since Pitch α Frequency)
(2) 512 Hz

Question 4.
(a) Differentiate between heat and temperature.
(b)
(1) Define Calorimetry.
(2) What is meant by Energy degradation ? [2]
(c) 200 g of hot water at 80° C is added to 300 g of cold water at 10° C. Calculate the final temperature of the mixture of water.Consider the heat taken by the container to be negligible, [specific heat capacity of water is 4200 J kg-1°C-1] [2]
(d) Fill in the blanks in the following sentences with appropriate words :
1. During the emission of a beta particle, the ……………number remains the same.
2. The reciprocal of focal length in ………….. is called power of a lens. [2]
(e) A mixture of radioactive substances gives off three types of radiations.
- Name the radiation which travels with the speed of light.
- Name the radiation which has the highest ionizing power. [2]
Answer:
Heat
(1) It is a form of energy,
(2) Unit is joule/calorie.
Temperature
(1) It the degree of hotness or coldness of a body.
(2) Unit is °C, F° or kelvin.
(b)
(1) Heat is a form of energy which flows from the body at a higher temperature to a body at a lower temperature. The measurement of the quantity of heat is called calorimetry.
(2) The dissipation of energy in the form of non useful energy (usually due to friction) is called Energy degradation.
(c) Let the final temperature be T °C.
Heat lost = Heat gained (H = me Δr)
200 x 4.2 x (80 – T) = 300 x 4.2 x (T – 10)
2(80 – T) = 3 (T – 10)
160 – 2T = 3T – 30
=> 5T = 190
∴ T = 38 °C.
(d)
(1) Mass Number
(2) metre
(e)
(1) γ (Gamma) radiations
(2) α (Alpha) radiations.
Section II (40 Marks)
Attempt any four questions from this section.
Question 5.
(a)
(1) What is meant by an ideal machine ?
(2) Write a relationship between the mechanical advantage (M.A.) and velocity ratio (V.R.) of an ideal machine.
(3) A coolie carrying a load on his head and moving on a frictionless horizontal platform does no work. Explain the reason why. [3]
(b)
Draw a diagram to show the energy changes in an oscillating simple pendulum. Indicate in your diagram how the total mechanical energy in it remains constant during the oscillation. [3]
(c)
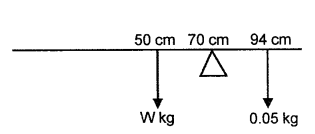
A uniform metre scale can be balanced at the 70.0 cm mark when a mass of 0.05 kg is hung from the 94.0 cm mark.
(1) Draw a diagram of the arrangement.
(2) Find the mass of the meter scale. [4]
Answer:
(a)
(1) A machine with 100% efficiency is called an ideal machine.
(2) MA. = V.R.
(3) Because the angle between the force applied (vertically upwards) and displacement of load (along the horizontal) is 90°.
∴ W = Fd cos θ
∴W = Fd cos 90° = 0
(b)
At extreme position A and B, RE. is maximum = mgh
K.E. is zero
Total energy RE. + K.E. = mgh
At the mean position C
P.E is zero
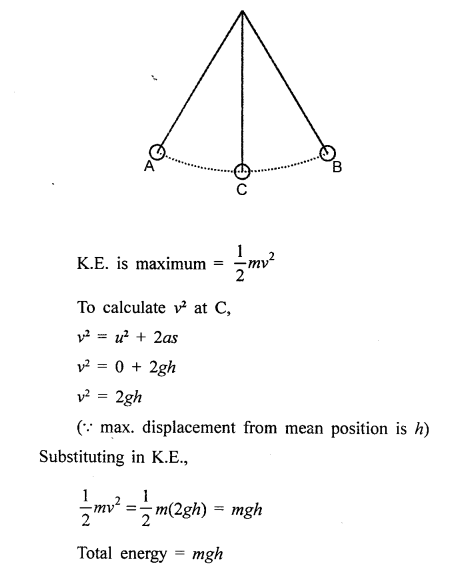

Question 6.
(a)
(1) State the laws of refraction of light.
(2) Write a relation between the angle of incidence (i),angle of emergence (e), angle of prism (A) and angle of deviation (δ) for a ray of light passing through an equilateral prism. [3]
(b)
(1) Suggest one way, in each case, by which we can detect the presence of :
- Infrared radiations
- Ultraviolet radiations.
(2) Give one use of infrared radiations. [3]
(c)
An object is placed in front of a lens between its optical centre and the focus and forms a virtual, erect and diminished image.
- Name the lens which formed this image.
- Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of the image with the above stated characteristics. [4]
Answer:
(a)
(1) The laws of refraction of light are :
- The incident ray, the normal and the refracted ray lie in the same plane.
- The sine of angle of incidence bears a constant ratio with the sine of angle of refraction for a given pair of medium.
(2) i + e = A + δ k
(b)
(1)
- Infrared radiations : Mercury rises rapidly if a blackened bulb thermometer is kept in these radiations.
- Ultraviolet radiations : By their chemical activity on dyes.
(2) Use of Infrared radiations : Used for therapeutic purposes by doctors.
(c)
(1) Concave lens.
(2)
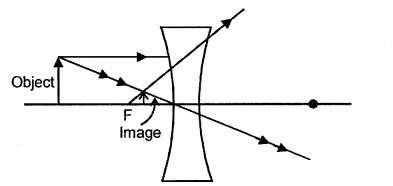
Question 7.
(a)
(1) Name the type of waves which are used for sound ranging.
(2) Why are these waves mentioned in (i) above, not audible to us ?
(3) Give one use of sound ranging. [3]
(b)
A man standing 25 m away from a wall produces a sound and receives the reflected sound.
(1) Calculate the time after which he receives the reflected sound if the speed of sound in air is 350 m s-1.
(2) Will the man be able to hear a distinct echo ? Give a reason for your answer. [3]
(c)
(1) Name two safety devices which are connected to the live wire of a household electrical circuit.
(2) Give one important function of each of these two devices. [4]
Answer:
(a)
(1) Ultrasonic waves.
(2) Ultrasonic waves frequency is above 20,000 Hz whereas human audibility range is only till 20,000 Hz.
(3) Use of sound ranging : Can be used in radar.
(b)
(1)
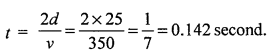
(2) Yes, because the least time for distinct echo to be heard is 0.1 second.
(c)
(1) Fuse and Switch.
(2) Fuse is used to limit the flow of current. Switch is used to start or stop the flow of current.
Question 8.
(a)
(1) Draw a graph of Potential difference (V) versus Current (I) for an ohmic resistor.
(2) How can you find the resistance of the resistor from this graph ?
(3) What is a non-ohmic resistor ? [3]
(b)
(1) An electric bulb is marked 100 W, 250 V. What information does this convey ?
(2) How much current will the bulb draw if connected to a 250 V supply ? [3]
(c) Three resistors are connected to a 12 V battery as shows in the figure given below :
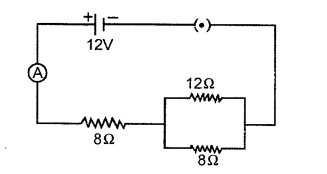
(1) What is the current through the 8 ohm resistor ?
(2) What is the potential difference across the parallel combination of 6 ohm and 12 ohm resistor ?
(3) What is the current through the 6 ohm resistor ? [4]
Answer:
(a)
(1)
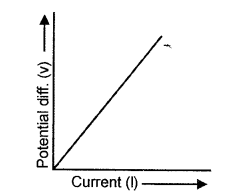
(2) Resistance = Slope of the graph
(3) A non-ohmic resistor does not follow Ohm’s Law.
(b)
(1) It means that if a bulb is given a 250 V supply, it will consume 100 J of energy in each second.
(2) Let P = VI

Question 9.
(a)
(1) Explain why the weather becomes very cold after a hailstrom.
(2) What happens to the heat supplied to a substance when the heat supplied causes no change in the temperature of the substance ? [3]
(b)
(1) When 1 g of ice at 0° C melts to form 1 g of water at 0°C them, is the latent heat absorbed by the ice or given out by it ?
(2) Give one example where high specific heat capacity of water is used as a heat reservoir.
(3) Give one example where high specific heat capacity of water is used for cooling purposes. [3]
(c)
250 g of water at 30°C is present in a copper vessel of mass 50 g. Calculate the mass of ice required to bring down the temperature of the vessel and its contents to 5°C. Specific latent heat of fusion of ice = 336 × 103 J kg-1 Specific heat capacity of copper vessel = 400 J kg-1 °C-1 Specific heat capacity of water = 4200 J kg-1 °C-1[4]
Answer:
(a)
(1) After the hailstorm, ice absorbs heat energy required for melting from the surroundings, so the temperature of the surroundings fall further down and we feel cold.
(2) Heat is stored as latent heat which is used in the change of state of the substance.
(b)
(1) Latent heat of fusion is released by ice.
(2) Hot water bottles used for fomentation.
(3) Drinks get cooled more quickly by adding pieces of ice at 0°C than the ice cold water at 0°C.
(c)
Heat lost by ice = Heat gained by water + Heat gained by copper vessel
Let the mass of ice needed by M kg.
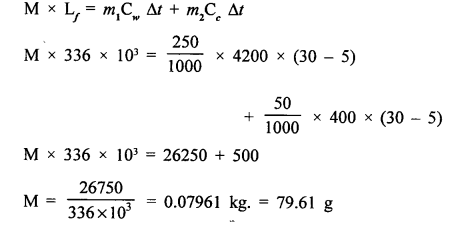
Question 10.
(a)
(1) Why can nuclear fusion not possible to generate electricity ?
(2) When an alpha particle gains two electrons it becomes neutral and becomes an atom of an element which is rare gas. What is the name of this rare gas ? [3]
(b)
(1) Define radioactivity.
(2) What happens inside the nucleus that causes the emission of a beta particle ?
(3) Express the above change in the form of an equation. [3]
(c)
(1) Name the isotopes of an element which are used in fusion reaction.
(2) The nucleus ..2°2X emits an alpha particle and forms the nucleus Y. Represent this change in the form of an equation.
(3) What changes will take place in the mass number and atomic number of the nucleus Y if it emits gamma radiations ? [4]
Answer:
(a)
(1) As yet it is not possible to control nuclear fusion. Therefore nuclear fusion cannot be used to generate electricity.
(2) Helium gas.
(b)
(1)Radioactivity is a random nuclear phenomenon in which spontaneous emission of a, (3 or 7 -radiations from the nuclei of atoms during their decay takes place.
(2)In an unstable nucleus, number of neutrons are more than number of protons. In such a case, a neutrons may change to proton to achieve stability by emitting an electron called beta particle.
(3).
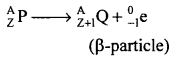
(c)
(1) Isotopes of hydrogen used in nuclear fusion reaction are deutrium ^H2) and tritium QH3).
(2)

(3) During gamma emission there is no change in mass number and atomic number.
More Resources
- A New Approach to ICSE Physics Part 2 Class 10 Solutions
- ICSE Solutions for Class 10 Mathematics
- ICSE Solutions for Class 10 Physics
- ICSE Solutions for Class 10 Chemistry
- ICSE Solutions for Class 10 Biology
- ICSE Solutions for Class 10 History and Civics
- ICSE Solutions for Class 10 Geography
- ICSE Solutions for Class 10 English Literature and Language
- Merchant of Venice Workbook Answers – ICSE Class 10 English
- Treasure Trove A Collection of ICSE Poems Workbook Answers
- Treasure Trove A Collection of ICSE Short Stories Workbook Answers
- ICSE Solutions for Class 10 English – A Collection of Poems & Short Stories
- ICSE Solutions for Class 10 Hindi
- Selina ICSE Solutions for Class 10 Maths
- Selina ICSE Solutions for Class 10 Physics
- Selina ICSE Solutions for Class 10 Chemistry
- Selina ICSE Solutions for Class 10 Biology
- New Simplified Chemistry Class 10 ICSE Solutions
- Frank ICSE Solutions for Class 10 Maths
- Frank ICSE Solutions for Class 10 Physics
- Frank ICSE Solutions for Class 10 Chemistry
- Frank ICSE Solutions for Class 10 Biology
Hope given A New Approach to ICSE Physics Part 2 Class 10 Solutions Model Test Paper -2 are helpful to complete your science homework.
If you have any doubts, please comment below. APlusTopper try to provide online science tutoring for you.